Gnetol, a Resveratrol Derivative Ameliorates Malathion-Induced Neurotoxicity through Modulating Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in N2a Cells
Received Date: Oct 08, 2017 / Accepted Date: Oct 16, 2017 / Published Date: Oct 23, 2017
Abstract
Malathion is a highly neurotoxic organophosphate (OP) pesticide which is in wide use. It is known for its high toxicity to insects, which is caused by inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity, and for being neurotoxic to humans and other mammals. The present study mainly focused on potential effect of 2,3’,5’,6-tetrahydroxy-trans-stilbene (gnetol) on malathion-induced neuronal cell death in N2a mouse neuroblastoma cells. Malathion activated lysosomal cathepsin B release, resulting in defective autophagy and induction of apoptotic cell death. Interestingly, gnetol (5, 10, and 20 μM) protected cells from apoptosis by regulating heart fatty acid binding protein 3 (hFABP3) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, leading to improvements in the cellular and nuclear morphological changes induced by malathion. Gnetol induced autophagy by reducing lysosomal cathepsin B release as assessed by immunofluorescence staining, which ameliorated apoptotic cell death in N2a cells. Furthermore, the neurite outgrowth and the NGF level were upregulated by gnetol treatment. Taken together, gnetol, a resveratrol derivative, may protect neuronal cells against malathion-mediated apoptosis and potentiate neuritogenesis.
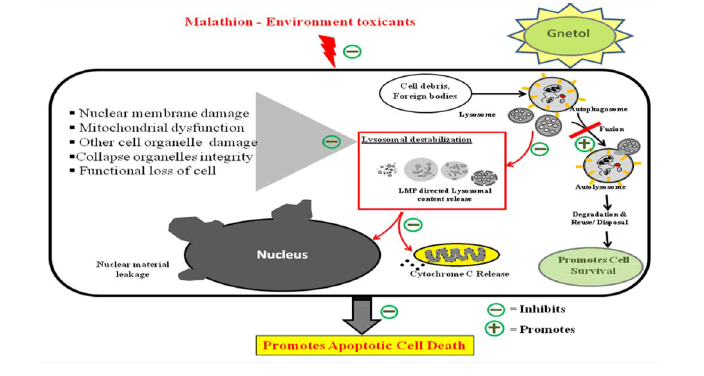
Graphical Abstract
Schematic representation of the proposed role of gnetol on lysosomal destabilization in malathion-induced apoptosis in N2a neuroblastoma cells
Keywords: Malathion; Autophagy; Gnetol; Phytochemicals; Neurodegenerative disease; Lysosomal destabilization
Citation: Venkatesan R, Park YU, Lee TH, Kim SY (2017) Gnetol, a Resveratrol Derivative Ameliorates Malathion-Induced Neurotoxicity through Modulating Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in N2a Cells. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 7: 388. Doi: 10.4172/2161-0460.1000388
Copyright: © 2017 Venkatesan R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 8129
- [From(publication date): 0-2017 - Dec 19, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 7096
- PDF downloads: 1033
