Thesis Open Access
Upper Cretaceous to Neogene Palynology of the Rawat Basin, White Nile State, Sudan
Mohammed Z1*, Awad MZ1 and Eisawi A2
1Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, University of Khartoum, Sudan
2School of Applied Earth Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology, Al-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Mohammed Z
Department of Geology, Faculty of Science
University of Khartoum, P.O. Box 123, Khartoum, Sudan
Tel: 00249922974760
Fax: 32111111
E-mail: m.zeeko@hotmail.com
Received Date: March 09, 2017; Accepted Date: April 18, 2017; Published Date: April 23, 2017
Citation: Mohammed Z, Awad MZ, Eisawi A (2017) Upper Cretaceous to Neogene Palynology of the Rawat Basin, White Nile State, Sudan. J Earth Sci Clim Change 8:397. doi: 10.4172/2157-7617.1000397
Copyright: © 2017 Mohammed Z, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Earth Science & Climatic Change
Abstract
The palynology of the Upper Cretaceous to Neogene non-marine succession in the Rawat Basin, White Nile State Sudan was investigated. An attempt was made to determine the relative age, and depositional environment of the studied interval. Based on the stratigraphic distribution of selected pollen and spores from two exploration wells, seven informal palynozones from the Campanian to the Neogene are proposed. The zones, in stratigraphically ascending order, are as follows: Assemblage Zone I, Campanian (Gelhak Formation); Assemblage Zone II, Maastrichtian (Melut Formation); Assemblage Zone III, Eocene (Yabus Formation); Assemblage Zone IV, Oligocene (Adar Formation); Assemblage Zone V, Oligocene/Miocene (Jimidi Formation); Assemblage Zone VI, Miocene (Miadol Formation); Assemblage Zone VII, Miocene/Pliocene (Daga and Agor formations). The ages are based on stratigraphic ranges of marker species in contemporaneous basins in Africa and South America and a series of assemblage species such as Ladakhipollenites lehmanii, Triorites sp (Zone I), Proteacidites sigalii (Zone II), Proxapertites operculatus (Zone III), Deltoidospora cf. africana (Zone IV), Magnastriatites howardii (Zone V), Cyathidites minor (Zone VI), Verrucatosporites usmensis (Zone VII). The paleo-environment of deposition were determined to range from fluvial to lacustrine environments.
Keywords
Assemblage zones; Palynostratigraphy; Late cretaceous; Neogene; Rawat basin; Sudan
Introduction
The Rawat Basin is one of the rift basins in the interior of Sudan that formed after breakup of Gondwana during the late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous and the opening of the South Atlantic.
The basin lies in the northern part of White Nile Rift system, around 350 km south of Khartoum City between latitudes 11.6 – 12.8 N and longitudes 31.6 – 32.9 E. It is located around 400 km to the southeast of the CASZ and represents the northern extension of the Melut Basin and shares global sedimentary and architectural features. The basin is up to 175 km long and 50 km wide and locally contains up to 4000 m of Upper Cretaceous to Neogene sediments.
Due to the lack of surface exposures in the Rawat Basin, oil exploration has provided much of the information on the basin history.
Based on seismic and log interpretations eight formations have been identified for the Rawat Basin, which are analogous to Northern Melut Basin. The formations from the bottom to top include: Gelhak, Melut, Yabus, Adar, Jimidi, Miadol, Daga and Agor.
Palynology is the most important biostratigraphic tool for studying the nonmarine successions of the Rawat and adjacent basins in southern Sudan.
Two oil fields were discovered in the Rawat basin but were not developed. The integration of the evolution of the sedimentary environments with time; timing is to be deduced from the palyanological evolution will help in understanding the basin characterization and reservoir properties and help in assessing and adopting suitable production technology.
The main objective of this study is to establish a pollen/spore zonation for the Rawat Basin, based on the identification of qualitative and quantitative changes of palynofloras in the sections studied. The successions in several deep wells in the Rawat Basin consist of sandstones, clay stones, and siltstones deposited with fluvio-lacustrine environments.
Material and Methods
A total of 25 ditch-cutting samples from two deep wells (M-1 and M-2) located in the Rawat Basin together with their corresponding log data (gamma ray, SP and resistivity logs) form the data base for the present investigation. The two wells penetrate whole the basin and combined together to give a complete dating for all formations in the Rawat Basin.
Preparation of palynological slides was carried out in the Petroleum Laboratory Research and Study (PLRS) in Khartoum, Sudan.
One slide per sample was comprehensively scanned and the abundance of pollen grains, spores, and other palynomorph types was determined. Counts were made along the traverse lines and the positions of the specimens were noted. Coloured microphotographs were made using transmitted light microscope Leica DM LB equipped with a digital camera Leica, type DFC 280, serial No. 022611304. Wellpreserved specimens were chosen for image processing and presented in the Plates 1-5.
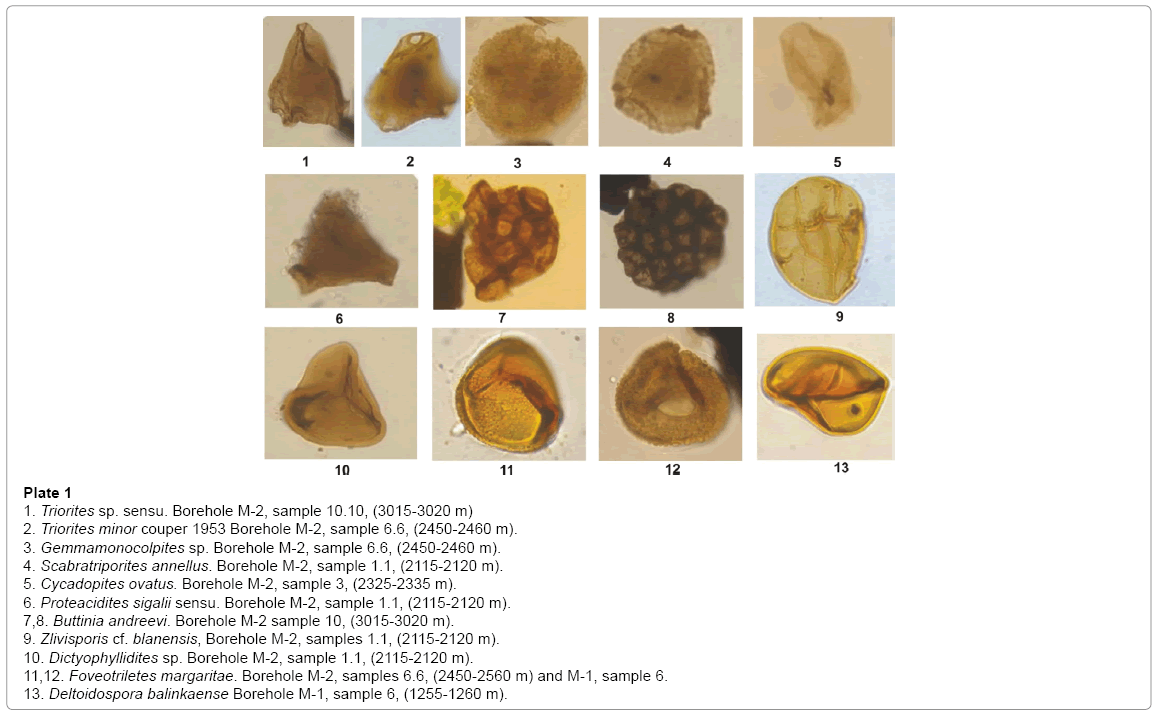
Plate 1: 1. Triorites sp. sensu. Borehole M-2, sample 10.10, (3015-3020 m) 2. Triorites minor couper 1953 Borehole M-2, sample 6.6, (2450-2460 m). 3. Gemmamonocolpites sp. Borehole M-2, sample 6.6, (2450-2460 m). 4. Scabratriporites annellus. Borehole M-2, sample 1.1, (2115-2120 m). 5. Cycadopites ovatus. Borehole M-2, sample 3, (2325-2335 m). 6. Proteacidites sigalii sensu. Borehole M-2, sample 1.1, (2115-2120 m). 7,8. Buttinia andreevi. Borehole M-2 sample 10, (3015-3020 m). 9. Zlivisporis cf. blanensis, Borehole M-2, samples 1.1, (2115-2120 m). 10. Dictyophyllidites sp. Borehole M-2, sample 1.1, (2115-2120 m). 11,12. Foveotriletes margaritae. Borehole M-2, samples 6.6, (2450-2560 m) and M-1, sample 6. 13. Deltoidospora balinkaense Borehole M-1, sample 6, (1255-1260 m).
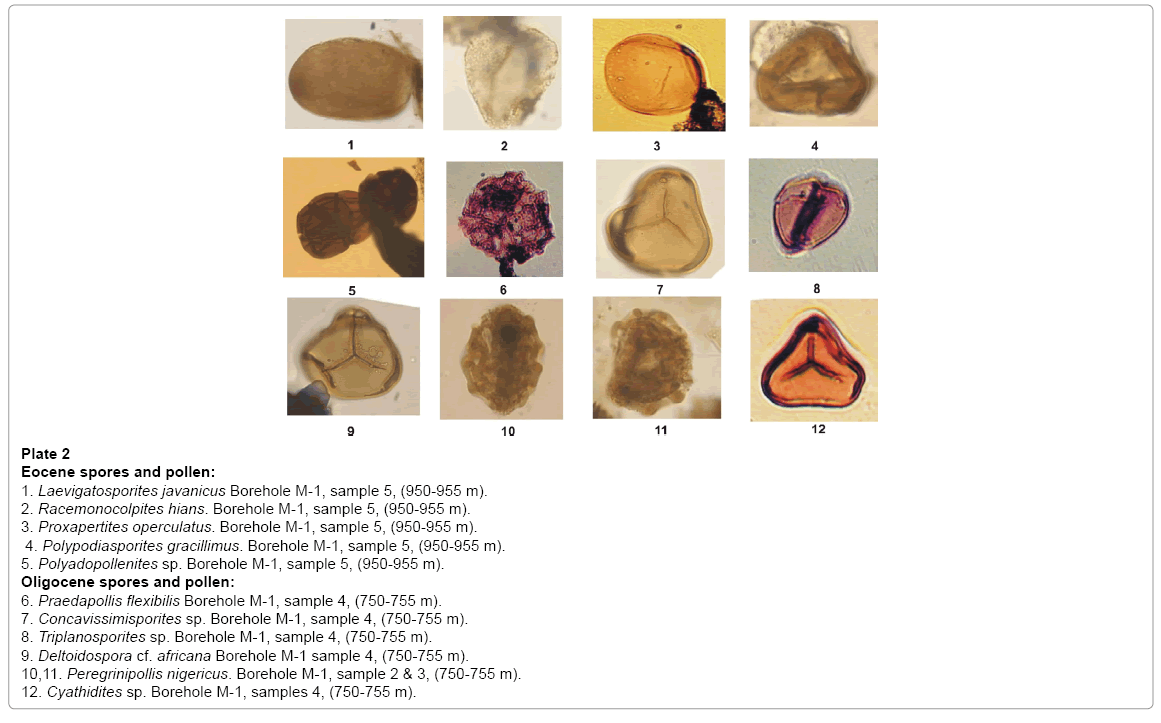
Plate 2: Eocene spores and pollen:
1. Laevigatosporites javanicus Borehole M-1, sample 5, (950-955 m).
2. Racemonocolpites hians. Borehole M-1, sample 5, (950-955 m).
3. Proxapertites operculatus. Borehole M-1, sample 5, (950-955 m).
4. Polypodiasporites gracillimus. Borehole M-1, sample 5, (950-955 m).
5. Polyadopollenites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 5, (950-955 m).
Oligocene spores and pollen:
6. Praedapollis flexibilis Borehole M-1, sample 4, (750-755 m).
7. Concavissimisporites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 4, (750-755 m).
8. Triplanosporites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 4, (750-755 m).
9. Deltoidospora cf. africana Borehole M-1 sample 4, (750-755 m).
10,11. Peregrinipollis nigericus. Borehole M-1, sample 2 & 3, (750-755 m).
12. Cyathidites sp. Borehole M-1, samples 4, (750-755 m).
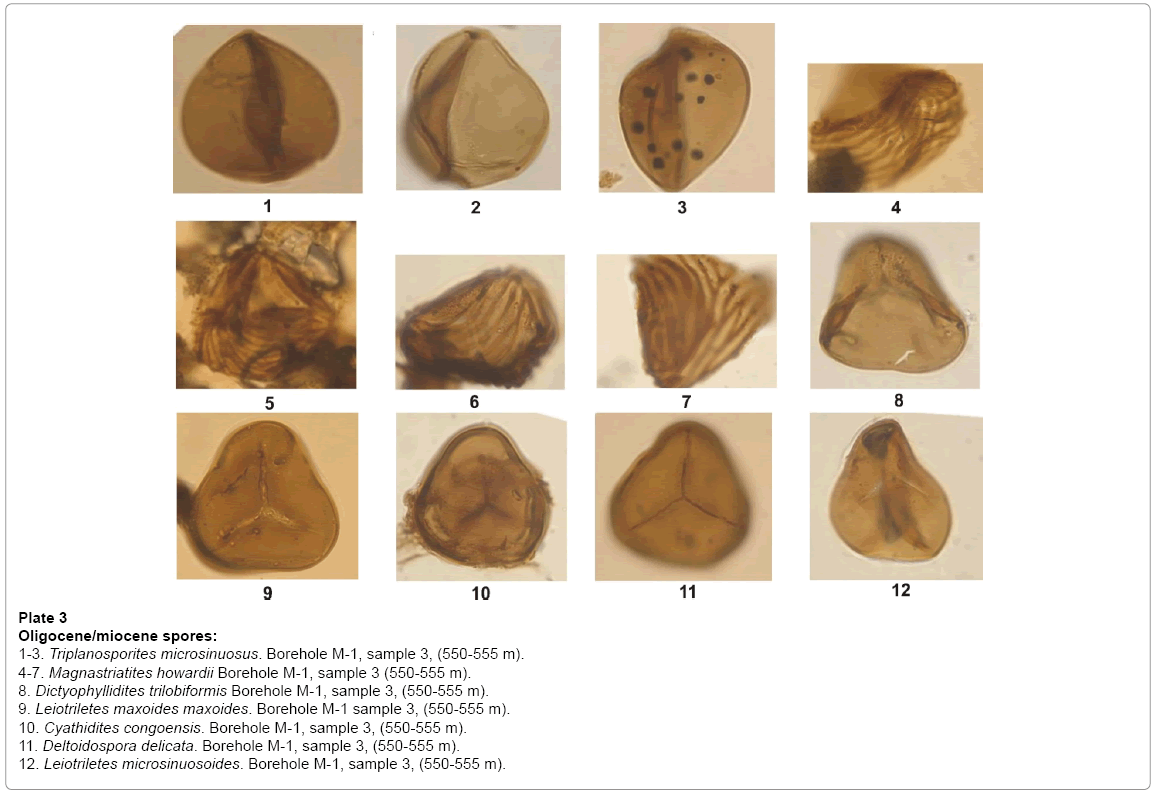
Plate 3: Oligocene/miocene spores:
1-3. Triplanosporites microsinuosus. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
4-7. Magnastriatites howardii Borehole M-1, sample 3 (550-555 m).
8. Dictyophyllidites trilobiformis Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
9. Leiotriletes maxoides maxoides. Borehole M-1 sample 3, (550-555 m).
10. Cyathidites congoensis. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
11. Deltoidospora delicata. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
12. Leiotriletes microsinuosoides. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
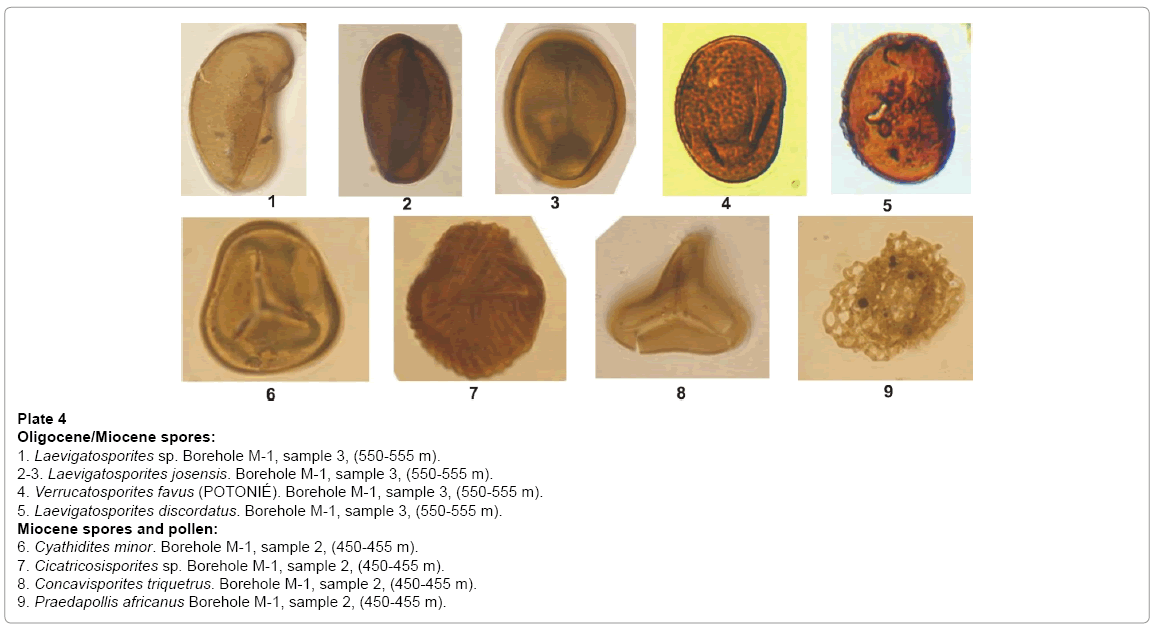
Plate 4: Oligocene/Miocene spores:
1. Laevigatosporites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
2-3. Laevigatosporites josensis. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
4. Verrucatosporites favus (POTONIÉ). Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
5. Laevigatosporites discordatus. Borehole M-1, sample 3, (550-555 m).
Miocene spores and pollen:
6. Cyathidites minor. Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
7. Cicatricosisporites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
8. Concavisporites triquetrus. Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
9. Praedapollis africanus Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
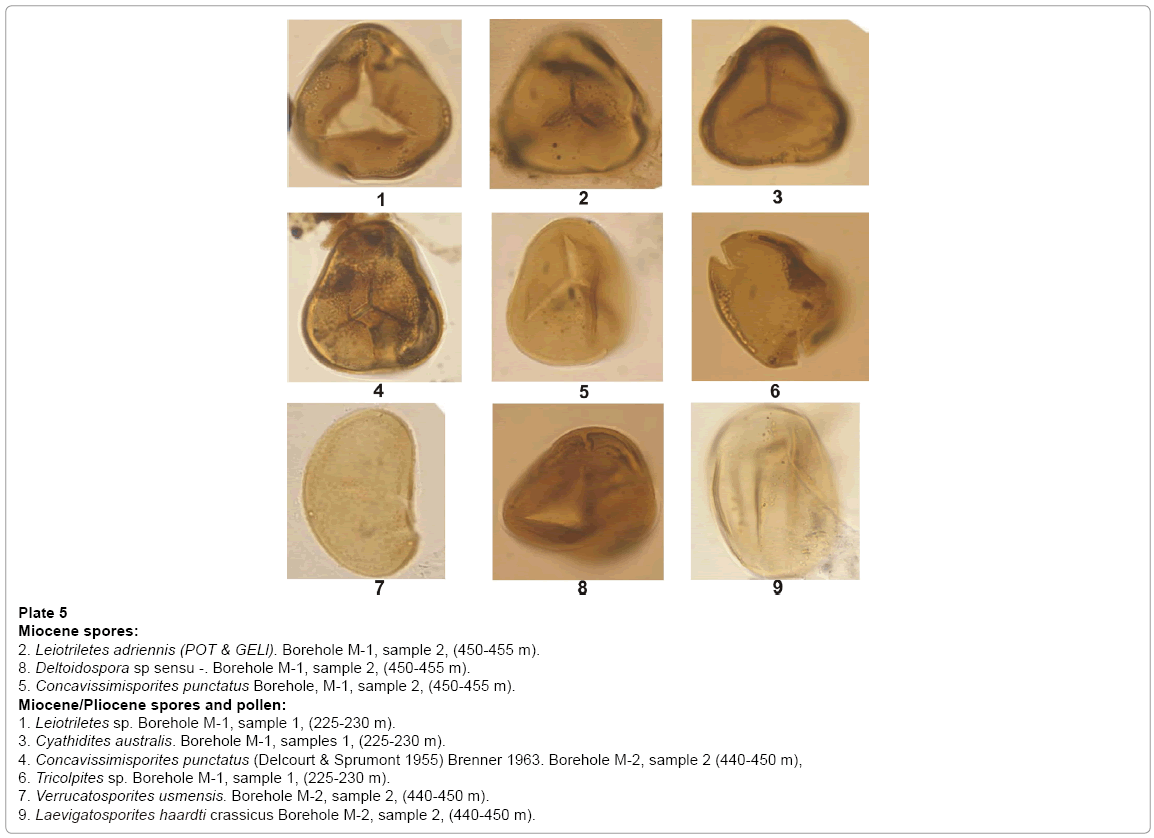
Plate 5: Miocene spores:
2. Leiotriletes adriennis (POT & GELl). Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
8. Deltoidospora sp sensu -. Borehole M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
5. Concavissimisporites punctatus Borehole, M-1, sample 2, (450-455 m).
Miocene/Pliocene spores and pollen:
1. Leiotriletes sp. Borehole M-1, sample 1, (225-230 m).
3. Cyathidites australis. Borehole M-1, samples 1, (225-230 m).
4. Concavissimisporites punctatus (Delcourt & Sprumont 1955) Brenner 1963. Borehole M-2, sample 2 (440-450 m),
6. Tricolpites sp. Borehole M-1, sample 1, (225-230 m).
7. Verrucatosporites usmensis. Borehole M-2, sample 2, (440-450 m).
9. Laevigatosporites haardti crassicus Borehole M-2, sample 2, (440-450 m).
Palynostratigraphy
The Rawat Basin palynofloras are generally characterized by wellpreserved miospores. Most of the Paleogene and Neogene samples yielded rich and diverse palynomorphs. Due to an extensive sand-rich interval at the Gelhak Formation and at the mid of the Melut Formation, a large sample gap prevents confident biostratigraphic definition of the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Based on log interpretations, several unconformities have been identified at the top of the formations.
The palynofloras are dominated by bryophytic, pteridophytic spores and angiosperm pollen. Gymnosperm pollen grains are infrequent and low in diversity.
Many of the palynomorphs in this study are assignable to pollen species previously described from Africa and South America.
Palynostratigraphic results and biozones: The Rawat Basin palynoflora is characterized by fairly well-preserved miospores of terrestrial origin. The palynofloral composition is dominated mainly by pteridophyte–bryophyte spores e.g. Concavissimisporites, Cyathidites, Deltoidospora, Laevigatosporites and Zlivisporis. Angiosperm pollen and gymnosperm pollen grains are rare and less diverse include among others: Proxapertites, Proteacidites, Triorites, Praedapollis are rare and less diverse.
Based on the stratigraphic distribution of the guide forms in relevant phytogeographic provinces seven palynofloral assemblage zones for the interval spanning the Late Cretaceous to Neogene have been proposed for the Rawat Basin. This zonation is correlated with previous schemes established in Sudan and West Africa. These are described and discussed below.
Assemblage Zone I
Gelhak formation: (Basement-1454 m) in well M-1 and (B.C- 2168 m) in Well M-2.
Suggested age: Campanian.
The oldest zone in the Rawat Basin is characterized by the occurrence of Ladakhipollenites lehmanii, Triorites sp., Triorites minor, Longapertites microfoveolatus, Buttinia andreevi, Cycadopites ovatus, Foveotriletes margaritae, Gemmamonocolpites sp.
Discussion: Ladakhipollenites lehmanii reported from the Maastrichtian of Somalia [1] and Campanian of Melut Basin [2]. Butina andreevi was reported from the Campanian-Maastrichtian of the Sudan [3] and from the Maastrichtian of Somalia. Triotites sp reported from Campanian to Maastrichtian of Sudan, Foveotriletes margaritae together with B. andreevi were reported from Campanian-Maastrichtian of Nigeria [4,5]. Longapertites microfoveolatus was originally described as Monocolpopollenites sp from the Campanian of Senegal and Senonian of Ivory Coast. It was later reported from the Paleocene and Late Campanian-Early Maastrichtian strata in Nigeria. The species was also recorded from the Maastrichtian of Somalia. Late Maastrichtian– Paleocene strata of central Sudan and together with Cycadopites ovatus have been reported from Campanian of Melut Basin. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone I.
Assemblage Zone II
Melut formation: (1454-1130 m) in well M-1 and (2168-1701 m) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Maastrichtian.
The rocks found in this zone are part of an extensive development of lake system during the starting of the second rift phase in which fine grained clays and siltstone was deposited. Important and well known Maastrichtian spore-pollen includes; Proteacidites sigalii, Zlivisporis cf. blanensis, Scabratriporites annellus, Monocolpites marginatus, Deltoidospora balinkaense and Dictyophyllidites sp.
Discussion: P. sigalii was reported from the Maastrichtian strata of West, North Africa and Sudan [6,7]. Also P. sigalii together with Deltoidospora balinkaense have also been reported from the Maastrichtian of Somalia. Zlivisporis blanensis was reported from Upper Cretaceous of Nigeria and from the Turonian to Early Maastrichtian and Maastrichtian of Sudan respectively. Scabratriporites annellus has been reported from the Maastrichtian of Nigeria, Egypt and Sudan [8] respectively. Monocolpites marginatus was reported in Paleocene, Maastrichtian and Campanian-Maastrichtian strata of Nigeria. It has also been recorded in Campanian-Maastrichtian and Maastrichtian strata of Sudan [9]. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone II.
Assemblage Zone III
Yabus formation: (1130-964 m) in well M-1 and (1701-995 m) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Eocene.
This zone is recognized by the occurrences of Proxapertites operculatus, Racemonocolpites hians, Laevigatosporites javanicus, and Polypodiaceoisporites gracillimus.
Discussion: Proxapertites operculatus has been described from the Paleocene strata of Colombia [10] and Paleocene Early Eocene in tropical areas and Sudan [11]. It has also been recorded from the Maastrichtian-Paleocene and Mid-Eocene strata in Nigeria and Sudan. Racemonocolpites hians recorded from Mid Eocene-Miocene strata of Cameroon and Nigeria [12]. Laevigatosporites javanicus was reported from Eocene in Indonesia, and Middle Tertiary of Nigeria [13]. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone III.
Assemblage Zone IV
Adar formation: (964-641 m) in well M-1 and (995-706 m) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Oligocene.
The rocks found in this zone are fine grained clays and siltstone deposited in a lacustrine system during the end of the second rift phase. This zone is recognized by the occurrences of Praedapollis flexibilis, Deltoidospora cf. africana, Triplanosporites sp, Peregrinipollis nigericus, Cyathidites sp and Concavissimisporites sp.
Discussion: Praedapollis flexibilis reported from Mid-Eocene to Lower Pliocene of Nigeria and Cameroon and Early Miocene of Sudan. Peregrinipollis nigericus reported from Mid Eocene to Pliocene, Nigeria and Cameroun. Upper Eocene to Oligocene in Sudan. Upper Eocene- Miocene of Cameroon. Deltoidospora africana has originally been described from the Neogene of Burundi [14]. It was later reported from the Oligocene-Miocene of central Sudan. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone IV.
Assemblage Zone V
Jimidi formation: (641-502 m) in well M-1 and (706-518 m) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Oligocene/Miocene.
The sedimentary sequence of this zone appears continuously in the seismic section. It could have been deposited during the tectonic relaxation (Third rift phase) in Oligocene/Miocene. Important and well known spore-pollen includes; Magnastriatites howardii, Cyathidites congoensis, Triplanosporites microsinuosus, Leiotriletes maxoides, Deltoidospora delicata, Dictyophyllidites trilobiformis, Leiotriletes microsinuosoides, Laevigatosporites discordatus, Laevigatosporites josensis and Verrucatosporites favus.
Discussion: Magnastriatites howardii was recorded from the Oligocene-Miocene and Early Miocene of the Sudan. Triplanosporites microsinuosu was reported from Oligocene to Pliocene in Europe. [15] and Miocene of Niger Delta [16]. Leiotriletes maxoides was recorded from the Middle Oligocene to Pliocene in Germany. Middle Tertiary in Nigeria. Leiotriletes microsinuosoides indicates Oligocene to Miocene in Europe and Miocene of Niger delta. Laevigatosporites josensis, L. discordatus and Verrucatosporites favus were reported from Middle Tertiary in Nigeria, and Eocene to Miocene in Eastern Europe. Deltoidospora delicate, Cyathidites congoensis, and Dictyophyllidites trilobiformis were reported for the first time from the Neogene of Burundi and Miocene-Pliocene of Sudan. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone V.
Assemblage Zone VI
Miadol formation: (502-387 m) in well M-1 and (518-484 m) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Miocene.
The suggested age of this zone is Miocene based on the identification of Praedapollis africanus, Cicatricosisporites sp, Concavisporites triquetrus, Cyathidites minor, Leiotriletes sp, Deltoidospora sp and Leiotriletes adriennis.
Discussion: Praedapollis africanus has been reported from the Upper Eocene to Lower Miocene of Cameroon and Nigeria. Oligocene/ Miocene of Sudan. Concavisporites triquetrus has been described for the first time from the Neogene of Burundi. It later reported from the Oligocene/Miocene of Sudan. Cyathidites minor is common in the Tertiary strata of Sudan and India [17]. Deltoidospora sp was reported from Middle Tertiary, Nigeria. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone VI.
Assemblage Zone VII
Miadol formation: (387 m-surface) in well M-1 and (484 msurface) in well M-2.
Suggested age: Miocene/Pliocene
The youngest identification zone in Rawat Basin is considered to be Miocene/Pliocene in age. The useful flora markers include; Concavissimisporites punctatus, Cyathidites australis, Verrucatosporites usmensis and Tricolpites sp and Laevigatosporites haardtii.
Discussion: Salard-Cheboldaeff indicates the first downhole occurrence of Verrucatosporites usmensis in the Pliocene. Germeraad indicates a range of throughout the Tertiary in northern South America and also in the high Pliestocene of Africa. V. usmensis and Laevigatosporites haardti indicate Miocene-Pliocene of Sudan. Concavissimisporites punctatus and Cyathidites australis has been reported from Miocene-Pliocene of Sudan [18]. The combined stratigraphic ranges of the aforementioned taxa suggest a Campanian age for the Assemblage Zone VII.
Conclusion
Based on the stratigraphic ranges of selected pollen and spores, seven informal assemblage palynozones spanning the Late Cretaceous to Neogene were identified in the Rawat Basin. The zones are: Assemblage Zone I (Campanian); Assemblage Zone II (Maastrichtian); Assemblage Zone III (Eocene); Assemblage Zone IV (Oligocene); Assemblage Zone V (Oligocene/ Miocene); Assemblage Zone VI (Miocene); Assemblage Zone VII (Miocene/Pliocene). The age determinations are generally based on the known stratigraphic ranges of pollen and spores in the coastal basins of West Africa which have some marine age control in contrast to the continental basins of southern Sudan.
References
- Schrank E (1994) Palynology of the yesomma formation in Northern Somalia: A study of pollen, spores and associated phytoplankton from the Late Cretaceous Palmae Province. Palaeontographica, Abteilung B 231: 63-112.
- Eisawi AA (2007) Palynological and palaeo-environmental interpretation of the Late Cretaceous to Tertiary strata of the Melut Basin (Southeast Sudan).
- Awad MZ (1994) Stratigraphic, palynological and palaeoecological studies in the East-Central Sudan (Khartoum and Kosti Basins), Late Jurassic to Mid-Tertiary. Berliner geowissAbh A.
- Boboye OA (2013) Palynostratigraphic and palaeoecological studies of the Cretaceous strata in the Bornu Basin, northeastern Nigeria.
- Ojo O, Akande SO (2006)Sedimentological and palynological studies of the patti formation Southeastern Bida Basin Nigeria: Implications of Paleoenvironments and Paleogeography. Nape Bullten 19: 61-67.
- Lawal O, Moullade M (1986)Palynological biostratigraphy of Cretaceous sediments in the upper Benue Basin, NE Nigeria. Micropaléont 29: 61-83.
- Kaska HV (1989) A spore and pollen zonation of Early Cretaceous to Tertiary non-marine sediments of central Sudan. Palynology 54: 79-90.
- Salard-CheboldaeffM (1990) Intertropical African Palynostratigraphy from cretaceous to late quaternary times. J African Earth Sci 11: 1-24.
- Eisawi A, Schrank E (2009) Terrestrial palynology and age assessment of the Gedaref Formation (eastern Sudan). J African Earth Sciences 54: 22-30
- Van Der HT (1956) Description of some genera and species of fossil pollen and spores. BolGeol (Bogotá) 4: 111-117.
- Germeraad JH, Hopping CA, Muller J (1968) Palynology of tertiary sediments from tropical areas. Rev of Palaeobotany and Palynology 6: 189-348.
- Legoux O (1978) Quelquesespéeces de pollen caractéristiques du Néogène du Nigéria. Bullletin des Centres de Recherche Exploration-Production Elf-Aquitaine 2: 265-317.
- Takahashi J, Jux U (1989) Palynology of middle cenozoic lacustrine deposits from the Jos plateau, Nigeria. Natural Science 29: 181-367.
- Sah SCD (1967) Palynology of an upper Neogene profile from Rusizi Valley (Burundi). Mus Roy Afr Cent TervurenBelg Ann Ser Oct SciGeol 57: 1-173.
- Krutzsch W (1962) Atlas der mittel- und jungtertiärendispersenSporen- und Pollen- sowie der Mikroplanktonformen des ördlichenMitteleuropas.
- Bankole S (2010) Palynology and stratigraphy of three deep wells in the NeogeneAgbada Formation, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Implications for Petroleum Exploration and Paleoecology.
- Stead DT, Awad MZ (2005) Palynological zonation of Cenozoic non- marine sediments, Muglad Basin, Sudan.
- Eisawi A, Schrank E (2008) Upper cretaceous to Neogene palynology of the Melut Basin South-east Sudan. Palynology 32: 101-129.
Relevant Topics
- Atmosphere
- Atmospheric Chemistry
- Atmospheric inversions
- Biosphere
- Chemical Oceanography
- Climate Modeling
- Crystallography
- Disaster Science
- Earth Science
- Ecology
- Environmental Degradation
- Gemology
- Geochemistry
- Geochronology
- Geomicrobiology
- Geomorphology
- Geosciences
- Geostatistics
- Glaciology
- Microplastic Pollution
- Mineralogy
- Soil Erosion and Land Degradation
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 5581
- [From(publication date):
April-2017 - Aug 23, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 4357
- PDF downloads : 1224