Page 45
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 3 (Suppl)
Mod Chem Appl, an open access journal
ISSN: 2329-6798
Global Chemistry 2017
September 04-06, 2017
September 04-06, 2017 | London, UK
5
th
Global Chemistry Congress
Catalytic synthesis of environmental friendly polymer poly lactic acid via continuous reactive extrusion: Recent
trends
Satya P Dubey, Hrushikesh A Abhyankar, Veronica Marchante
and
James L Brighton
Cranfield University, UK
T
he disposal of large amount of polymer waste is one of the major challenges of this century. Use of bio-degradable polymers
obtained from sustainable sources presents a solution to this problem. Poly lactic acid (PLA), a bio-degradable polymer,
can be synthesized from sustainable sources as corn, starch, sugarcane and chips. Ring opening polymerization (ROP) of lactide
monomer using metal/bimetallic catalyst (Sn, Zn or Al) is the preferred method for synthesis of PLA. However, the PLA synthesized
using such catalysts may contain trace elements of the catalyst. These catalyst traces are known carcinogens and as such should be
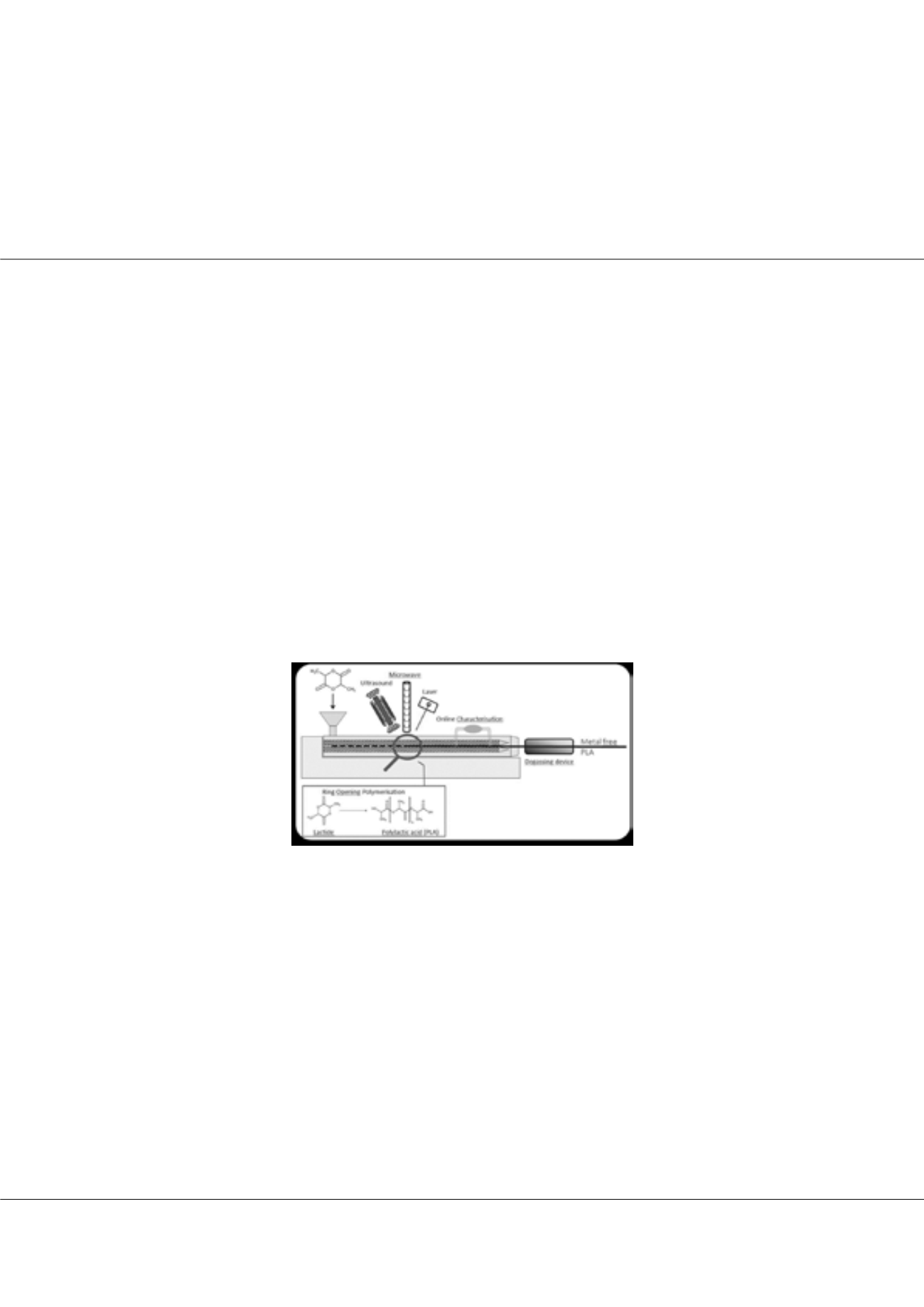
(ideally) eliminated from the process. Continuous reactive extrusion of lactide monomer (using the suitable reaction input has the
potential to increase the throughput, and this route has been explored in the literature. In this work, reactive extrusion experiments
using stannous octoate Sn(Oct)
2
and tri-phenyl phosphine (PPh)
3
, were considered to perform ROP of lactide monomer using the
microwave as an alternative energy (AE) source for activating and/or boosting the polymerization (Figure 1). Implementation of
a microwave generator in a section of the extruder is one of the novelties of this research. A simulation model of ROP of PLA was
formulated to estimate the impact of reaction kinetic and AE source on the polymerization process. Ludovic® software was used for
the simulation of continuous reactive extrusion of the process. Experimental and simulated results were compared for the validation
of the methodology. This work also highlights the advantages and drawbacks of most conventional metal catalysts, the effect of
alternative energies on reaction mechanism, and safe and efficient production of PLA.
Biography
Satya P Dubey is a Research Associate at Cranfield University, UK. He has his expertise in several aspects of material sciences such as polymer, bio-polymer,
nano-materials, composites, sustainable material, metal-polymer interfaces etc. His diligent, open and contextual evaluation model based on environmental friendly
polymer synthesis creates new pathways for improving polymer industry. He developed this model after years of experience in research, evaluation, teaching and
administration both in basic material chemistry research as well as in developing the mathematical model in several research institutions worldwide. The current
development made by him considered as a step forward for the production of biodegradable and bio-compostable polymer through more safer and greener method.
s.p.dubey@cranfield.ac.ukSatya P Dubey et al., Mod Chem Appl 2017, 5:3(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2329-6798-C1-005