Make the best use of Scientific Research and information from our 700+ peer reviewed, Open Access Journals that operates with the help of 50,000+ Editorial Board Members and esteemed reviewers and 1000+ Scientific associations in Medical, Clinical, Pharmaceutical, Engineering, Technology and Management Fields.
Meet Inspiring Speakers and Experts at our 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events with over 600+ Conferences, 1200+ Symposiums and 1200+ Workshops on Medical, Pharma, Engineering, Science, Technology and Business
Short Communication Open Access
Ecological Media Reveal Community Structure Shifts in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Train
| Bergmann RC, Wright DA and Ralebitso-Senior TK* | |
| School of Science and Engineering, Teesside University, Borough Road, Middlesbrough, Teesside, TS1 3BA, UK | |
| Corresponding Author : | Ralebitso-Senior TK School of Science and Engineering Teesside University, Borough Road, Middlesbrough Teesside, TS1 3BA, UK Tel: +44 1642 342525 Fax: +44 1642 342401 E-mail: K.Ralebitso-Senior@tees.ac.uk |
| Received April 04, 2015; Accepted April 28, 2015; Published April 30, 2015 | |
| Citation: Bergmann RC, Wright DA, Ralebitso-Senior TK (2015) Ecological Media Reveal Community Structure Shifts in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Train. J Bioremed Biodeg 6:293. doi:10.4172/2155-6199.1000293 | |
| Copyright: © 2015 Bergmann RC, et al. This is an open-a ccess article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Related article at Pubmed Pubmed  Scholar Google Scholar Google |
|
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation
Abstract
Unique ecological/habitat media derived from four phases of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed the highest diversity (2.55-2.86) and evenness (0.79-0.87) for the raw sewage (R) medium. Richness was, however, inoculum- and media-dependent hence inocula R and P recorded the highest counts on media A and F, respectively.
| Keywords |
| Municipal wastewater; Habitat media; Ecological index; Community structure |
| Introduction |
| The continuing need for robust, sustainable and reliable (bio) technologies that are also characterized by minimal carbon emissions/footprints must be matched by an equally growing and sound knowledge base of the underpinning microbial communities. Despite their analytical power/capacity, ecogenomic tools do not provide phenotypic or physiological characterization of novel and previously uncultivated microbial strains [1]. A discrepancy that limits a more complete understanding of microbial and process dynamics. Although research continues on culturing strains that were considered unculturable, particular focus is on soil ecosystems [2-4]. A limited understanding exists, in particular, of the phenotypes underpinning a key biotechnology, wastewater treatment. |
| As a result, directed research must address the well-documented limitations of molecular-based methods [5] so that seemingly important community members or representatives of functionally significant groups can be cultivated for further analyses. Despite the debate for/against cultivation, with/without molecular analyses [6,7], the approach has been exemplified by many researchers [1,4,8-11] who used different approaches, and remains essential to elucidate the physiological responses of process microbial communities for subsequent exploitation. |
| Materials and Methods |
| Habitat media preparation and inoculation |
| Samples (1 L) were collected from four stages of a municipal wastewater treatment plant - raw sewage (R), primary settlement tank (P), aeration tank (mixed liquor) (A) and final effluent (pre-UV treatment; F). Following thorough gentle mixing, 50 mL aliquots were centrifuged (15,000 rpm x g; 15 minutes, 4°C) and the supernatants series filtered (Whatman: Grade 2; Nalgene: 0.45 μm; 0.2 μm) and autoclaved (121°C; 20 minutes; 15 lb psi). Each sterile filtrate was mixed 1:1 (v/v) with autoclaved 2X technical agar (Oxoid, U.K.) and allowed to set at room temperature for 48 hours prior to duplicate inoculations with 100 μL of 10-fold dilution of the original wastewaters. |
| Colony DNA extraction and PCR |
| Following incubation at 25°C for 72 hours, total colony scrapes were re-suspended in 200 μL sterile saline (0.9% w/v NaCl) for DNA extraction (FastDNA™ SPIN Kit, MP Biomedicals, U.K). The 16S rRNA gene (V3 region) was amplified with the F357GC/R518 primer set [12] with 1 μL DNA templates. The PCR was made [13] with 25 μL reaction volumes on a Primus 96 Plus (MWG Biotech, Ebersberg, Germany) and amplicons (5 μL) visualised on 1.5% (w/v) agarose gels stained with SYBR Safe (Molecular Probes, Eugene, U.S.A). |
| DGGE community profiling |
| DGGE profiling [12] used an Ingeny Phor U system (Ingeny, Leiden, The Netherlands). Amplicons (20 μL) were loaded onto a 10% (w/v) polyacrylamide gel with a 30-65% denaturing gradient and electrophoresed (18 h; 60°C; 100V) in 0.5× TAE buffer. The gels were stained for 20 minutes with SYBR Gold (Molecular Probes, Eugene, U.S.A.) and digitised (Alpha Imager Gel Documentation System; ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, U.S.A.). Bands per lane were quantified (Phoretix 1D Pro gel analysis software; TotalLab, Newcastle, U.K.) and cluster analysed by the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic averages (UPGMA) [14,15]. |
| Ecological index and statistical analyses |
| Bacterial community diversity, evenness and similarity were assessed by the Shannon-Wiener diversity (H’), Shannon evenness (E) [16] and Sørensen indices [17], respectively. Inoculum- and media-dependent differences in community structure, taxa richness and community similarity were evaluated by two-way ANOVA tests (Microsoft Office Excel 2007; Microsoft, Redmond, U.S.A) |
| Results and Discussion |
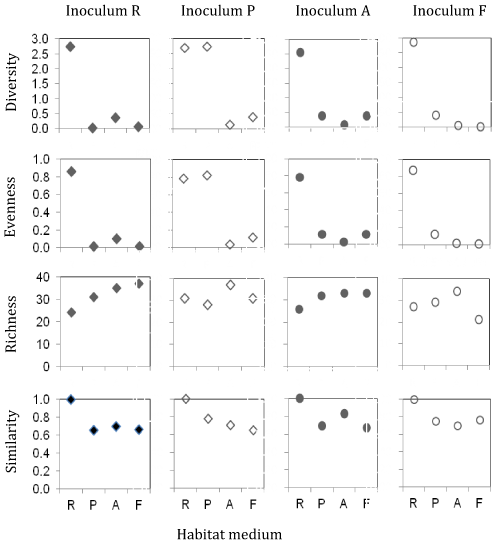
| For all inocula, the Shannon-Wiener diversity (2.7 ± 0.06) and evenness (0.8 ± 0.02) were highest after cultivation on the raw sewage medium with statistically significant (p=0.0009) decreases recorded (0.4, H’; 0.12, E) for the other three media (Figure 1). These findings probably related to the high nutrient availability in the raw sewage tank and decreased types/concentrations of the subsequent [18]. Only the community from the primary settlement tank inoculated on its respective medium showed similarly high diversity and evenness values as the raw sewage culture, indicating a marked medium change. |
| In general, the average taxa richness of all inocula increased (27 ± 1.5 to 34 ± 1) through the treatment process indicating a change in the selection pressure [18,19]. The one exception was for the P-inoculum cultured on its respective medium, which decreased from 31 to 28. The Sørensen index of similarity indicated comparable community composition throughout the treatment process and suggested that species abundance only varied at different stages. |
| Emergent research has been made to culture previously uncultured microbial strains from soil ecosystems with only limited investigations for wastewater management. This is in direct contrast to the multiple molecular-based analyses that have been applied, developed and optimised to characterise the complex microbial communities in different wastewater biotechnologies. Matching and complementing genotypic tools with culture-based (phenotypic) analyses will facilitate: (i) identification of novel strains; (ii) quantification of their upper and lower physiological limits and function characterisation; (iii) culture maintenance of important monocultures/ communities [20]; and (iv) more informed exploitation in wastewater treatment plants for increased efficiency/stability/reliability. |
| Conclusion |
| This study exemplified the use of wastewater-based media to culture microbial communities that characterized specific phases of a continuous treatment train. DGGE-based analysis then facilitated measurements of diversity, evenness, taxa richness and similarity between treatment stages. Future work should entail detailed physiological/phenotypic studies of the cultivated strains/communities and, subsequently, sequencing to allow genotypic comparisons with these and uncultured wastewater species in existing databases. |
| Acknowledgements |
| This study was supported partly by the Teesside University SAR13 scheme. |
References
|
Figures at a glance
 |
| Figure 1 |
Post your comment
Relevant Topics
- Anaerobic Biodegradation
- Biodegradable Balloons
- Biodegradable Confetti
- Biodegradable Diapers
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Biodegradable Sunscreen
- Biodegradation
- Bioremediation Bacteria
- Bioremediation Oil Spills
- Bioremediation Plants
- Bioremediation Products
- Ex Situ Bioremediation
- Heavy Metal Bioremediation
- In Situ Bioremediation
- Mycoremediation
- Non Biodegradable
- Phytoremediation
- Sewage Water Treatment
- Soil Bioremediation
- Types of Upwelling
- Waste Degredation
- Xenobiotics
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 13988
- [From(publication date):
May-2015 - Sep 01, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 9399
- PDF downloads : 4589
