Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Nasal Cavity with Neural-Type Rosettes: A Diagnostic Challenge
Received: 28-Apr-2012 / Accepted Date: 25-May-2012 / Published Date: 30-May-2012 DOI: 10.4172/2161-119X.1000115
Introduction
The Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma (BSCC) is an aggressive high grade variant of squamous carcinoma mainly seated in larynx, hypopharynx and base of tongue [1]. A few cases have been reported in the sinonasal tract [2-7] and rarely with a growth pattern of neural type rosettes.
The correct identification of this tumour in small endoscopic biopsy is a diagnostic challenge even with the proposed immunohistochemical procedure [5,9,10], because the squamous component is scan and difficult to identify in the tumoral tissue.
We report a case of BSCC with true neural-type rosettes growing in the right nasal fossa with extensions that go from the middle turbinate to the choanae. In this area the differential diagnosis include, high grade basaloid tumours with glandular adenoid pattern such as: small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma (grade 3 of Hyams), adenocarcinoma of intestinal-type and non intestinal-type and salivary gland type Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) of solid pattern.
Case Report
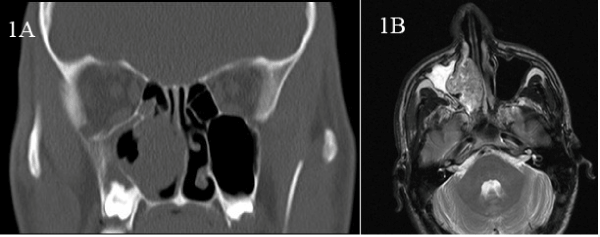
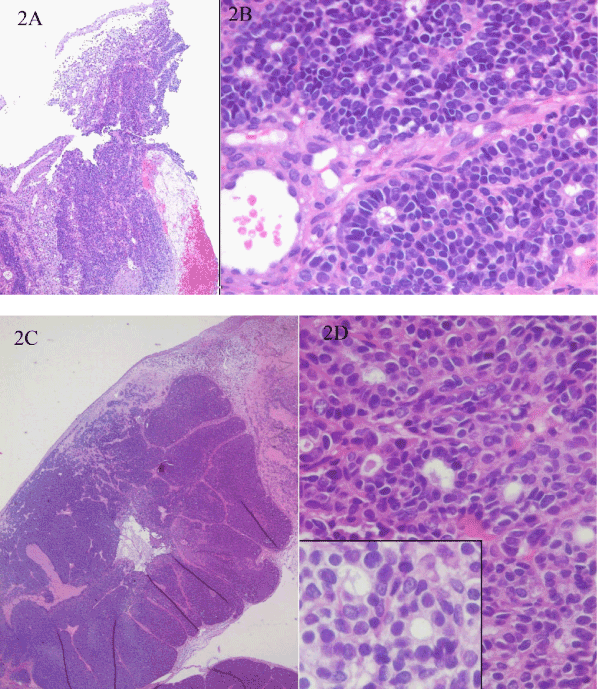
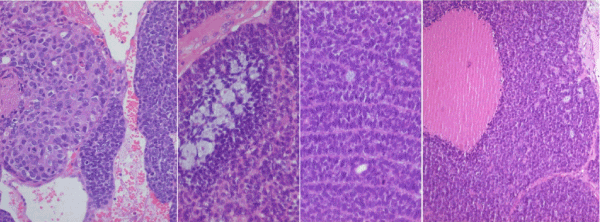
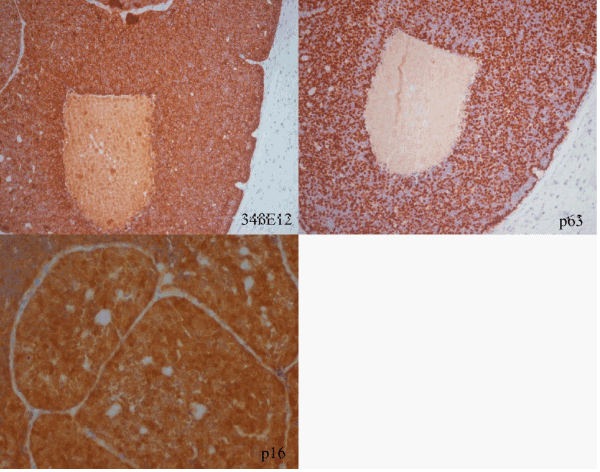
A 30-year-old man, non smoker, with 3 weeks history of nasal obstruction and some nasal bleeding. The endoscopic procedure showed a polypoid smooth mass of 45 x 30 mm. CT scan and MRI showed mass effect with heterogeneous signal which infiltrate the middle wall of maxillary sinus (Figure 1a and 1b). The laboratory tests were normal. The endoscopic biopsy showed 3 small fragments of about 3 mm each, the greatest of them with basaloid cells forming rosettes of neural-type with central lumen (Figure 2a and 2b). They were positive for AE1/AE3, CK7, CK8-18 and negative for neuroendocrine markers, CK20, CDX-2 or neurofilaments; expression of S-100 was focal only in intratumoral dendritic Langerhans' cells. With the initial diagnosis of -Non intestinal-Non salivary Adenocarcinoma, a surgical endonasal resection was performed. Pathologic examination (Figure 2c, 2d and 3) showed at low power a puzzle fashion (jig sawlike pattern) with several patterns of growth: solid with and without necrosis, microcystic, trabeculated and rosettes of neural-type compounds of basaloid pleomorphic cells. The squamous components were scanty and they were observed -in situ- as well as in invasive areas. Prominent interstitial and pericellular hyalinosis was also observed. Lymphovascular or perineural invasion was not found. The atypical cells revealed a diffuse and strong reaction for 34ßE12, CK7, p63 and p16 markers and they were negative for chromogranin-A, synaptophysin, CD56 and CEA (Figure 4). Molecular analysis for HPV using PCR was positive for genotypes 16, 33 and 58. A final diagnosis of BSCC with HPV associated was established. There is not evidence of relapses or metastasis 12 months after of standard treatment.
Figure 2: (a) Low power light microscopy of the endoscopic biopsy with predominant basaloid appearance and invasive pattern (Hematoxylineosin stain. original magnification 4x). (b) High power showing neural-type rosettes with secretion into the lumen (Hematoxylin-eosin stain. original magnification 40x). (c) The surgical resection large lobules with compact nests of basaloid cells and jig saw-like pattern, necrosis, prominent interstitial and pericellular hyalinosis and peripheral palisading (Hematoxylin-eosin stain. original magnification 4x). (d) Detail of scanty squamous cell component (Hematoxylin-eosin stain. original magnification 40x).
Discussion
BSCC was described using morphological criteria by Wain et al. [1] in the larynx, hypopharynx and base of the tongue. Out of the head and neck region, there are reports in other sites, including lung, esophagus, anus, cervix and penis [11-13].
Several cases in the nasal cavity with or without sinus affectation have been reported [2-4,6,7]. Wieneke et al. [5] reported the largest case series related to the sinonasal tract with 14 cases, 64% of them the (9-13) growing in the nasal cavity, 3 in the paranasal sinuses and 2 in both areas. Clinically, most cases present nasal obstruction and/or nasal bleeding, as in our case.
The growth patterns of BSCC is assorted and this heterogeneous arrangement varies among different cases reported. Some of the growing patterns of the BSCC result especially unusual and they lead often to a diagnostic pitfall. To the best of our knowledge, there is only one series with two cases showing -true neural-type rosettes- [5], as in our case. Wain et al. [1] described ductal structures that may be misinterpreted as neural-type rosettes. The spindle pattern has been reported very few times in this site [5,8].
The differential diagnosis in small endoscopic biopsy of BSCC with neural-type rosettes include, first at all, the small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, which can have rosettes, but the nuclear molding, crush artifact, dot-like keratin pattern and neuroendocrine markers clearly separate this entity of the BSCC. The olfactory neuroblastoma grade 3 of Hyams usually negative for CK, EMA, CEA or CD99, but positive for neurofilaments and endocrine markers. The high grade adenocarcinoma of intestinal type is CK7 negative and positive for CDX-2, MUC-2 and CK20 positives as opposite to non-intestinal adenocarcinomas [14]. Furthermore the solid variant of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) should be also considered. In the distinction between BSCC and AAC, absence of myoepithelial cells and the presence of dot-like vimentine expression in BSCC can be helpful. S-100 protein reactivity is not helpful in the differential diagnosis, and when observed, it usually corresponds to intermingled dendritic cells [15].
The diagnostic of BSCC needs to identify the squamous component which can be either in-situ carcinoma, invasive or abrupt keratinization into basaloid nodules. The strong positive reaction for 34ßE12 and p63 may also help in its identification.
Recently a report [16] of sinonasal carcinomas of different histotypes (including two cases of BSCC) relates the HPV presence with better 5-year progression-free survival. Woolgar et al. [17] suggest the idea that the oropharynx BSCC is not an uniform entity. Emphasis must be placed on the fact that despite the morphology, when arising in the oropharynx and it is HPV-positive, BSCC has a biology and prognosis apparently equivalent to the typical HPV-positive oropharyngeal SCC.
Finally, the BSCC of the sinonasal tract is unusual, involving all nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The presence of true neural-type rosettes is an event very unusual in this entity and should be considered a wide differential diagnosis versus other tumours of this area. Although in lesser extent than the oropharynx, the BSCC of the nasal cavity can be related to HPV, in which case it is mandatory testing for p16/HPV.
References
- Wain SL, Kier R, Vollmer RT, Bossen EH (1986) Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the tongue, hypopharynx, and larynx: report of 10 cases. Hum Pathol 17: 1158-1166.
- Weiss LM, Movahed LA, Butler AE, Swanson SA, Frierson HF Jr, et al. (1989) Analysis of lymphoepithelioma and lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas for Epstein-Barr viral genomes by in-situ hybridization. Am J Surg Pathol 13: 625-631.
- Wan SK, Chan JK, Tse KC (1992) Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the nasal cavity. J Laryngol Otol 106: 370-371.
- Banks ER, Frierson HF Jr, Mills SE, George E, Zarbo RJ, et al. (1992) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 40 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 16: 939-946.
- Wieneke JA, Thompson LD, Wenig BM (1999) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the sinonasal tract. Cancer 85: 841-854.
- Lu SY, Eng HL, Huang CC, Chien CY, Lui CC, et al. (2006) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the sinonasal tract: report of two cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134: 883-885.
- Lee JS, Ko IJ, Jun SY, Kim JY (2009) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma in nasal cavity. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2: 207-210.
- Altrabulsi B, Carrizo F, Luna MA (2006) Spindle basaloid squamous carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: immunohistochemical and clinicopathological study of three cases. Ann Diagn Pathol 13: 149-153.
- Coletta RD, Almeida OP, Vargas PA (2006) Cytokeratins 1, 7 and 14 immunoexpression are helpful in the diagnosis of basaloid squamous carcinoma. Histopathology 48: 773-774.
- Chapman-Fredricks J, Jorda M, Gomez-Fernandez C (2009) A limited immunohistochemical panel helps differentiate small cell epithelial malignancies of the sinonasal cavity and nasopharynx. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 17: 207-210.
- Moro D, Brichon PY, Brambilla E, Veale D, Labat F, et al. (1994) Basaloid bronchial carcinoma. A histologic group with a poor prognosis. Cancer 73: 2734-2739.
- Kobayashi Y, Nakanishi Y, Taniguchi H, Sekine S, Igaki H, et al. (2009) Histological diversity in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus 22: 231-238.
- Chaux A, Lezcano C, Cubilla AL, Tamboli P, Ro J, et al. (2010) Comparison of subtypes of penile squamous cell carcinoma from high and low incidence geographical regions. Int J Surg Pathol 18: 268-277.
- Stelow EB, Mills SE, Jo VY, Carlson DL (2010) Adenocarcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. Adv Anat Pathol 17: 262-269.
- Cardesa A, Zidar N, Ereno C (2005) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma in WHO Pathology and Genetics Head and Neck Tumours Ed. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. IARC Press, Lyon 124-125.
- Alos L, Moyano S, Nadal A, Alobid I, Blanch JL, et al. (2009) Human papillomaviruses are identified in a subgroup of sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas with favorable outcome. Cancer 115: 2701-2709.
- Woolgar JA, Lewis JS Jr, Devaney KO, Rinaldo A, Coskun HH, et al. (2011) Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: a single squamous cell carcinoma subtype or two distinct entities hiding under one histologic pattern? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268: 161-164.
Citation: López Duque JC, Cacho G, Martín Arregui FJ, Gómez JJ, Etxezárraga MC, et al. (2012) Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Nasal Cavity with Neural- Type Rosettes: A Diagnostic Challenge. Otolaryngology 2:115. Doi: 10.4172/2161-119X.1000115
Copyright: © 2012 López Duque JC, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15870
- [From(publication date): 6-2012 - Jun 16, 2024]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 11494
- PDF downloads: 4376