Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
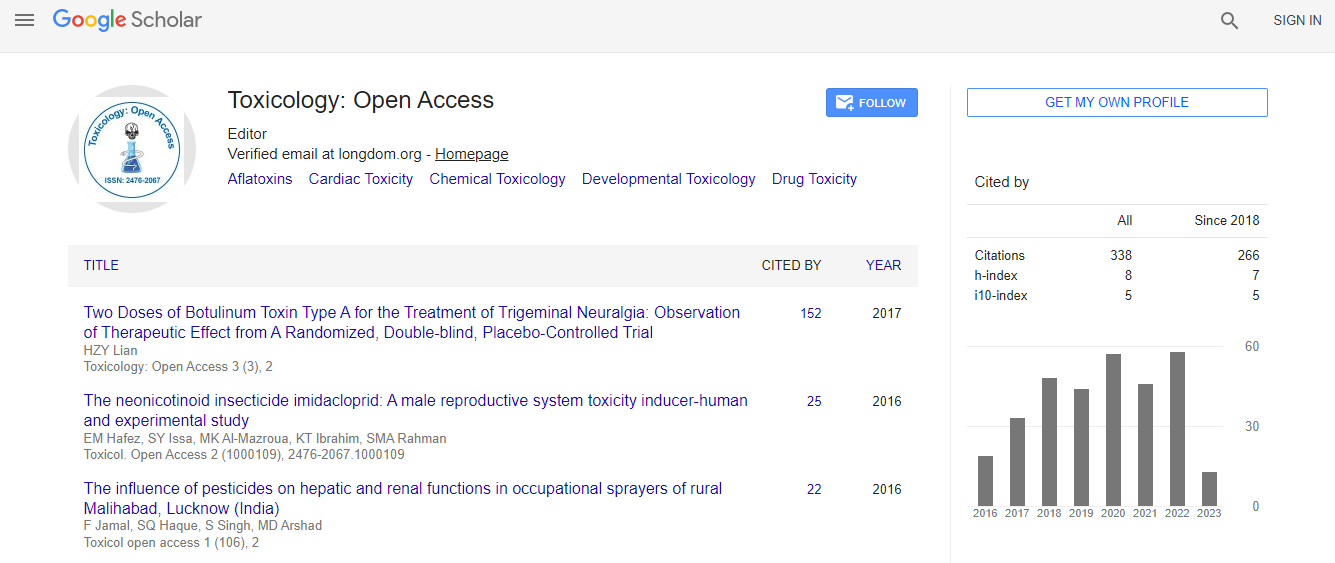
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 336
Toxicology: Open Access received 336 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Natural products as drug leads for neurodegenerative diseases; Alzheimer and Dementia
8th World Congress on Toxicology and Pharmacology
Heba Handoussa, Reham Wagdy, Alaa Selim, Reham AbdelKader, Nabila Hamdi and Nesreen El Sayed
German University in Cairo, Egypt
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Toxicol Open Access
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: Alzheimerâ�?�?s disease (AD) and Dementia are multifactorial neurodegenerative disorders driven by various pathogenic events with neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Phenolics are widely known for their different beneficial characteristics, they could be considered as promising therapeutic agents against neurodegenerative diseases. Aim: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the potential effect of some Egyptian medicinal plants; Bauhinia variegate (Bv) and Egyptian Nutraceuticals; Corchorus olitorius (Co) & Majorana hortensis (Mh) to ameliorate neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis accompanied by these neurodegenerative diseases. Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Several parameters were used to evaluate the phenolic content in these medicinal plants; cognitive impairment via assessment of neurobehavioral tests, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress which are characteristic features of neurodegenerative diseases. Findings: Bauhinia variegata showed significant improvement in neurobehavioral even with the least dose studied; 50 mg/ kg in Y-maze through enhancing mean % alternation by 57.55% and reduction in A�?²42 levels was observed with same dose of 39.89% and increment of superoxide-dismutase level by 80% while Corchorus olitorius & Majorana hortensis significantly improved recognition memory that was shown to be altered in the LPS group and COX-2 inflammatory markers were reduced by (CO) and (Mh) compared to the LPS group proven by immunohistochemistry investigation. Conclusion & Significance: These findings suggest that phenolics within these medicinal plants may be useful in protection against Dementia and neuroinflammation through enhancement of cognition and limiting neurodegeneration and modulating the proinflammatory pathway. Recommendations: The high edible phenolics intake could be prophylactically protective against several neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Publications :â�?¢ Sobeh M, ElHawary E, Labib R, Handoussa H and Ayoub N (2016) Identification of phenolic secondary metabolites from Schotia brachypetala Sond. (Fabaceae) and demonstration of their antioxidant activities in Caenorhabditis elegans. PeerJ, PubMed 27896020.
â�?¢ Farag M, Handoussa H, Fekry MI, Wessjohann LA (2016) Metabolite profiling in 18 Saudi date palm fruit cultivars and their antioxidant potential via UPLC-qTOF-MS and multivariate data analyses. Food Function 7 (2): 1077-86.
â�?¢ Handoussa H, Mandour Y, Swilam N Hanafi R and Mahran L (2015) Structural docking studies of COX-II inhibitory activity for quercetin metabolites derived from Corchorus Olitorius and Vitis Vinifera. International Journal of Food Properties 2377-2384.
â�?¢ Yara Hassaan Y, Handoussa H, El-Khatib A, Linscheid M, Sayed N and Ayoub N (2014) Evaluation of plant phenolic metabolites as a source of Alzheimer's drug leads biomed research international. Article ID 843263.
â�?¢ Handoussa H, Hanafi R, Eddiasty I, El-Gendy M, Linscheid M, Mahran L and Ayoub N (2013) In vitro and in vivo antiinflammatory and cytotoxic capacities of dietary phenolics isolated from Corchorus olitorius and Vitis vinifera. Journal of Functional Foods 5 (3): 1204-1216.
Biography
Heba Handoussa has completed her PhD at German University in Cairo (GUC), Faculty of Pharmacy and Biotechnology. She has a considerable experience in undergraduate teaching where she functions as an Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutical Biology. Her research areas are plant secondary metabolism analysis and familiarity with multiple mass spectrometers and techniques (i.e. GC/MS, LC/MSn). Besides awareness of several spectroscopic techniques to identify, isolate and purify the bioactive phytochemical compounds she is also having responsibilities in postgraduate studies’ supervising Bachelor’s, Master’s and PhD theses in the same field. She has been probing novel bioactive molecules with possible anti-inflammatory, molecular targeted HCC therapy, anticancer, neuroprotective, antidiabetic and other pharmacological activities. She is the main author of several published articles in many reputable scientific journals in the field of Pharmacy and reviewer in number of journals related to the field of Pharmacy.
Email: heba.handoussa@guc.edu.eg

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi