Page 30
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5
Journal of Pharmaceutical Care & Health Systems
Pharma Middle East 2018
November 05-07, 2018
November 05-07, 2018 Abu Dhabi, UAE
18
th
Annual
Pharma Middle East Congress
Anteneh Assefa et al., J Pharma Care Health Sys 2018, Volume 5
DOI: 10.4172/2376-0419-C4-035
Physicochemical characterization of the starch fromEthiopian potato (
Plectranthus edulis
)-Apotential
pharmaceutical excipient
Anteneh Assefa
1
, Anteneh Belete
2
and Tsige Gebre-Mariam
2
1
Wachemo University, Ethiopia
2
Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia
S
tarch from the tubers of Ethiopian potato (
Plectranthus edulis
) (Fam. Lamiaceae) has been isolated and examined for its
chemical composition, amylose content and physicochemical properties. The yield of starch was about 80.4% on dry weight
basis. The proximate composition of the starch on dry weight basis was found to be 0.14% ash, 0.21% lipid, 0.43% protein
and 99.22% starch. The amylose content was 30.6%. Its true density and moisture content values were 1.47 g/ml and 11.2%,
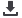
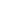
respectively. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of the starch granules showed characteristic morphology that was by large
oblong (elliptical) with some oval-shaped granules. The starch has normal granule size distribution with a mean particle size of
36.20 µm. The DSC thermograms of
P. edulis
starch obtained from starch-water mixtures (1:1), exhibited higher T0 (69.2 °C),
Tp (74.3 °C) and Te (83.3 °C) values than those of potato starch. X-ray diffraction pattern of the starch was typical B-type with
a distinctive maximum peak at 17.5° 2θ. The starch possesses higher swelling power and moisture sorption pattern but lower
solubility values than those of potato starch at all temperatures studied. Considering the high yield value and some similar
physico-chemical properties to those of potato starch,
P. edulis
(Ethiopian potato) can be explored as an alternative source of
starch for various applications.
Biography
Anteneh Assefa is currently working as a Lecturer of Pharmaceutics and Pharmacology at Wachemo University, Ethiopia. He is an expertise of pharmaceutical
dosage form design and drug supply chain management.
ante2011@gmail.com