Research Article Open Access
Sociological Study of the Modern Social Networks’ Role in the Identity of the Citizenship in the Iranian Youth
Seyfollah Seyfollahi and Alimorad Musapu*Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Tehran, Iran
- *Corresponding Author:
- Alimorad Musapur
Islamic Azad University
Science and Research Branch
Tehran, Iran
Tel: 44865179-82
E-mail: mosapuor1376@gmail.com
Received Date: August 04, 2016; Accepted Date: September 22, 2016; Published Date: September 29, 2016
Citation: Seyfollahi S, Musapu A (2016) Sociological Study of the Modern Social Networks’ Role in the Identity of the Citizenship in the Iranian Youth. J Civil Legal Sci 5: 218. doi: 10.4172/2169-0170.1000218
Copyright: © 2016 Seyfollahi S, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Civil & Legal Sciences
Abstract
“Identity of the citizenship” includes the recognition of the rights and duties of the citizenship, and” human interactions “is one of factors of shaping it which has been changed under the influence of the modern social networks. This research has been done with the title of “sociological study of modern social networks in the identity of the citizenship in the Iranian youth “using a combination method, and the techniques of interviews and questionnaires were used to collect the required data. Validity of questionnaires is estimated 91% by Cranach’s α. The statistical population consisted of 16–18 years old youth from Tabriz. The sampling method was casual classified relational method and the sample size was 372 persons. The results showed that there was a negative average correlation between the variables of civil factors, political factors of the legal aspect of the identity of the citizenship and the use of social networks and there was a positive average correlation between the variables of cultural factors of the legal aspect of identity of the citizenship and the use of social networks.
Keywords
Identity of the citizenship; Civil factors; Political factors; Cultural factors; Modern social networks
Introduction
One of the consequences of the emergence and spread of modern social networks in the community is fundamental change in human interactions. Interactive and ubiquitous structure of networks was important factors to attract millions of eager users to join them. Communicative action that occurs among users and Web content providers is a sign of a process of socialization in terms of applied sociology, because the content of these networks influences the users in terms of values and norms systems.
These networks, as a place for unlimited intercultural interactions, data transfer, exchange of knowledge and ideas along with entertainment, have created new opportunities for users to form and manifest the identity of citizenship, in a manner that the people are faced with lots of resources of identification and their identity seeking process has been formed universally. In addition, the modern social networks allow the users to create their favorite identity [1], so we can say that the modern social networks, play a fundamental role in shaping the identity of the citizenship for users alongside shaping social relations. One of the diverse types and multiple identities of people is identity of the citizenship that contains a set of common fundamental values, attitudes and rules involving a sense of belonging, commitment and respect for common heritage and also recognizing the rights and duties of the citizenship [2]. Turner believes that citizenship consists of a social requirements and rights that make a legal identity for people in an urban society [3].
According to the National Development Management Center of modern social networks in 2016, more than 45 million people in Iran are able to participate in modern social networks. These informational and communicational capacities created by modern social networks are the basis for the initial question of the present research: What role the new social networks play in identifying the Iranian young citizens?
Adel Pour and colleagues [4], Saroukhani and others [5], Shabani [6], Ren and colleagues [7], Taylor [8], Cheung and Lee [9], Lee and others [10] who have examined the relationship between the social networks and the identity, show that there is a relationship among the duration of attendance, participation and use of social networks with the sociocultural identity, political identity, historical identity and ethnic, religious and national identity, and world identity of the users, and all the results, referring to social networks, show that changing social networks to affective phenomena in interactive and relationship patterns among humans, modern social networks will be effective in changing the users identity. Some findings refer to the major role of the social networks in highlighting collective commitment and social identity, and promote participation and user compatibility with civil interests. Some refer to the role of these networks to homogenize the world in terms of culture and ideas, and totally they believe the social networks are a factor in socialization.
According to the study findings and theories of some sociologists such as Giddens, Castells, and Turner and others, about the impact of mass media, it can be concluded that modern social networks effect on different aspects of identity of the citizenship in young users. So, author’s approach in this study is that in addition to accepting the role of different social structures, and the role of modern social networks in identifying the users, it focuses on the actions and movements of young social network users. Among these, the role of social networks is not in one-way and it is not of the world view institutions and dominant cultures, because users of these networks are actors who select and interpret the social and cultural networks contents and information’s purposefully. In addition, cultural, social, political and economical structure of society, in which micro and macro relations are shaped, will be effective in membership of users in different groups on the network and the selection process and their perceptions of the information’s and contents in these networks. In fact, although the membership in social networks effect on all public and private aspects of young user activities, these young people as social actors have the will and are not affected passively by virtual atmosphere, but this influence and reception is thoughtful, and young users organize their interactions within social networks according to different social structures.
Concept of “identity of the citizenship”
The “citizen” word is an English vocabulary and is derived word “city”, and originally comes from the Latin word “civility”. This word in Latin is the equivalent for the word “police” and in Greek it means the “city”. According to Anthony Giddens, a citizen is a member of a political community who has rights and duties in relation to this membership [11]. Being a citizen as a “normal” form, means having the right to vote and taking political positions, benefitting from equality before the law and having the right to exploit the various government benefits and services, respectively. In addition, being a citizen requires having obligations such as obeying the law, paying tax and defending the country in critical conditions [12]. From the sociological viewpoint, citizenship includes taking advantages of series of civil, political, social and economic rights developed by qualified institutions and structures [13]. According to Aizin and Turner[14] there are less emphasis on legal rules and more emphasis on norms, practices, meanings and identities in the sociological definition of citizenship. Citizenship aspects include: 1) civil aspect of citizenship 2) the political aspect of citizenship 3) socio-economic dimension aspect of citizenship 4) cultural aspect of citizenship.
According to various definitions of identity of the citizenship, it can be said that the identity of the citizenship has two fundamental aspects citizenship rights and duties that each has some components. The legal identity of the citizenship involves some components of civilization, culture and politics which have been studied in this research.
Operational Definition of the Identity of the Citizenship
Two fundamental aspects of rights of the citizenship and duties of the citizenship have been considered for identity of citizenship that each involves another dimension. The legal dimension of identity of citizenship consists of civil, cultural and political dimensions and duty role of the identity of the citizenship consists of legislation, universalism and social tolerance.
Forty-six items were used for measuring the dependent variables of the identity of the citizenship. Exploratory factor analysis and validity analysis were used to determine variable dimensions of this structure. Before goodness and capability analysis, and factor analysis, “modern social networks” were examined by KMO1 and BTS2 test. The results of these tests indicate the fact that, first, how good idea was the idea of factor analysis for these items? These statistics indicate that how extent common factors can be able to explain the variance of variables. “Mentioned statistic range is between zero and one. If the value of this statistic is between 0.50 and 0.69, it shows the suitability of extent of correlation for the set of variables for factor analysis, and it shows more than 0.70 which is very suitable correlation for factor analysis. Secondly, D3or determinant indicates whether the correlation matrix between these questions is “single matrix” or not? If it is single, it will not be possible to perform factor analysis properly (Table 1).
| Factor | Titles of factors | Items | Factor value | Special factor value | Percentage of explained variance | Coefficient Validity of the scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor: legal dimension of identity of citizenship fa |
Civil factor Civil Civil factors |
1. I can comment on various social and political affairs freely and without any feeling of limitation. I feel that I have freedom of speech. 2. I can talk about various social and political affairs freely and without any feeling of limitation. I feel that that I have freedom of speech. 3. I can select my religion freely and without any feeling of limitation and say my religion. In fact I have freedom of selection and religion. 4. I can interact freely with anyone and any group that I’m willing to engage in them. In fact, I enjoy the freedom in social interactions and communications. 5. I can freely access to my required information and knowledge. In fact, I feel that freedom of access to information is very achievable in society. 6. In our society, everyone is equal before law and there is no difference and no orientation towards different groups of people before the law. 7. Any discriminatory and one-sided judgment in our society for men and women is forbidden, and all women and men are equal. 8. Any discriminatory and one-sided Judgment in our society for different ethnicities (Persians, Turks, Kurds, Baluchis, etc.) is prohibited and all people of every nation are equal. 9. Any discriminatory and one-sided judgment in our society for Shiites and Sunnis is forbidden and people of all religious communities are equal. 10. No one has the right to offense anyone in social and cultural issues, and all are protected by law against any aggression. |
0.845 0.817 0.749 0.686 0.657 0.551 0.479 0.478 0.479 0.478 0.459 |
4.283 | 21.73 | 80/. |
| Political factor Political factors |
1. Iranian youth have the right to vote and the law protects of their voting rights. 2. Each Iranian youth can be responsible for filling a job and responsibility at various levels in the government, and there is a need and capability to get a responsibility. 3. Every Iranian young people, women or men with any political and religious tendencies and ethnic groups can participate freely in the political process and activities. 4. Iranian young people access to required information freely without restrictions. 5. I think all human beings are free and equal with any gender and with any language. 6. All of the youth have right to protest against public and social affairs. |
0.830 0.763 0.718 0.628 0.139 0.286 |
2.455 2.925 12.73 |
16.375 | 713/. 705/. |
|
| Cultural factors | 1. Every young people can travel any favorite place without any restrictions in the world. 2. Iranian youth are in a high mobility in the field of cultural issues and their mobility is clear in the cultural issues particularly in accepting cultural elements. 3. Young people can comfortably speak and write in their native language (Persian, Turkish, Kurdish, etc.) and there are no restrictions in speaking and writing in their native languages. 4. In Iran, all young people have the right to live in their customs, language and culture and there are not any limitations. 5. Each Iranian youth can easily learn national language (Farsi) and national customs and they can introduce themselves by it. 6. Each Iranians young people can communicate and interact without any restrictions with other nations and different cultures. 7. As a young man, I respect for all peoples with different cultures and ethnic groups, and I should respect them despite all of cultural differences. 8. The superiority of one culture over another is not a sign of difference in cultures. |
0.730 0.704 0.679 0.614 0.596 0.535 0.460 0.458 |
Determinant = 1.644 Alpha =/0 91
Kaiser- Meyer- Olkin measure of sampling adequacy =689 /.
Bartlett Test of Sphericity =36260725 Significance =000
Table 1: Results of factor analysis and reliability analysis of the items related to the legal aspect of the identity of the citizenship.
In general, study of modern social networks role in the formation of a new legal dimension of the identity of citizenship for Iranian Youth is the main purpose of the present research. The trivial goals are:
1- The study of the state of the identity of the citizenship in its legal dimension among Iranian youth.
2- The study of modern social networks role in its legal dimension among Iranian youth
3- The study of consequences of modern social networks role in the identity of the citizenship among youth.
4- Providing strategies and suggestions to optimize the role of social networks in the identity of the citizenship among Iranian youth.
Research Hypothesis Includes
1- It seems that modern social networks play a role in the identity of the citizenship from the viewpoint of civil aspect (as one of the legal aspect of identity of the citizenship) for Iranian young users.
2- It seems that modern social networks play a role in the political aspect of the identity of the citizenship (as one of the legal aspect of the identity of the citizenship) for Iranian young users.
3- It seems that modern social networks play a role in the cultural aspect of the identity of the citizenship (as one of the legal aspect of the identity of the citizenship) for Iranian young users.
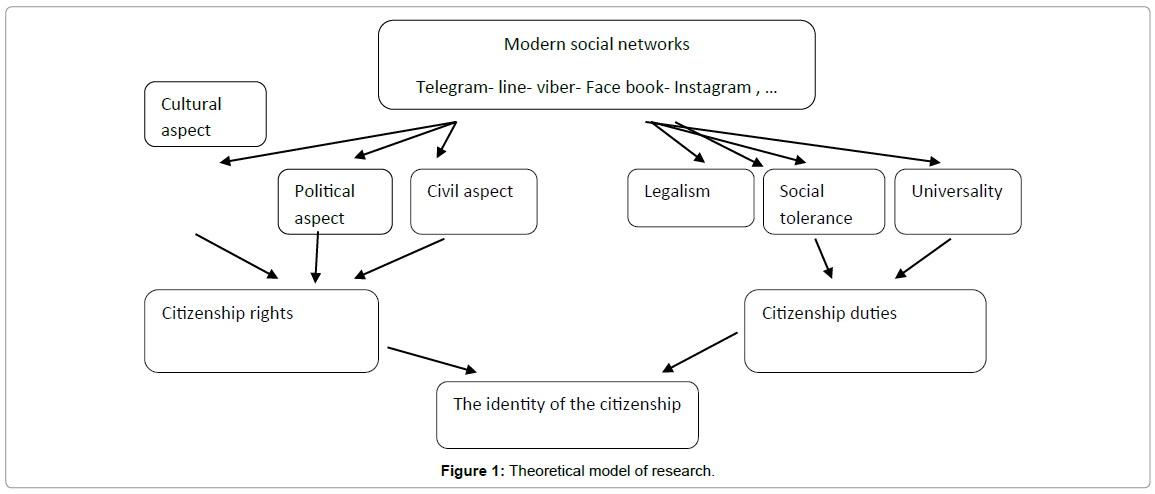
Theoretical Model of Research
Figure 1 shows the Theoretical model of research.
Tools and methods
Due to the nature of this research, the most appropriate method is the combination way or multi-way style. In the first stage in order to gather the required information, interview techniques and written questionnaires techniques were used to collect field data. The questionnaire is based on theoretical foundation and research findings adopted in the form of 56 questions, and its validity estimated 0 91% by Cranach’s α, respectively. The statistical population consisted of all 16 to 18-year-old youth educating in five educational zones of the pedagogical department with abundance of 51210 in Tabriz using classified sampling, 372 young people were selected by potential efficiency of 1% and coefficient reliability of 99% The obtained data were analyzed by SPSS software.
Research Findings
Distribution of studied young people in terms of gender
The statistical sample in this study includes 372 patients who are 188 men and 184 women; it means 50.5% men and 49.5% women constituted the statistical sample.
Distribution of studied young people in terms of age
Youth age distribution of the study shows the age range of 16–18 years. Frequency of age group related to 16 years old contains 114 subjects i.e., 33.2% statistical sample and 17-year-old age group with a frequency of 115 subjects i.e., 33.5%, and 18 years old with a frequency 114 subjects i.e., 33.2%.
Distribution of studied young people from the viewpoint of educational level
In Statistical sample, 123 subjects, i.e., 33.1 percent were studying in high school in the second grade and 126 subjects i.e. 33.9 percent in the third grade and 123 subjects i.e. 33.1 percent in preuniversity grade.
Rate of using the social networks in the studied youth per day in terms of hours
According to the data, 22.6 percent of young subjects have used the social networks less than 1 hour, 37.4 percent between 1 to 2 hours, 24.5 percent between 3 to 4 hours, 8.9 percent between 5 and 6 and 6.7 percent more than 6 hours (Table 2).
| Items | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Less than one hour | 84 | 22.6 |
| 1 to 2 hour | 139 | 37.4 |
| 3 to 4 hour | 91 | 24.5 |
| 5 to 6 hour | 33 | 8.9 |
| More than 6 to hour | 25 | 6.7 |
| Total | 372 | 100 |
Table 2: Frequency distribution of using the modern social networks in young subjects.
Frequency Distribution in Terms of Type of using the Modern Social Networks among Youth
27.8 percent of young subjects have used the modern social networks to exchange information and ideas, 22.2 percent for entertainment and recreation, 19.7 percent to chat with friends and greeting with relatives, 13.1 percent to spend time and escape from loneliness, 8.4 percent for the news of community, 4.3 percent for teaching and learning issues, 3.3 percent for sending and receiving photos and videos and 1.3 percent to receive unannounced news of TV (Table 3).
| Kind of using | Frequency | percent |
|---|---|---|
| To exchange information and ideas | 176 | 27.8 |
| for entertainment and recreation | 141 | 22.2 |
| To chat with friends and greeting with relatives | 125 | 19.7 |
| To spend time and escape from loneliness | 83 | 13.1 |
| To receive the news of community | 53 | 8.4 |
| to teach and learn issues | 27 | 4.3 |
| to send and receive photos and videos | 21 | 3.3 |
| To receive the unannounced news of TV | 8 | 1.3 |
| total | 634 | 100 |
Table 3: Frequency distribution in terms of type of using for modern social networks in studied young subjects.
Research Hypothesis
1. It seems that the modern social networks have a role in the civil dimension of identity of the citizenship (as one of the legal dimension in identity of the citizenship) for young subjects.
According to the data, there were relatively moderate negative and linear correlation between civil factor variables of identity of the citizenship and amount use of the modern social networks (Table 4).
| Variables | Rate of using the modern social networks | |
|---|---|---|
| Civil factor in the identity of the citizenship | The correlation coefficient Significant n |
425 % ** 0/004 372 |
Table 4: The correlation coefficient of using the modern social networks and civil factor in the identity of the citizenship.
2. It seems that modern social networks have a role in the political dimension of the identity of the citizenship (as one of the legal dimension of the identity of the citizenship) for young subject
According to the data of the table 4, there were relatively moderate negative and linear correlation between political factor variable of identity of citizenship and amount use of the modern social networks (Table 5).
| Variables | Rate of using the modern social networks | |
|---|---|---|
| Political factor in the identity of the citizenship | The correlation coefficient Significant n |
438 % ** 0/004 372 |
Table 5: The correlation coefficient of using the modern social networks and political factor in identity of citizenship.
3. It seems that modern social networks have a role in the cultural dimension of the identity of the citizenship (as one of the legal dimension of the identity of the citizenship) for young subjects.
According to the data of table 5, there were relatively moderate negative and linear correlation between cultural factor variable of the identity of the citizenship and the amount of using the modern social networks (Table 6).
| Variables | Rate of using the modern social networks | |
|---|---|---|
| Political factor in the identity of the citizenship | The correlation coefficient Significant n |
297 % ** 0/004 372 |
Table 6: The correlation coefficient of using the modern social networks and political factor in identity of citizenship.
4. It seems that with some solutions we can direct the role of the modern social networks toward more applied roles (The role of awareness and education) among youth.
According to collected opinions and comments of the young user’s of the social modern networks we can recommend some solutions for improving the role of the networks among the youth (Table 7).
| Order | item |
|---|---|
| 1 | Creating organized groups dealing with production and distribution of contents required by youth according to their mental states and ages. |
| 2 | Ads making people aware and making a new culture for advantages and disadvantages of the membership in the modern social networks |
| 3 | Creating an opportunity for improving the relation of the parents and teachers with the teenagers and the youth. |
| 4 | Flexibility and an attitude in society toward the youth and teens and their emotional needs |
| 5 | Changes in the school conditions from open prisons to group game spaces and operational lessons instead of theory lessons. |
| 6 | Creating situations for group and physical games such as football, volleyball etc., and gatherings in neighborhoods |
| 7 | Creating situation for spending time with parents and children together |
| 8 | Supporting, manufacturing, purchasing and distributing movies loved by the youth. |
| 9 | Selecting policy of honesty and transparency in broadcasting news from national media |
| 10 | Making coordinative situation among social institutions of families in schools and media in terms of supervision of education department |
| 11 | Making new culture in society in terms of consumption |
| 12 | Setting up native and national networks based on national values and norms |
Table 7: Solutions for making the modern social networks role applicable among the youth.
5. Using the modem social networks in terms of gender
Based on test statistics of difference in averages (Sig: 0/003 and t: 2, 99) it can be said that there is a significant difference between men and women users in social networks in level of using the networks (Table 8).
| The youth | n | Average | S d | T | df | sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 188 | 2,57 | 1,19290 | 2,99 | 364,73 | 0,003 |
| women | 184 | 2,22 | 1,03455 |
Table 8: T-test for comparing level of using the modern social networks among women compared to men.
6. Role of modern asocial networks in identity of the citizenship in terms of gender
Based on statistics, there is a significant difference among men and women who use the networks in criteria of civil, political and cultural factors (Table 9).
| The youth | n | Indices | average | SD | T | df | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| men | 188 | Civil | 2,93 | 0/325 | -7,53 | 370 | 000 |
| women | 184 | 3,467 | 0/731 | ||||
| men | 188 | Political | 4,01 | 0/947 | -3,188 | 370 | 0/002 |
| women | 184 | 0/834 | 4,40 | ||||
| men | 188 | Cultural | 4,07 | 0/751 | -10,17 | 370 | 000 |
| women | 184 | 3,30 | 0/712 |
Table 9: t-test. Comparing the condition of the criteria among women compared to men.
7. Comparing condition of the identity of the citizenship among young in terms of level of education
Based on data from variance analysis with Sig=000 and F=48, 3, it can be argued that there is a significant difference between users with different educational level (Table 10).
| Source of changes | Total squares | freedom | Average squares | F | sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among groups between groups total |
352,67 1330,85 1692,53 |
2 367 369 |
176,338 3,651 |
48,30 | 000 |
Table 10: Variance analysis test, comparing condition of the identity of the citizenship in terms of their educational level.
Discussion and Conclusion
Social scientists believe that the identity is formed in social interactions and by engagement of an individual with the society. Presence of values and norms as historical and social truth has a key role in the formation of the individual identity.
In fact, individuals enter social networks with a wide source of concepts, thoughts and cultural affairs and seek to interpret content of virtual atmosphere.
In this regard, Castles believes that in network world where the internet has a key role, people encounter different identities, culture and speeches. People potentially can resist against it.
Since the youth join social networks and interpret their contents in a selective way, we can study the youth interactions not with a structural or postmodernism view but with an interpretive view. Accordingly there is no full interpretation with macro interpretation in content of social networks.
So we may count dual role for modern social networks in relation with idea of the citizenship identity. So that social networks can play a role in strengthening the users’ citizenship identity networks as well as they can have a destructive role in the identity of the citizenship by decanting different beliefs. Playing each of the above roles in modern social networks needs social structures of the society. Since the virtual space of the networks’ self-awareness exists in social structures, the identity in this atmosphere is a mixed identity. This identity is not a pre-made identity. Identity of users is made in this atmosphere. Hence, the stronger structures, the greater contest we will have.
Suggestions and Applied Solutions
According to the current research findings some solutions are presented for improving the identity of the citizenship in teens and youth of the society and applied use of the modern social networks in this field:
1. Direction of the management structure should seek to provide security and protecting the civil rights of the people. One of them is the free access to data and information which is possible through the young users of the modern social networks.
2. In the current research, the condition of the identity of the citizenship for youth and teens who use the networks, was under the average. Therefore it is necessary for the authorities to provide a condition to improve the identity of the citizenship in legal dimensions with the implementation of the principles of the constitution and executive guarantees to implement its principles.
References
- Bennett A (2006) Culture and Everyday life, London, Thousand Oaks, New Delhi, SAGE publication.
- Muhammadi MA , Sheiani M, Roshanfekr P (2012 ) Factors Related to Citizenship Identity in Tehran. J Soc Wel 10: 65-88.
- Rahimi M (2008 ) Study of the sense of citizenship among students of Faculty of Humanities.
- Pour Adel S, Ghasemi V (2015 ) The impact of Facebook on cultural identity Isfahan young. Journal of Iranian culture.
- Sarookhani B , Asadullah (2013 ) The Internet , globalization and cultural identity of the young in Iran.
- Sheiani M (2005) Citizenship status and obstacles to its realization in Iran. PhD thesis in sociology
- Ren Y, Kraut R, Kiesler S (2007) Applying Common Identity and Bond Theory to Design of Online Communities, Org Stu 28: 377-408.
- Tyler T (2012) Social networking and Globalization, Medit J Soc Sci.
- Cheung CMK, Lee MKO (2010) A theoretical model of intentional social action in online. Decs Sup Sys 49: 24-30.
- Lee J, Lee H (2010) The computer-mediated communication network: exploring the linkage between the online community and social capital. New Media & Soc 12: 711-727.
- Giddens A (1989) Sociology. Polity press.
- Castells M (2008) The New Public Sphere: Global Civil Society, Communication Networks, and Global Governance. AAAPS 616: 78-93.
- Falks K (2012) Citizen translation by Mohamedtaghi dellfroz.
- Turner BS (2001) The erosion of citizenship. Bri J Soc 52: 189-209.
Relevant Topics
- Civil and Political Rights
- Common Law and Equity
- Conflict of Laws
- Constitutional Rights
- Corporate Law
- Criminal Law
- Cyber Law
- Human Rights Law
- Intellectual Property Law
- International public law
- Judicial Activism
- Jurisprudence
- Justice Studies
- Law
- Law and the Humanities
- Legal Philosophy
- Legal Rights
- Social and Cultural Rights
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 3520
- [From(publication date):
November-2016 - Aug 18, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 2540
- PDF downloads : 980