Page 108
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 11
Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics
ISSN: 0974-276X
Structural Biology 2018
September 24-26, 2018
September 24-26, 2018 | Berlin, Germany
14
th
International Conference on
Structural Biology
Towards new therapeutic derivatives-
in silico
-based design of new kinase inhibitors against
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Mohd Shahbaaz
and
Alan Christoffels
University of Western Cape, South Africa
I
norganicpolyphosphate (PolyP) plays anessential role inbacterial virulence anddrug tolerance.The genome of
Mycobacterium
tuberculosis
encodes for two polyphosphate kinases (PPK-1, Rv2984 and PPK-2, Rv3232c) and poly phosphatases (PPX-1,
Rv0496 and PPX-2, Rv1026) for maintenance of intracellular Poly P levels. The mapping of metabolic pathways indicated
Rv2984 as an essential drug target involved in the drug resistance of
M. tuberculosis
. Consequently, a library of 18 compounds
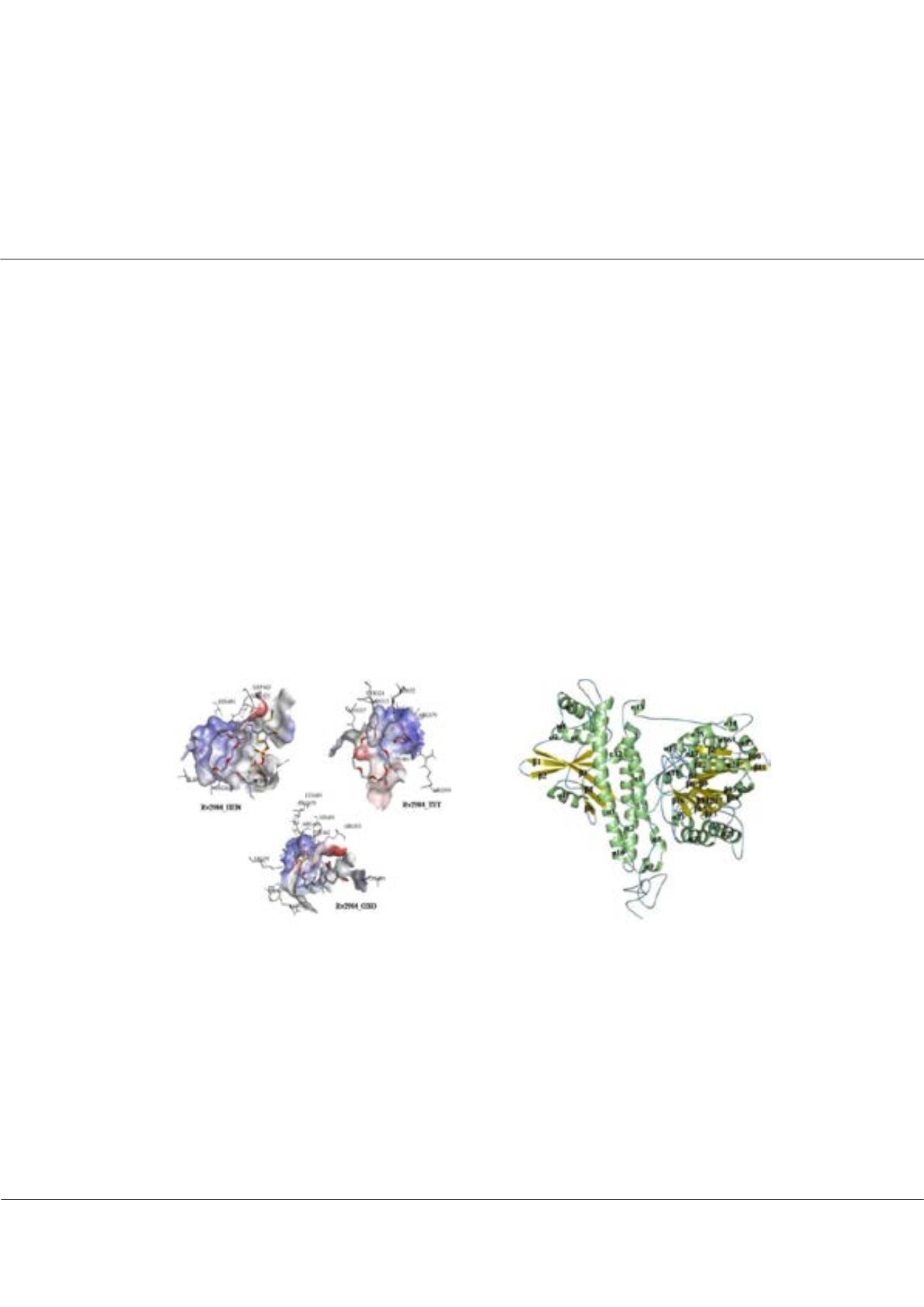
was designed by altering the scaffolds of know inhibitors and were subjected to the virtual screening against Rv2984. The
top three scoring inhibitors were selected which showed the free energy of binding 8.2–9 kcal mol-1 and values of inhibition
constant falls in the range of 255–866 nM. The binding affinities of these selected molecules were compared with the first line
drugs isoniazid and rifampicin. These observations indicated that the selected inhibitors showed relatively higher binding
affinity against Rv2984. Furthermore, these docked complexes were further analyzed using 100 ns molecular dynamics (MD)
simulations in explicit water conditions. Through the assessment of obtained trajectories, the interactions between the protein
and the inhibitors were evaluated using MM/PBSA technique, which calculates the total interaction energies between -100 kJ
mol-1 to -1000 kJ mol-1. This study will facilitate the process of drug designing against
M. tuberculosis
and the outcomes can
be validated using experimental inhibition studies. In conclusion, the designed derivatives inhibit the activity of Rv2984 more
efficiently and outcomes will be validated using experimental inhibition studies.
Recent Publications:
1. Cloete R, Oppon E, Murungi E, Schubert W D and Christoffels A (2016) Resistance related metabolic pathways for
drug target identification in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BMC Bioinformatics 17:75.
2. Singh M, Tiwari P, Arora G, Agarwal S, Kidwai S, et al., (2016) Establishing Virulence Associated Polyphosphate
Kinase 2 as a drug Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scientific Reports 6:26900.
Biography
Mohd Shahbaaz has expertise in the field of Computational Chemistry and Bioinformatics. He is currently working as a Postdoctoral Fellow in South African
National Bioinformatics Institute (SANBI), University of Western Cape, South Africa. He is currently working on the development of novel drug molecules against
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
under the supervision of Professor Alan Christoffels.
Mohd Shahbaaz et al., J Proteomics Bioinform 2018, Volume 11
DOI: 10.4172/0974-276X-C2-116
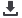
Figure 1:
The predicted structure of Rv2984
showing the characteristic L shaped topology
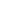
Figure 2:
The complexes of top three scoring
designed derivatives.