Research Article Open Access
Salmonella Food Poisoning Associated With Macaroni Salad in a Labourers Camp- State of Qatar, 2010
Zaher Nazzal1*, Hanaa Said2, Mohd Al-Hajri3 and Osman Tamim4
1Specialist Community Medicine (ABCM), An-Najah National University/ Faculty of Medicine- Nablus/ Palestine, Qatar
2Medical Researcher- Head of Quality Department, PHC-Qatar
3Specialist Community Medicine (ABCM), Manager of HP & CDC, DPH, Supreme Council of Health- Qatar
4Specialist Public Health, CDC Department- Supreme Council of Health- Qatar
- Corresponding Author:
- Zaher Nazzal
Specialist Community Medicine (ABCM)
An-Najah National University/ Faculty of Medicine- Nablus/ Palestine, Qatar
E-mail: nazzal@najah.edu
Received Date: March 28, 2012; Accepted Date: April 28, 2012; Published Date: April 30, 2012
Citation: Nazzal Z, Said H, Al-Hajri M, Tamim O (2012) Salmonella Food Poisoning Associated With Macaroni Salad in a Labourers Camp- State of Qatar, 2010. J Community Med Health Educ 2:145. doi: 10.4172/2161-0711.1000145
Copyright: © 2012 Nazzal Z, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education
Keywords
Food borne outbreak; Case-control study; Salmonella group D; State of Qatar
Introduction
Food-borne infections are common and constitute an important health and economic burden globally. Among the factors responsible for this burden are centralization and globalizations of food supply, increasing microbial resistances to antibiotic and growth of immunosuppressed subpopulations [1,2]. Many studies indicate that most outbreaks of food borne acute gastroenteritis occur in places of mass feeding such as institutions, schools, restaurants, mess halls, and military units [3-9].
Non-typhoidal Salmonella is one of the most reported causes of food-borne infections [1]. Food products of animal origin (contaminated meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products) are considered the most commonly identified source of Salmonella Infection [3,8- 13]. Eating undercooked eggs or meals prepared with uncooked eggs is a well-defined risk factor; in the last two decades, many Salmonella outbreaks related to raw or undercooked egg consumption have been reported in deferent parts of the world [1,3,14-16].
Salmonella bacteria are classified into different groups (B, C, D, and E); within each there are many serotypes. More than two thousands of Salmonella serotypes have been described and all of them are considered pathogenic. Amongst them; S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium are the most commonly reported [17].
During a holiday week, in Nov 2010 an outbreak of non-typhoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis occurred in Rass Laffan industrial city in the State of Qatar, where hundreds of thousands of labourers work in the gas and oil industry. Most of these labourers live inside the city in different camps. In one of these camps that mainly accommodate Filipino workers, about 300 workers developed signs and symptoms of acute gastroenteritis. Stool samples were collected from 6 case; all of which were positive for Salmonella group D. The present outbreak was investigated to determine its original source and to decide on its possible food vehicle to stop the current outbreak and prevent later ones.
Subjects and Methods
Epidemiological investigation
Case definition: For the purpose of this epidemiological investigation we defined a case as “A person with diarrhoea (three or more loose stools during a 24-hours period) who has attended the Filipino Mess Hall (RLM2) in the five days after 16th Nov 2010”.
Case finding: The cases were found through the mandatory reporting of food poisoning disease by peripheral health services to the Communicable Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) department at the Supreme Council of Health (SCH) and by enquiry among the regional primary health centres and hospitals. Preliminary epidemiological investigation suggested that human infection with Salmonella was probably associated with the ingestion of food at the Filipino Mess Hall at Rass Laffan industrial city.
Case-control study: To determine if a particular food item was associated with the outbreak a case–control study was conducted. Of the total 300 cases, 85 were randomly selected to participate in the study. Besides, 85 controls were randomly selected. A control subject was defined as any person who is served by the Filipino Mess Hall and lives in the same campus with cases and who didn’t experience gastrointestinal illness.
A questionnaire was developed by the CDC investigation team to collect information on the outbreak. It included questions on personal characteristics, types of symptoms experienced, date and time of onset, duration of illness, and consumptions of different food items at the Filipino Mess Hall on 16th Nov. The meals eaten the day prior to the outbreak (16th Nov) were determined from the menu and all food items in these meals were included in the questionnaire. The interview was conducted on 24th and 25th of Nov by a trained Filipino Nurses. The same questionnaire was used for both cases and control.
Environmental investigation
We inspected the work process and food stores, catering hall, dishes and utensils, washing halls and accommodation and we took water samples.
Microbiological investigation
Stool samples were taken from 6 patients and from all thirty one food handlers who are involved in preparing and cocking the food at the Filipino Mess Hall. Samples of the food served for the labourers were taken from the Filipino Mess Hall and were transferred to the lab for microbiological examination. Food samples included all leftover food of the three meals served on 16th Nov and random samples of the leftover food served on 17th, 18th, and 19th Nov. No leftover eggs were found from the day 16th Nov.
Statistical Analysis
Data entry and statistical analysis were done using the SPSS version 17. Univariate analysis was carried out using a chi-squared test in order to investigate the association between the food items and the disease. As well, odds ratio and confidence intervals were calculated.
Results
The total number of gastroenteritis cases in this outbreak was 300 among the approximately 1050 attendees, giving an overall attack rate of 28.5%. Majority of the cases were mild; less than 5% needed treatment with IV fluid, and none of them was admitted to hospital.
Epidemiological investigation
A total of 84 cases and 80 controls were interviewed during the investigation. All of them were male Filipino labourers. Their median age was 34 years (range: 22-58 years) with no difference between cases and controls. Table 1 presents the clinical complaints experienced by the cases. Diarrhoea seemed to be the most frequent symptom followed by abdominal cramps. None of the interviewed cases reported underlying medical condition.
| Symptom | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 84 (100%) |
| Abdominal Pain | 81 (96%) |
| Body ache | 79 (94%) |
| Headache | 77 (91%) |
| Fever | 74 (88%) |
| Vomiting | 47(56%) |
Table 1: Prevalence of symptoms among cases.
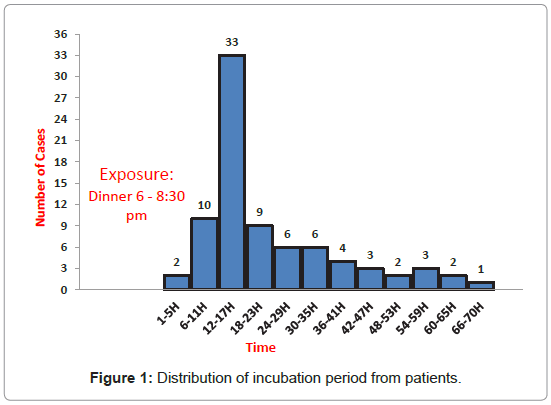
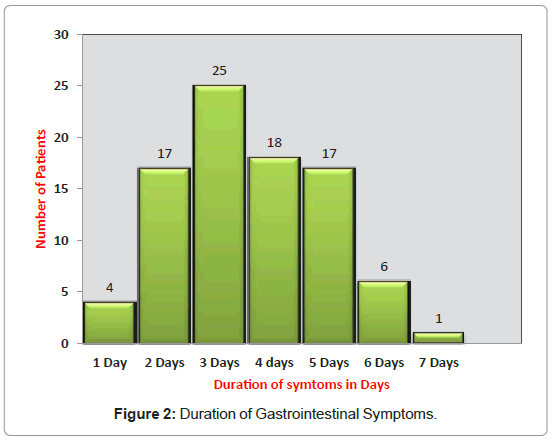
The outbreak started late in the evening of 16th Nov and peaked midday day on 17th Nov and ended within 3 days of its start as demonstrated by the epidemic curve (Figure 1). The median incubation periodI was 15 hours; it ranged between 4 and 67 hours. The median illness duration was 3 days, ranged between 1 and 7 days (Figure 2).
From the initial analysis, it was established that dinner (Rice, Beef, Vegetables, and Macaroni Salad) consumed several hours prior to the onset of symptoms, was the most likely source of outbreak. The probability of eating the dinner among the cases was much higher compared to controls with OR 42 (CI: 10-182). From the dinner menu items, ill persons (97.3%) were significantly more likely than well persons (27.3%) to report eating macaroni salad. The overall OR is 109 (CI: 25-484). Additionally, odds ratios of 7.6, 19.4, and 7.1 were observed with the consumption of rice at lunch time, rice at dinner time, and beef sticks at dinner time, respectively. However, a majority of labourers who consumed the rice and beef also consumed the macaroni salad at dinner time (Table 2).
| Food Items | Cases | Controls | OR* | CI$ | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | ||||||
| Breakfast | Steamed rice (B) | 66 (79.5%) | 54 (69.2%) | 1.7 | 0.8- 3.5 | 0.134 |
| Fried black tuna | 42 (51.2%) | 45 (58.4%) | 0.74 | 0.4-1.4 | 0.36 | |
| Fried egg plant | 53 (64.4%) | 43 (55.1%) | 1.48 | 0.8- 2.8 | 0.22 | |
| Lunch | Steamed rice(L) | 78 (94.0%) | 53 (67.1%) | 7.6 | 2.8-21.2 | <0.001 |
| Roasted Buttered Chicken | 68 (81.9%) | 56 (71.8%) | 1.78 | 0.8-3.7 | 0.127 | |
| Sinigang Soap | 48 (59.3%) | 32 (42.1%) | 2.0 | 1.0 - 3.7 | 0.32 | |
| Dinner | Steamed rice (D) | 79 (94.0%) | 36 (45.6%) | 19.4 | 6.8- 51.6 | <0.001 |
| Beef stick | 71 (84.5%) | 34 (43.6%) | 7.1 | 3.3- 14.8 | <0.001 | |
| Steamed vegetables | 37 (46.8%) | 17 (21.8%) | 3.2 | 1.4- 5.8 | 0.002 | |
| Macaroni salad | 82 (97.6%) | 21 (27.3%) | 109.3 | 25- 484 | <0.001 | |
$ Confidence Interval
Table 2: Comparison of Food exposure between cases and controls with Odds Ratio and Confidence Interval.
Environmental investigation
Based on our inspection, we noticed that personal hygiene was satisfactory and all food handlers had valid health certificates. However, the regular check up in Qatar doesn’t require the food handlers to do stool cultures. Water coolers were used for drinking water and tab water was used for food preparation and cooking. Water samples couldn’t be analyzed due to technical problems in transporting them.
Microbiological investigation
Six stool samples from the cases were cultured for common bacterial gastrointestinal pathogens. All of these samples were positive for Salmonella group D. Thirty one stool samples from the food service workers at the Filipino Mess Hall were also collected for culture. Three of them were positive for Salmonella group D. None of the food items showed growth of microorganism. Further investigation into the preparation of the macaroni salad revealed that the chief cook used row egg while preparing macaroni salad; he used around 225 raw eggs, discarded the yolk and poured the egg white to complement the Mayonnaise of the Macaroni. This occurred 5 to 6 hours before serving the meal.
Discussion
The outbreak of gastroenteritis, reported on 17th Nov 2010, was initially assumed to be a food-borne outbreak, caused by one of the common food-borne diseases pathogens. This assumption was based on the short incubation period and abrupt onset, symptomatology and the food consumption history. The epidemic curve and sharing of a common meal by a group were compatible with a common- source outbreak.
Description of the food causing the outbreak is essential when investigating an outbreak and detecting the pathogen in the suspected food is not always possible, in which case epidemiological methods are used to decide on the food that caused the outbreak [18].
The data collected from the questionnaire and microbiological analysis indicated that Salmonella group D is the possible causative agent and macaroni salad, prepared with raw eggs, is the possible food vehicle, though not detected in the food culture. Although other food items showed high odds ratio of illness, such as rice and beef, this is likely due to correlation between eating these items and eating macaroni salad as evidenced by the high proportion of labourers reporting eating macaroni salad in addition to these items. The odds ratio of illness associated with eating macaroni salad was substantially higher than that for rice or beef.
The clinical picture of this outbreak is consistent with Salmonellosis [17,19] and similar to what was described by others [11,12,20,21] where the majority of cases presented with diarrhoea, abdominal cramps and fever. The median incubation period is 15 hours and ranged between 4 and 57 hours which is also consistent with Salmonellosis [17,19] and similar to what have been reported in Spain [4], Singapore [7], Switzerland [11], and KSA [21].
In the outbreak reported here, the macaroni salad was prepared by adding huge quantity of raw eggs to improve the taste 5 to 6 hours prior to serving. The long interval between the preparation of the macaroni salad and the time the dinner was served made it possible for contamination and bacterial multiplication. It is recommended by CDC that foods with potential for Salmonella contamination shouldn’t be kept in the temperature range of 4.6 Co to 60 Co for more than two hours, to prevent bacterial growth [22].
Shell eggs have been reported as the source of many Salmonella food borne infection, both in developed and developing countries, which can be due to break down in any step from the egg production at the farm tell it is served to the consumer.
Other possible source of infection here is the asymptomatic carrier food handlers; approximately 1% of adults infected with non-typhoidal salmonellosis may excrete the organism for > 1 year [17]. Food handler who are found to be positive in the course of investigation, are most often infected due to exposure to contaminated food and are less commonly shown to be the source of infection [1]. However, their role as a source of infection can’t be excluded, and they may still be considered as a possible source of contamination in this outbreak.
The findings of this investigation are subjected to certain limitations; the first that no eggs remained for testing, the second is the lack of the molecular analysis and typing of the Salmonella subgroups, and the third that taking the meal history many days later; subject it to recall bias.
In the preparation of food for large gatherings, care should be taken in the food preparation such as proper food handling, clean workplace and equipment and uncontaminated food products. As well, food should not be prepared long time before serving; if this not feasible, proper storage is necessary.
Food handlers must be taught that eggs can be harboured by Salmonella, cooked eggs rather than raw ones must be used while preparing the food and prepared food must be stored under refrigeration. In addition, samples of all food items used in the meal should be collected and stored.
Conclusion
Information obtained from the epidemiological and microbiological analysis led to the conclusion that the etiologic agent of this outbreak is Salmonella group D, and the most probable food vehicle of transmission is Macaroni salad. As well, it indicated that consumption of shell eggs, in particular raw eggs or food containing it, is a significant risk factor of Salmonella infection. It highlights the fact that excessive production of foods for holidays or special events, in the absence of necessary precautions, represents a potential public health threat. This requires that food handlers should be educated that intact fresh eggs can harbour Salmonella, foods made from eggs must be cooked, and prepared food must be stored under refrigeration.
References
- Lynch M, Tauxe R (2009) Salmonellosis: Nontyphoidal. In: Brachman P, Abrutyn E, editors. Bacterial infections of human, epidemiology and control. 4th edn. New York: Springer Science & Business Media. 677-698.
- Rocourt J, Moy J, Vierk K, Schlundt J (2003) The present state of foodborne disease in OECD countries. Geneva: Food Safety Departmet- WHO.
- Tansel O, Ekuklu G, Otkun M, Otkun MT, Akata F, et al. (2003) A food-borne disease caused by salmonella enteritidis. Yonsei Med J 44: 198-202.
- Camps N, Domínguez A, Company M, Pérez M, Pardos J, et al. (2005) A foodborne outbreak of salmonella infection due to overproduction of egg-containing foods for a festival. Epidemiol Infect 133: 817-822.
- Schmid D, Schandl S, Pichler AM, Kornschober C, Berghold C, et al. (2006) Salmonella enteritidis phage type 21 outbreak in Austria, 2005. Euro Surveill 11: 67-69.
- Jelastopulu E, Venieri D, Komninou G, Kolokotronis T, Constantinidis TC, et al. (2006) Outbreak of acute gastroenteritis in an air force base in Western Greece. BMC Public Health 6: 254.
- Lee VJ, Ong AE, Auw M (2009) An outbreak of salmonella gastrointestinal illness in a military camp. Ann Acad Med Singapore 38: 207-211.
- Liu L, He HF, Dai CF, Liang LH, Li T, et al. (2004) Salmonellosis outbreak among factory workers - Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China, July 2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1: 35-38.
- (2010) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Multiple-Serotype salmonella gastroenteritis outbreak after a reception- connecticut, 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 59: 1093-1097.
- Vaeteewootacharn K, Sutra S, Vaeteewootacharn S, Sithigon D, Jamjane O, et al. (2005) Salmonellosis and the food chain in Khon Kaen, Northeastern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 36: 123-129.
- Urfer E, Rossier P, Méan F, Krending MJ, Burnens A, et al. (2000) Outbreak of salmonella braenderup gastroenteritis due to contaminated meat pies: clinical and molecular epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect 6: 536-542.
- van Cauteren D, Jourdan-da Silva N, Weill FX, King L, Brisabois A, et al. (2009) Outbreak of salmonelaa enterica serotype muenster infection associated with goat's cheese, France, March 2008. Euro Surveill 14.
- Bruun T, Sørensen G, Forshell LP, Jensen T, Nygard K, et al. (2009) An Outbreak of salmonella typhimurium infections in Denmark, Norway and Sweden, 2008. Euro Surveill 14.
- (2000) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreaks of salmonella serotype enteritidis infection associated with eating raw or undercooked shell eggs - United States, 1996-1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 49: 73-79.
- Indar-Harrinauth L, Daniels N, Prabhakar P, Brown C, Baccus-Taylor G, et al. (2001) Emergence of salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 in the Caribbean case-control study in Trinidad and Tobago, West Indies. Clin Infect Dis 32: 890-896.
- Doorduyn Y, Van Den Brandhof WE, Van Duynhoven YT, Wannet WJ, Van Pelt W (2006) Risk factors for salmonella enteritidis and typhimurium (DT104 and non- DT104) infections in the Netherlands: predominant roles for raw eggs in enteritidis and sandboxes in typhimurium infections. Epidemiol Infect 134: 617-626.
- Braam P (2004) Salmonellisis. In: Heymann D, editor. Control of communicable diseases manual. 18th edn. Washington: American Public Health Association 469-473.
- Kawabata A, Ishikawa K, Iwasaki Y, Aoki K, Takagi S, et al. (2006) Food poisoning outbreak of salmonell enteritidis caused by box lunch in shiga prefecture, Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis 59: 406-407.
- Food-borne Diseases In: Gormach S, Falagas M (2001) 5-Minutes Infectious Diseases Consult. First edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 188-189.
- Stein-Zamir C, Tallen-Gozani E, Abramson N, Shoob H, Yishai R, et al. (2009) Salmonella enterica outbreak in a banqueting hall in Jerusalim: the unseen hand of the epidemiological triangle? Isr Med Assoc J 12: 94-97.
- Aljoudi AS, Al-Mazam A, Choudhry AJ (2010) Outbreak of food borne salmonella among guests of a wedding ceremony: the role of cultural factors. J Family Community Med 17: 29-34.
- US CDC, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases. Salmonella enteritidis
Relevant Topics
- Addiction
- Adolescence
- Children Care
- Communicable Diseases
- Community Occupational Medicine
- Disorders and Treatments
- Education
- Infections
- Mental Health Education
- Mortality Rate
- Nutrition Education
- Occupational Therapy Education
- Population Health
- Prevalence
- Sexual Violence
- Social & Preventive Medicine
- Women's Healthcare
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 16970
- [From(publication date):
April-2012 - Dec 22, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 12164
- PDF downloads : 4806