Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
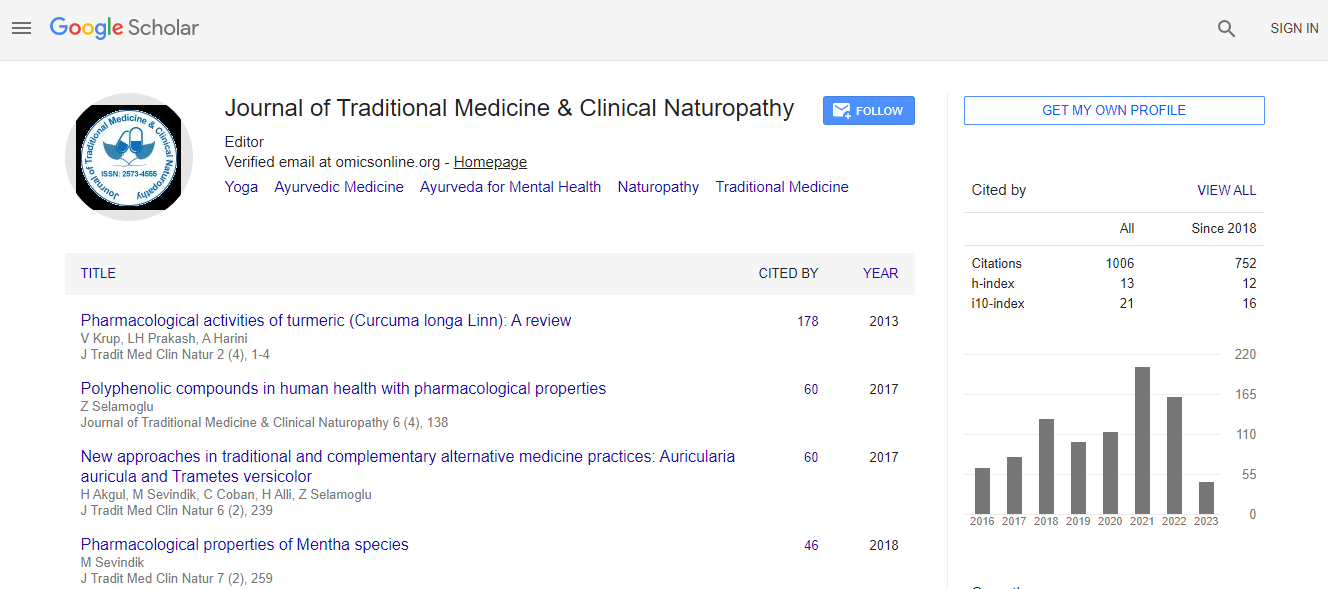
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1504
Journal of Traditional Medicine & Clinical Naturopathy peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effect of salicylic acid application on vegetative growth, phenolic metabolites, antioxidant capacity and essential oil composition in drought stressed Eriocephalus africanus L.
World Congress on Traditional and Complementary Medicine
Osama Salama, Noha Khalil, Mostafa I Fekry, Mokhtar Bishr and Soheir El-Zalabani
Future University in Egypt, EgyptCairo University, EgyptMepaco Medifood, Egypt
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Tradit Med Clin Natur
Abstract
Drought is among the most common agricultural stresses that significantly influence both growth and metabolic activities of plants. In this study an aromatic herb Eriocephalus africanus L. (Asteraceae) was cultivated under diverse watering regimens alongside foliar spraying with a plant hormone, Salicylic Acid (SA), at three concentrations (1, 2 and 3 mM) to observe the effect of drought stress and SA on its secondary metabolites. Total Flavonoid and Polyphenol contents (TFC and TPC, respectively) were calculated. TFC was raised by 54% in drought stressed plants sprayed with the highest SA concentration (3 mM) relative to control plants. Likewise, TPC increased by 35% in the same treatments. Consequently, the DPPH radical scavenging activity improved more than two-folds in the same treatment relative to control plants. UPLC-ESIMS/ MS profiles of the extracts of control plants were compared to those of treatment with highest TPC. Among identified polyphenols, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid predominated in both samples, although detected in a greater percentage in the treated plants. The essential oil was hydro-distilled from the aerial parts of plants from all treatments; highest yield (1.05±0.03% v/w) was obtained from drought stressed plants sprayed 2 mM SA. Artemisia ketone prevailed in the GC/MS chromatograms of all oil samples, with highest yield (42%) recorded in plants sprayed with the same SA concentration.Biography
Osama Salama is Vice President of Future University, Cairo, Egypt. He received his Doctor of Natural Sciences, (Dr. Nat. Sc.) in Phytochemistry from Institute of Pharmacy, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, Zürich, (ETHZ) Switzerland. His experience covers academia and industry. Prof. Salama spent about 20 years in R&D and QC for pharmaceutical drugs. His experience covers pharmaceutical development, preclinical development, clinical trials supplies and regulatory affairs. He has supervised and participated in innovation of two novel drugs for treatment of Schistosomiasis & Fasciolcasis and HCV. He has published about 100 research papers in national and international Journals.
E-mail: osalama99@hotmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi