Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
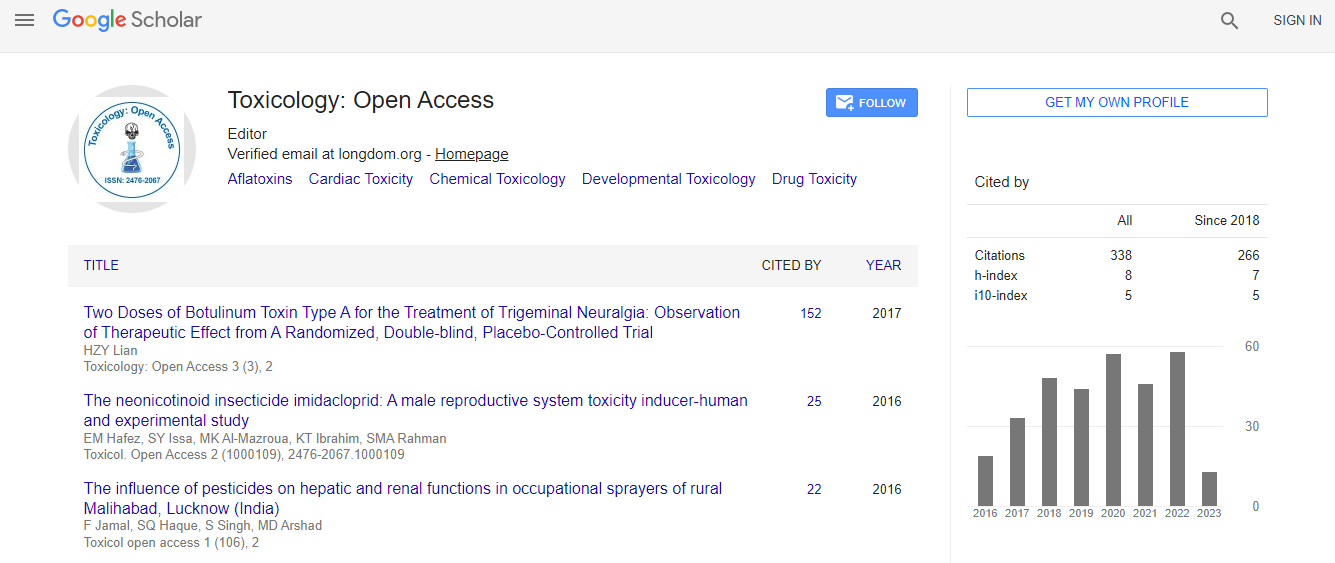
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 336
Toxicology: Open Access received 336 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Possible neuroprotective mechanisms of ginseng and rutin in experimental model of head injury induced cognitive dysfunction
8th World Congress on Toxicology and Pharmacology
Anil Kumar, Hitesh Dhar and Puneet Rinwa
Panjab University, India
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Toxicol Open Access
Abstract
Introduction: Head injury is a major cause of disability and death. Possible role of neuroinflammation, nitric oxide, microglia and oxidative stress have been suggested in the pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury related complications such as cognitive dysfunction. Objective: Therefore, the present study was designed to explore the possible role of ginseng and rutin and its interaction with nitric oxide modulator and microglial inhibitor against experimental of head injury induced behavioral, biochemical and molecular alterations. Materials & Methods: Wistar rats were exposed to head injury by using weight-drop method. Following injury and a postinjury rehabilitation period of two weeks, animals were administered vehicle/drugs for another two weeks. Results: Traumatic brain injury caused significant memory impairment in Morris water maze task as evident from increase in escape latency and total distance travelled to reach the hidden platform. Time spent in target quadrant and frequency of appearance in target quadrant was also significantly decreased in head trauma rats. Further, there was a significant increase in oxidative stress (elevated malondialdehyde, nitrite concentration and decreased reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase and catalase levels), neuroinflammation (TNF-�± and IL-6) and acetylcholinesterase levels in both cortex and hippocampal regions of traumatized rat brain. Ginseng (100-200 mg/kg), Rutin (20-80) treatment for two weeks significantly attenuated all these behavioral, biochemical and molecular alterations, suggesting their neuroprotective effect. Further, combination of sub effective doses of ginseng (50 and 100 mg/kg) or rutin (40, 80) with microglia inhibitor as well as nitric oxide modulators significantly modulates their protective effect respectively. The present study suggests that these flavanoids produce their neuroprotective effect by involving microglial as well as nitric oxide pathways. Conclusion: The study further provides a hope that these flavanoids could be used effectively for the management of brain traumatic injury and related complication.Biography
Email: Kumaruipspu@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi