Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
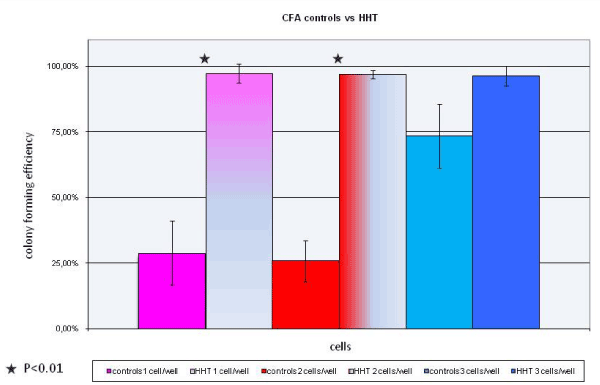
In the last few years’ stem cell research contributed to gain a fundamental understanding of how organisms grow and develop and how tissues are maintained throughout adult life. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are self renewing, multipotent cells that are present in many adult tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, trabecular bone and muscle. More recently they have been found also in skin, liver and other tissues. Dermal skin-derived fibroblasts exhibit mesenchymal surface antigen immunophenotype and differentiation capabilities versus the three main mesenchymal tissues (bone, fat and cartilage). Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia affects 1 in 5000 people and leads to abnormal blood vessel formation in skin and mucous membranes. We isolated human dermal fibroblasts from patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) and healthy controls. In order to evaluate future applications of these cells in tissue engineering we compared mesenchymal properties (self-renewal, differentiation potential) of human gingival fibroblasts isolated from healthy and HHT-affected subjects using a combination of phenotypic (flow cytometry), morphologic (senescence), and functional (in vitro differentiation, colony forming unit assay and proliferation assay) criteria. Our results suggest that HHT cells were ideal candidates for tissue engineering.