Giant Chondroblastic Osteosarcoma Mandible-A Rare Case Report
Received: 23-Aug-2013 / Accepted Date: 15-Oct-2013 / Published Date: 23-Oct-2013 DOI: 10.4172/2161-119X.1000146
Keywords: Osteosarcoma, Mandibular tumors
255075Introduction
Osteosarcoma, the second most frequent primary malignant bone tumor, is usually found in long bones 42% occupying the femur, 19% in tibia, and 10% in the humerus. About 8% of all cases occur in the skull and jaw and other 8% in the pelvis [1]. Osteosarcoma of jaw is rare, aggressive malignant tumor which is characterized by formation of osteoid tissue. Jaw osteosarcomas usually presents in 3rd and 4th decade of life [2].
Mandibular tumor arises more frequently in posterior body and horizontal ramus [2]. The clinical manifestation of mandibular osteosarcoma are pain, swelling over bone and adjacent soft tissues, bulging and dislocation of tooth, lack of healing and swelling at the site of tooth extraction, and neurological disorders [3-5]. Osteosarcoma of mandible presents various clinical and histological aspects, as well as variable disease progression and outcome. The classical osteosarcoma is the most frequent variant, which develops in the medullary region of the bone and can be subdivided in osteoblastic, chondroblastic and fibroblastic histological types, depending upon the extracellular matrix produced by tumor cells [6]. Radiological appearance manifests as mixed radiolucent and radiopaque lesion, periodontal ligament widening, radiopaque masses with moth-eaten appearance, codman triangle and sunburst appearance [7].
Early detection of the tumor and early resection of the tumor are the keys to high survival rates [8]. The treatment protocols for osteosarcoma include radical or conservative surgery which is followed by radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Case Report
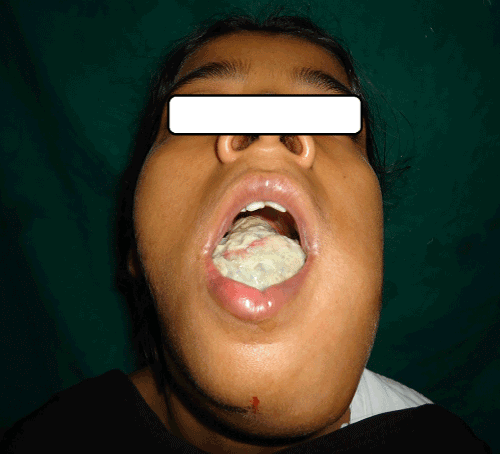
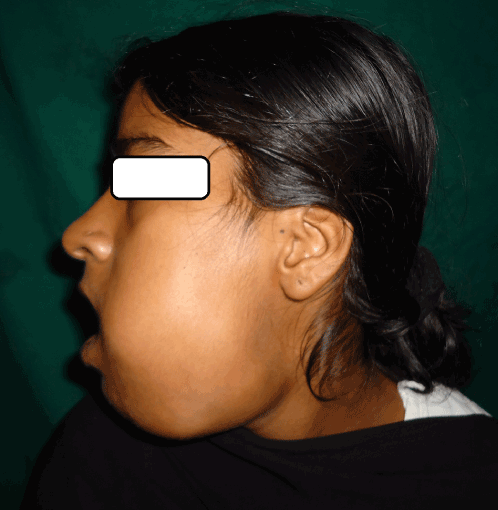
A 21 yr old female patient reported to our outpatient department with complaints of swelling in left lower jaw since 1 month. It was associated with pain which was severe, pricking and continuous in nature. The swelling was evident extra orally since 15 days. Past history revealed a tooth extraction of the left lower premolar tooth after the occurrence of dental carries, occasionally associated with oral bleeding. Intraorally, there was a huge growth on alveolar ridge in relation to lower left region extending from right canine to left 3rd molar region, was oval in shape, approximately 6×3.5 cm in size (Figure 1). On palpation, it was hard in consistency, having smooth surface, was tender on touch, nonpulsatile, nonmobile. The tongue was pushed to opposite side due to growth. On external examination swelling was present in lower third of jaw, ovoid in shape, approximately 6×5 cm in size, hard in consistency and tender, extending from midline up to left angle of mandible (Figure 2).
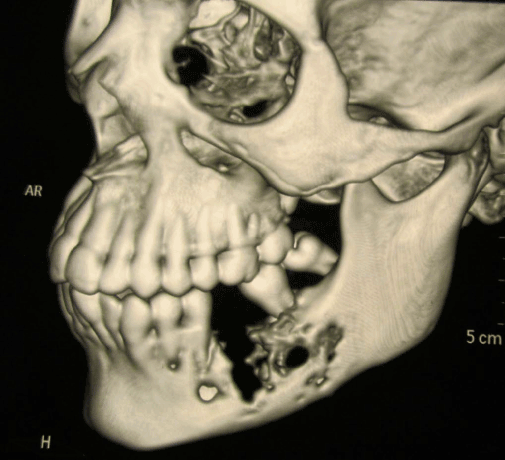
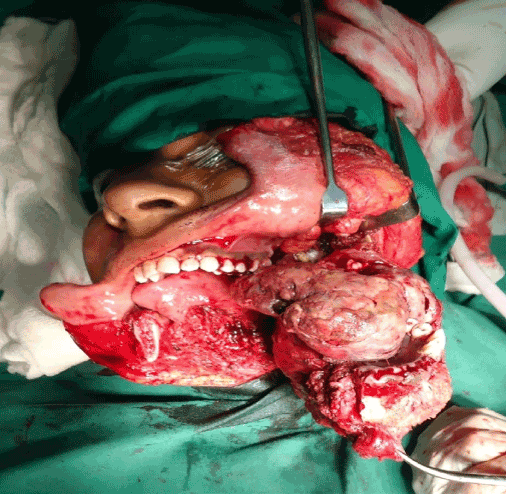
Orthopantomogram showed a mixed radiolucent radiopaque lesion extending from 2nd premolar to 2nd molar with loss of trabecular pattern. Noncontrast, multislice 3D CT of face and mandible showed an expansile mass lesion involving the left side of the mandible with extension of lesion in soft tissue mass with destruction of cortex in body of mandible (Figure 3). Biopsy from lesion was taken which was suggestive of osteogenic carcinoma of chondroblastic type. Patient was operated for wide local excision with hemimandibulectomy along with a margin of the normal surrounding tissue followed by post operative chemotherapy with cisplatin (Figure 4). Histopathology report was suggestive of chondroblastic type osteosarcoma. Patient was for follow up with us for 1 year with no signs of recurrence.
Discussion
Osteosarcoma is a rare tumor in maxillofacial region, its occurrence is 1/1, 00000 person per year [9]. Osteosarcoma may arise de novo or subsequent to previous irradiation. It can also be seen in preexisting Paget’s disease of bone and fibrous dysplasia. In the maxillomandibular region, most osteosarcoma have an osteoblastic nature, with deposition of a variable amount of osteoid matrix with minimal cytological atypia and usually with undifferentiated lesions [6,9]. In our case histological tumor was typical of the chondroblastic type. van ES et al. [10] in a study with 25 cases of osteosarcoma, observed that according to histological type of the tumor, patients with chondroblastic type osteosarcoma, treatment is well established in long bones, but it is not well understood when the condition involves the maxilla and mandible.
Histologically osteosarcomas can be classified according to the cellular differentiation as osteoblastic, chondroblastic and fibroblastic. In osteoblastic type atypical neoplastic osteoblasts exhibit considerable variation in shape and size, show large deeply staining nuclei and are arranged in disorderly fashion and these constitute 60% of jaw lesions. The chondroblastic type has been described to occur predominantly in head and neck region. In this type, tumor consists of atypical chondroid areas composed of pleomorphic and atypical binucleate cells, having large hyperchromatic nuclei and prominent nucleoli. The fibroblastic type is rare, especially in jaws. In myxomatous type there is atypical myxoid proliferation.
It is unclear that chemotherapy is beneficial in osteosarcoma of long bones, leading to significant changes in disease free survival rate. In most cases, the therapy of choice is radical surgical excision, since it provides a 5 yr survival rate over 80%.
In the present case, the lesion was diagnosed and surgical treatment was provided with hemimandibulectomy along with chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Maxillofacial osteosarcoma presents a wide spectrum of clinical, histological and radiological features. Therefore all these features need to be correlated to reach a conclusive diagnosis. It has a better prognosis if diagnosed and treated at an early stage.
References
- Ottaviani G, Jaffe N (2009) The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res 152: 3-13.
- Balwani SR, Tupaki JV, Barpande SR (2006) Parosteal osteosarcoma of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 10:10-14
- Mardinger O, Givol N, Talmi YP, Taicher S, Saba K, et al. (2001) Osteosarcoma of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radio/Endood 91: 445-451.
- Soares RC, Soares AF, Souza LB, dos Santos ALV, Pinto LP (2005) Osteosarcoma of the mandible, initially resembling a lesion of the dental periapex: a case report. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 71: 242-245.
- Khorate MM, Goel S, Singh MP, Ahmed J (2010) Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report and Review of Literature. J Cancer Sci Ther 2: 122-125.
- Bennet J.H. Thomas G, Evans AW, Speight PM (2000) Osteosarcoma of the jaw: A 30- yr retrospective review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 90: 323-333.
- Gaurd MS, John A, Umanji HR (2005) Osteosarcoma of the mandible: A case report. Journal of Indian Academy of Oral medicine & radiology 179: 110-113.
- Chindia ML, Guthua SW, Awange DO, Wakoli KA (2002) Osteosarcoma of the maxillofacial bones in Kenyans J Maxillofac Surg 26: 98-101.
- van ES RJJ, Kens RB, Van Der Wall I, koole R, Vemey A (1997) Osteosarcoma of the jaw bones : long term follow up 48 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac surg 26: 191-197.
Citation: Kedar S, Nagle S, Agarwal S, Bage S, Kothekar A, et al. (2013) Giant Chondroblastic Osteosarcoma Mandible-A Rare Case Report. Otolaryngology 3:146. DOI: 10.4172/2161-119X.1000146
Copyright: © 2013 Kedar S, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 22362
- [From(publication date): 11-2013 - Nov 07, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 17513
- PDF downloads: 4849