Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
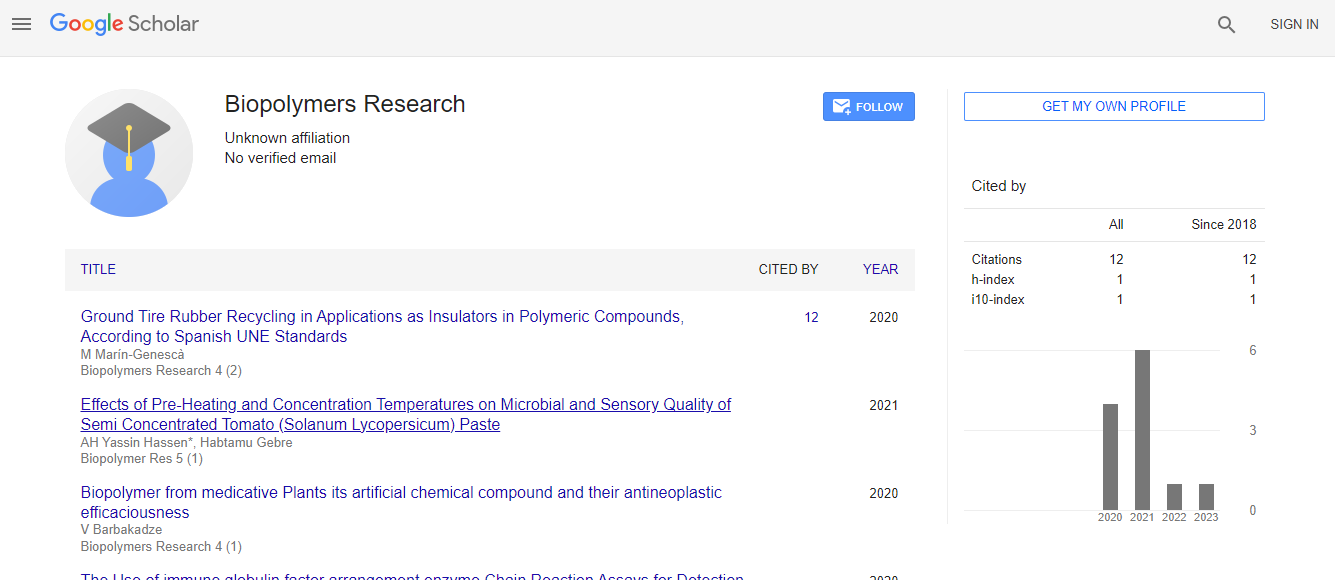
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 18
Biopolymers Research received 18 citations as per Google Scholar report
Biopolymers Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Wood Biopolymers
Industrial hardwoods such as Eucalyptus species, Betula pendula, and Acacia mangium required different chemical charges during kraft pulping and presented distinct profiles of polysaccharides removal. The corresponding kraft pulps showed different chlorine dioxide consumption during bleaching. Woods and corresponding kraft pulps were characterized by chemical methods, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, and gel permeation chromatography. The ease of lignin degradation and dissolution was essentially determined by differences in the proportion of syringyl and guaiacyl units and in the degree of condensation. The bleaching response was shown to be related also to the content of β-O-4 structures in the residual lignin. The relative stability of xylans during the pulping was suggested to be associated with differences in structure and molecular weight. The higher retention of Eucalyptus xylans was attributed essentially to their peculiar structure, including O-2-substituted uronic acid groups linked to other cell wall polysaccharides.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi