| Research Article |
Open Access |
|
| Mohammad Ali Javadi1, Mohammad Ali Tajick Ghanbary2* and Zahra Tazick3 |
| 1Department of Plant Pathology, Islamic Azad University of Damghan, Iran |
| 2Department of Microbiolog, Genetics & Agricultural Biotechnology Institute of Tabarestan, Sari, Iran |
| 3Department of Plant Protection, Sari Agricultural Sciences & Natural Resources University, Sari, Iran |
| *Corresponding authors: |
Mohammad Ali Tajick Ghanbary
Department of Microbiolog
Genetics & Agricultural Biotechnology Institute of Tabarestan
Sari, Iran
Tel: +989112546616
Fax: +981513822567
E-mail: m.tajick@sanru.ac.ir |
|
| |
| Received August 17, 2012; Published August 27, 2012 |
| |
| Citation: Javadi MA, Ghanbary MAT, Tazick Z (2012) Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Different Penicillia Isolated from Agricultural Soils. 1: 257. doi:10.4172/scientificreports.257 |
| |
| Copyright: © 2012 Javadi MA, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. |
| |
| Abstract |
| |
| In an experimental study, anti-bacterial activities of more than eighty soil inhabitant Penicillium isolates were evaluated. Isolates were cultured, simultaneously with bacteria: Pseudomonas syringae, P. viridiflava, Xanthomonas translucens, Agrobacterium tumefascines, Rathayiibacter iranicus, and one isolate of E. coli in PDB and the results were evaluated after one week. All tested isolates, had anti-bacterial activity against one or more bacterial strains tested. It seems that, most of the examined Penicillia, produce one or more antibacterial substances and are able to prevent growth and proliferation of bacteria in their habitat. |
| |
| Keywords |
| |
| Antibacterial activity; Soil fungi; Penicilium |
| |
| Introduction |
| |
| Part of the soil biological activity is a result of terrestrial fungi. Soil fungi, include various groups and belong to different taxonomic groups [1]. In between, Penicillium and Aspergillus are among the most abundant fungal flora of soils of different regions and are found in almost all areas of dry and wet soils [2]. In concept of soil biology, evaluation of soil biological activity can be performed in general and in all living organisms in the soil. Hence, separation and generalization of results is not possible for specific groups such as fungi and bacteria or actinomycetes. Until, each share will be determined in biological process series. To achieve this purpose, isolation, identification and study of specific biological features of different groups of microorganisms seems necessary [3]. In most biochemistry and soil biology sources, soil enzyme activities have been studied which are used as indicators for measuring the biological activity of soils [4]. Presumably, all of microorganisms that have studied for enzymatic activity are shared in results. Isolation and purification of secondary metabolites from soil and their specific evaluation is difficult due to biological and physical conditions of soils. Hence, in-vitro studies on production of secondary metabolites seem simple and reliable process, using pure cultures of producing microorganisms. Between different bundles of secondary metabolites, biologists are especially interested in antibiotics as growth inhibitors of other microorganisms. Fungi are one of the main producers of antibiotic substances that in different environments, particularly soil, are able to produce and effect on other microorganisms [2]. In this research, we tried to investigate the ability of producing antibacterial substances, and preventing the growth of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, by different Penicillium species which are isolated from various regions of agricultural soils of Iran. |
| |
| Materials and Methods |
| |
| Fungal isolates |
| |
| Fungi used in this study, were isolated by culturing soil suspension in potato dextrose agar containing 0.01g streptomycin sulfate and 0.03g Rose bengal antibiotics. Then, spore suspension of pure culture of isolates was prepared in sterile distilled water and was used for inoculation of treatments. |
| |
| Bacterial isolates |
| |
| Isolates of the bacteria were prepared of living cultures from laboratory of bacteriology, Department of Plant Pathology at the University of Agricultural Sciences of Sari, and Biotechnology Laboratory at Biotechnology Research Institute of Mashhad University. |
| |
| Isolates grown on NA medium and inoculum were prepared in sterile distilled water and were kept in the refrigrator. |
| |
| Assessment of production of bacterial growth inhibitors |
| |
| Penicillium obtained isolates, were cultured in 50 ml of potato dextrose agar medium (PDB) and were placed on shaker with 120 rpm speed [5]. Then 2 days later, were inoculated by bacterial prepared suspensions. Results were evaluated after one week rocking on shaker with observation of transparency or opacity in compared with control cultures. |
| |
| Results and Discussion |
| |
| Fungi belonging to different groups, have been studied for production of some secondary metabolites in laboratory and natural conditions [6] that led to introduction of genus and species which are superior in studied characteristics [3]. Metabolites can enhance abundance and biological components of soils or some of them can be effective in reducing population of soil living organisms. Also, metabolites can have some values as well as commercial and industrial importanc [7,8]. |
| |
| Most of the bacterial isolates used in this study were gram negative and plant pathogenic. Penicillium isolates were obtained from agricultural soil of some provinces of Iran which had various climate and different geology. |
| |
| Pseudomonas syringae is a rod shape, gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. It is a plant pathogen which can infect a wide range of plant species. Being Gram-negative bacteria, most Pseudomonas spp. are naturally resistant to penicillin and the majority of related betalactam antibiotics, but a number are sensitive to Piperacillin, Imipenem, Ticarcillin, Tobramycin, or Ciprofloxacin. As results show, it is the more resistant bacterium to secreted secondary metabolite of all Penicillium isolates used in this study. |
| |
| |
| Pseudomonas viridiflava is a fluorescent, gramnegative, soil bacterium that is a minor pathogen on plants [9]. As you can see in table 1, all of the Penicillium isolates can control its growth. |
| |
|
|
Table 1: Results of simultaneous culturing of bacteria and Penicillium isolates. |
|
| |
| Agrobacterium tumefaciens (updated scientific name: Rhizobium radiobacter) is the causal agent of crown gall disease (the formation of tumors) in over 140 species of dicot [10]. It is a rod shape, Gram negative soil bacterium. Among the Penicillium isolates, only E10 was unable to prevent its growth. |
| |
| Rathayibacter is a genus of bacteria in order Actinomycetales which are gram-positive soil organisms. Gram positive bacteria are more sensitive to secondary metabolites which affect cell wall. A75, A80 and C22 didn’t let this bacterium grow. |
| |
| E. coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms [11]. |
| |
| The results showed that most investigated fungi have the growth inhibitory activity against one or more inoculated bacteria. Some isolates did not let any inoculated bacterial grow, while some treatments had oscillations in the opacity of the medium, ultimately lead to transparency and to overcome bacterial growth which was accompanied by them. |
| |
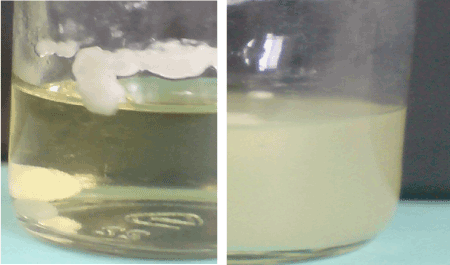
| Figure 1 shows the positive and negative treatments. |
| |
|
|
Figure 1: Positive and negative results from the treatment of bacterial strains and fungul isolates, left to right, positive and negative. |
|
| |
| The results of performed treatments with the soil sampling locations are shown in Table 1. |
| |
| Overall, more than 480 culture crosses were done, of which nearly 80 percent of them showed a positive results. |
| |
| In vitro culture results indicate the kind of events that can occur in micro-ecological environment of fungus life in farm soil. Our results showed that Penicillium species which are existed in agricultural soil are able to control some important plant pathogenic bacteria species. Further investigations and isolations of produced antibacterial substances can be effective to strengthen or reduction some helpful or harmful soil microorganisms. |
| |
| |
| References |
| |
- McLaughlin DJ, McLaughlin EJ, Lemke PA (2001) The Mycota, Volume VIII: Part B Systematics and Evolution. Springer Publication.
- Alexopoulos CJ, Mims CW, Blackwell M (1996) Introductory Mycology. John Willey and Sons Inc., New York.
- Lotfi A, Tajick Ghanbary MA, Ranjbar GA, Asgharzadeh A (2010) Screening of some Zygomycetes for cellulase Activity. Afr J Biotechnol 9: 4211-4216.
- Kossem A, Nannipieri P (1995) Soil cellulase activity. In: Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry.
- Sharif M (2009) A quick method for Metarhizium anisopliae isolation from cultural soils. American J of Agric and Biol Sciences 4: 152-155.
- Ekesi NK, Maniania, Mohamed SA, Lux SA (2005) Effect of soil application of different formulations of Metarhizium anisopliae on African tephritid fruit flies and their associated endoparasitoids. Biol Control 35: 83-91.
- Blondelle SE, Houghten RA (1996) Novel antimicrobial compounds identified using synthetic combinatorial library technology. Trends Biotechnol 14: 60-65.
- Petit P, Lucas EMF, Abreu LM, Pfenning LH, Takahashi JA (2009) Novel antimicrobial secondary metabolites from a Penicillium sp. isolated from Brazilian cerrado soil. Electron J Biotechnol 12: 8-9.
- Hu FP, Young JM, Fletcher MJ (1998) Preliminary description of biocidal (syringomycin) activity in fluorescent plant pathogenic Pseudomonas species. J Appl Microbiol 85: 365–371.
- Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martínez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2001) A revision of Rhizobium International Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51: 89-103.
- Vogt RL, Dippold L (2005) Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreak associated with consumption of ground beef. Public Health Rep 120: 174– 178.
|
| |
| |