Conditions of Oral Health
Received: 06-Nov-2020 / Accepted Date: 20-Nov-2020 / Published Date: 27-Nov-2020 DOI: 10.4172/2332-0702.1000265
Description
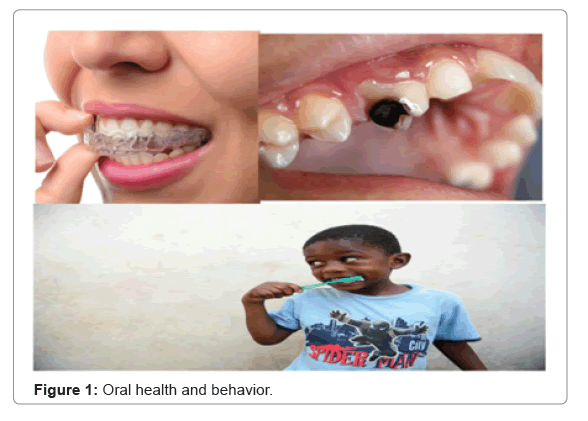
Oral fitness is a key indicator of ordinary health, well-being and excellent of life. It encompasses a vary of ailments and prerequisites that encompass dental caries, Periodontal disease, Tooth loss, Oral cancer, Oral manifestations of HIV infection, Oro-dental trauma, Noma and beginning defects such as cleft lip and palate [1] (Figure 1). The Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 estimated that oral ailments have an effect on 3.5 billion humans worldwide, with untreated dental caries being amongst the most well-known no communicable diseases. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, the incidence of oral most cancers used to be inside the pinnacle three of all cancers in some Asian-Pacific nations in 2018. The majority of oral fitness prerequisites are: Dental caries (tooth decay), periodontal diseases, Oral cancers, Oral manifestations of HIV, Oro-dental trauma, Cleft lip and palate, and Noma (severe gangrenous ailment beginning in the mouth basically affecting children). Most oral fitness prerequisites are mostly preventable and can be dealt with in their early stages.
Oral illnesses pose a principal fitness burden for many nations and have an effect on humans during their lifetime, inflicting pain, discomfort, disfigurement and even death. These illnesses share frequent danger elements with different main non-communicable ailments [2]. It is estimated that oral illnesses have an effect on almost 3.5 billion humans [3]. Untreated dental caries (tooth decay) in everlasting enamel is the most common fitness situation in accordance to the Global Burden of Disease 2017 [2]. More than 530 million youngsters go through from dental caries of main tooth (milk teeth). Severe periodontal (gum) disease, which may additionally end result in enamel loss, is additionally very common, with nearly 10% of the world populace affected. Oral most cancers (cancer of the lip or mouth) are one of the three most frequent cancers in some international locations of Asia and the Pacific [4]. Treatment for oral fitness prerequisites is highly-priced and generally no longer section of ordinary fitness insurance (UHC). In most high-income countries, dental remedy averages 5% of complete fitness expenditure and 20% of out-ofpocket fitness expenditure. Most low and middle income international locations are unable to grant offerings to stop and deal with oral fitness conditions. Factors contributing to oral illnesses are an unhealthy food plan excessive in sugar, use of tobacco and detrimental use of alcohol. Most oral health stipulations are generally preventable and can be handled in their early stages.
Transparency
Declaration of funding
This study had no funding resources.
Adherence to national and international regulations
Not applicable.
Author’s contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgment
None
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Petersen PE (2008) World Health Organization global policy for improvement of oral healthâ€World Health Assembly 2007. Int Dent J 58:115-21.
- World Health Organization (2011) Political declaration of the High-level Meeting of the General Assembly on the Prevention and Control of Non-communicable Diseases. 66th Session of the Unites Nations General Assembly. WHO.
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, et al. (2018) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet 392:1789-858.
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, et al. (2019) Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer 144:1941-1953.
Citation: Cho M, Khan H (2020) Conditions of Oral Health. J Oral Hyg Health 8: 265. DOI: 10.4172/2332-0702.1000265
Copyright: © 2020 Matsuo C, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2793
- [From(publication date): 0-2020 - Oct 31, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1978
- PDF downloads: 815