Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
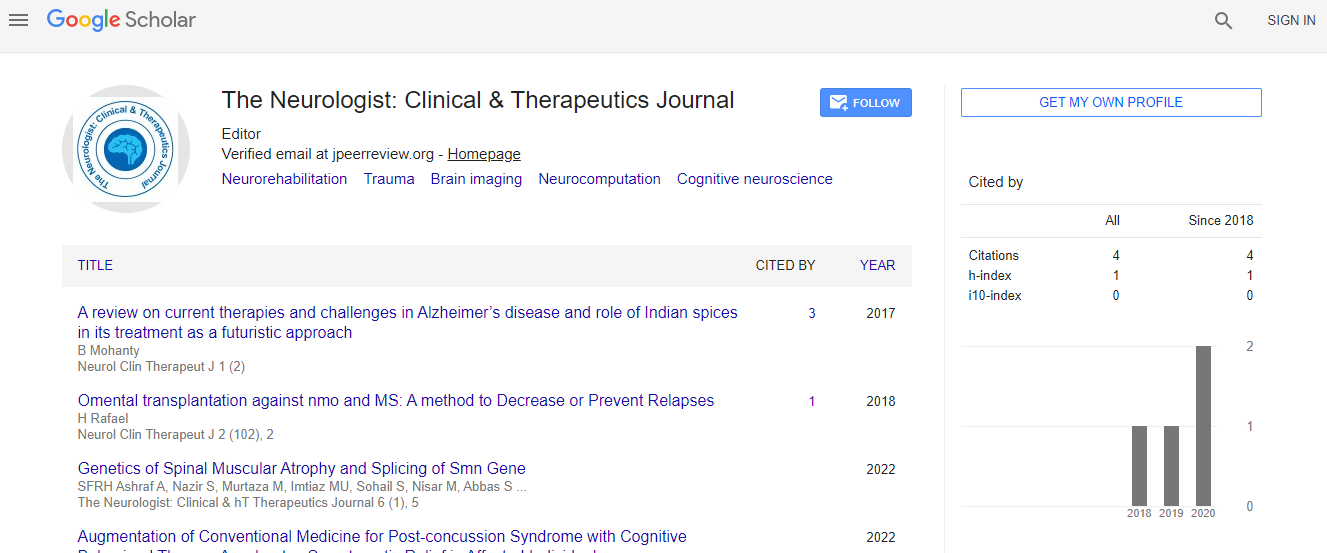
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 5
The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal received 5 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Share This Page
Editorial Board
Submit Manuscript
Journal Impact Factor 0*
Submit manuscript at or send as an e-mail attachment to the Editorial Office at neuropsych@scischolarsjournal.com
If you are interested in publishing with us or have any questions, please feel free to contact us directly on WhatsApp .
Table of Contents
About the Journal
The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal is an official peer reviewed journal for the rapid publication of articles on topics of current interest to physicians treating patients with neurological diseases. The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal with highest journal impact factor offers Open Access option to meet the needs of authors and maximize article visibility.
The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal includes a wide range of fields such as how neurologist treats disorders that affect the Neuropsychiatric disorders, Brain Disorders, Neurodegenerative diseases, Neurotic disorders, Neurorehabilitation, Trauma, Brain imaging, Neurocomputation, Cognitive neuroscience, Mood disorders, Child Behaviour, Mental illness, Seizure disorders, Spinal cord disorders etc., in its discipline to create a platform for the authors to make their contribution towards the journal and the editorial office promises a peer review process for the submitted manuscripts for the quality of publishing.
This peer reviewed medical journal is using Editorial Manager System for quality in review process. Editorial Manager System is an online manuscript submission, review and tracking systems. Review processing is performed by the editorial board members of The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal or outside experts; at least two independent reviewers approval followed by editor approval is required for acceptance of any citable manuscript. Authors may submit manuscripts and track their progress through this system, hopefully to publication. Reviewers can download manuscripts and submit their opinions to the editor. Editors can manage the whole submission/review/revise/publish process.
The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal is an academic journal which aims to publish most complete and reliable source of information on the discoveries and current developments in the mode of Research articles, Review articles, Case reports, Short communications, etc. in all areas of the field and making them freely available through online without any restrictions or any other subscriptions to researchers worldwide.
Neurologist
A physician who practices in neurology is called a neurologist. The neurologist treats all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous system (and its subdivisions, the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system); including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials and basic or translational research. While neurology is a non-surgical specialty, its corresponding surgical specialty is neurosurgery. During a neurological examination, the neurologist reviews the patient's health history with special attention to the current condition.
Neuroscience
Neuroscience (or neurobiology) is the scientific study of the nervous system. It is a multidisciplinary branch of biology that deals with the anatomy, biochemistry, molecular biology, and physiology of neurons and neural circuits. It also draws upon fields including mathematics, pharmacology, physics, engineering, and psychology. The earliest study of the nervous system dates to ancient Egypt. Trepanation, the surgical practice of either drilling or scraping a hole into the skull for the purpose of curing headaches or mental disorders, or relieving cranial pressure, was first recorded during the Neolithic period. Manuscripts dating to 1700 BC indicate that the Egyptians had some knowledge about symptoms of brain damage. The scientific study of the nervous system has increased significantly during the second half of the twentieth century, principally due to advances in molecular biology, electrophysiology, and computational neuroscience.
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery is the surgical specialization that treats diseases and disorders of the brain and spinal cord. Back pain can sometimes produce neurological symptoms such as numbness, muscle weakness, and loss of bowel and bladder control due to dysfunction at the nerve root. These symptoms are indicators that neurosurgery is required to treat the underlying cause of back pain as opposed to conservative treatments. Procedures to treat back pain under the realm of neurosurgery include discectomy, laminectomy, and spinal fusion surgery. In neurosurgery, there is a higher risk of further nerve damage and infection which may result in paralysis.
Neurophysics
Neurophysics (or neural physics) is the branch of medical physics dealing with the nervous system including the brain and the spinal cord and the nerves. It covers a wide spectrum of phenomena from molecular and cellular mechanisms to techniques to measure and influence the brain and to theories of brain function. It can be viewed as an approach to neuroscience that is based on solid understanding of the fundamental laws of nature.it to represent an emerging science which investigates the fundamentally physical basis for the brain, hence the physical structure involved in the cognition process. This combination of neuroscience and quantum physics is a new science called neurophysics.
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging or brain imaging is the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the nervous system. It is a relatively new discipline within medicine, neuroscience, and psychology. Neuroimaging utilizes a number of technologies to directly or indirectly produce images of the brain. Each technique is designed to convey distinct types of information, depending on the scientific or medical question at hand. There are different kinds of neuroimaging. Structural imaging offers a vision of the structure of the brain to enable diagnosis of larger-scale diseases, tumours, injuries, and stroke. Functional imaging is used to diagnose smaller tumours and diseases on a finer scale. Functional imaging also allows us to visualize the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions. Functional imaging is often used in neurological and cognitive science research. Given that most ethical dilemmas addressed in this module pertain to functional imaging, henceforth we will primarily concentrate on the applications and implications of technologies such as fMRI, CT, and PET scans.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy refers to general diseases or malfunctions of the nerves. Nerves at any part of the body can be damaged from injury or disease. Neuropathy is often distinguished according to the type or location of nerves that are affected or disease causing it. It is of three types: Peripheral neuropathy: When the nerve problem affects the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. These nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Cranial neuropathy: It occurs when any of the twelve cranial nerves (nerves that exit from the brain directly) are damaged. Autonomic neuropathy: It is damage to the nerves of the involuntary nervous system. Focal neuropathy is restricted to one nerve or group of nerves, or one area of the body.
Neuroimmunology
Neuroimmunology is a field combining neuroscience, the study of the nervous system, and immunology, the study of the immune system. Neuroimmunologists seek to better understand the interactions of these two complex systems during development, homeostasis, and response to injuries. It is a branch of immunology that deals especially with the interrelationships of the nervous system and immune responses and autoimmune disorders (as multiple sclerosis).
Neuropsychology
The study of the relationship between behavior, emotion, and cognition on the one hand, and brain function on the other. The brain is complex. Disorders within the brain and nervous system can alter behavior and cognitive function. Neuropsychologists evaluate and treat people with various types of nervous system disorders. Illnesses, injuries, and diseases of the brain and nervous system can affect the way a person feels, thinks, and behaves. Symptoms that may call for a neuropsychologist include: memory difficulties, mood disturbances, learning difficulties, nervous system dysfunction.
Neuroradiology
The field within radiology that specializes in the use of radioactive substances, x-rays and scanning devices for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system. Neuroradiology involves the clinical imaging, therapy, and basic science of the central and peripheral nervous system, including but not limited to the brain, spine, head and neck, interventional procedures, techniques in imaging and intervention, and related educational, socioeconomic, and medicolegal issues.
Neurorehabilitation
It is a complex medical process which aims to aid recovery from a nervous system injury, and to minimize and/or compensate for any functional alterations resulting from it. This involved exercises to correct muscle dysfunction. Neurorehabilitation should be holistic, patient-focused, inclusive, participatory, sparing, lifelong, resolving and community focused. Commonly treated problems include: Stroke recovery, Cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease, Brain injury, Anoxic brain injury, Traumatic brain injury, Multiple sclerosis, Post-polio syndrome, Guillain–Barré syndrome.
Neurodegeneration
Neurodegeneration refers to the progressive atrophy and loss of function of neurons, which is present in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Neurodegenerative disease is an umbrella term for a range of conditions which primarily affect the neurons in the human brain. Dementias are responsible for the greatest burden of neurodegenerative diseases. Parkinson's disease (PD) is recognized as the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer's dis- ease and affects 1% of the population worldwide.
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive decline. A neurodegenerative type of dementia, the disease starts mild and gets progressively worse destroying memory and other important mental functions. The total brain size shrinks with Alzheimer's - the tissue has progressively fewer nerve cells and connections. It is the most common cause of dementia in older adults; a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the gradual loss of cognitive ability in association with the neuropathological findings of abnormal protein aggregates (neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles) and neuron loss in the cerebral cortex.
Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism complex of symptoms including resting tremor, bradykinesia/akinesia, rigidity, and postural instability that are due to striatal dopamine deficiency or reduced function; may be seen in a variety of neurodegenerative disorders including idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD) which is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system, Lewy body dementia, corticobasal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy, multisystems atrophy. Parkinson's disease can cause neuropsychiatric disturbances, which can range from mild to severe. This includes disorders of speech, cognition, mood, behaviour, and thought. Cognitive disturbances can occur in the early stages of the disease and sometimes prior to diagnosis, and increase in prevalence with duration of the disease.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder of various causes characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures. Epilepsy is a chronic disorder that causes unprovoked, recurrent seizures. A seizure is a sudden rush of electrical activity in the brain. There are two main types of seizures. Generalized seizures affect the whole brain. Focal, or partial seizures, affect just one part of the brain. A mild seizure may be difficult to recognize. It can last a few seconds during which you lack awareness. Stronger seizures can cause spasms and uncontrollable muscle twitches, and can last a few seconds to several minutes. During a stronger seizure, some people become confused or lose consciousness. Afterward they may have no memory of it happening.
Convulsion
A sudden, violent, irregular movement of the body, caused by involuntary contraction of muscles and associated especially with brain disorders such as epilepsy, the presence of certain toxins or other agents in the blood, or fever in children. Symptoms include: Drooling or frothing at the mouth, Eye movements, Grunting and snorting, Loss of bladder or bowel control, Sudden falling, Teeth clenching, Temporary halt in breathing, Uncontrollable muscle spasms with twitching and jerking limbs, Unusual behavior like sudden anger, sudden laughter, or picking at one's clothing. The person may have warning symptoms before the attack, which may consist of: Fear or anxiety, Nausea, Vertigo, Visual symptoms (such as flashing bright lights, spots, or wavy lines before the eyes).
Cognitive Impairment
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) causes a slight but noticeable and measurable decline in cognitive abilities, including memory and thinking skills. A person with MCI is at an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's or another dementia. MCI that primarily affects memory is known as "amnestic MCI." MCI that affects thinking skills other than memory is known as "nonamnestic MCI." Diagnosed by Thorough medical history, Assessment of independent function and daily activities, Assessment of mental status, Neurological examination, Evaluation of mood and laboratory tests.
Dementia
It is a general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. Memory loss is an example. Alzheimer's is the most common type of dementia. It is not a specific disease. It's an overall term that describes a wide range of symptoms associated with a decline in memory or other thinking skills severe enough to reduce a person's ability to perform everyday activities. Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60 to 80 percent of cases. Vascular dementia, which occurs after a stroke, is the second most common dementia type.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis commonly known as MP results in nerve damage disrupts communication between the brain and the body. Multiple sclerosis causes many different symptoms, including vision loss, pain, fatigue and impaired coordination. The symptoms, severity and duration can vary from person to person. Some people may be symptom free for most of their lives, while others can have severe, chronic symptoms that never go away. Physiotherapy and medication that suppress the immune system can help with symptoms and slow disease progression. There are instances where a severe case of MS may bring about complications or side effects that can impact one's life span, however, most MS sufferers will not have a shortened life span.
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy is a general term describing a disease that affects the function or structure of your brain. There are many types of encephalopathy and brain disease. Some are permanent and some are temporary. Some are present from birth and never change, while others are acquired after birth and may get progressively worse. Symptoms include: Mental changes, Neurological symptoms like muscle weakness in one area, poor decision-making or concentration, involuntary twitching, trembling, difficulty speaking or swallowing and seizures. Diagnosed by blood tests, CT or MRI scan, EEG. Treatment may include medications or surgery to treat your symptoms or underlying cause.
Acute Stress Disorder
Experiencing, witnessing, or being confronted with one or more traumatic events can cause ASD. The events create intense fear, horror, or helplessness. Traumatic events that can cause ASD include: death, a threat of death to oneself or others, a threat of serious injury to oneself or others, a threat to the physical integrity of oneself or others. Approximately 6 to 33 percent of people who experience a traumatic event develop ASD. Symptoms include: Intrusion symptoms, Negative mood, Dissociative symptoms, Avoidance symptoms, Arousal symptoms. Treatment options include: a psychiatric evaluation, hospitalization, medication, exposure-based therapies, cognitive behavioral therapy.
Cerebral Palsy
It is considered a neurological disorder caused by a non-progressive brain injury or malformation that occurs while the child’s brain is under development. Cerebral Palsy primarily affects body movement and muscle coordination. Though Cerebral Palsy can be defined, having Cerebral Palsy does not define the person that has the condition. Long-term treatment includes physical and other therapies, drugs and sometimes surgery. There is no test that confirms or rules out Cerebral Palsy. In severe cases, the child may be diagnosed soon after birth, but for the majority, diagnosis can be made in the first two years. For those with milder symptoms, a diagnosis may not be rendered until the brain is fully developed at three to five years of age.
Sleep Disorders
Changes in sleeping patterns or habits that can negatively affect health. Types include: Restless legs syndrome-A condition characterized by a nearly irresistible urge to move the legs, typically in the evenings. Jet lag- A sleep disorder that can affect those who travel quickly across multiple time zones. Narcolepsy- A chronic sleep disorder that causes overwhelming daytime drowsiness. Sleepwalking- The act of getting up and walking around while asleep. Obstructive sleep apnea- Intermittent airflow blockage during sleep. Insomnia-Persistent problems falling and staying asleep.
Journal Highlights
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
h-index
Articles published in The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal has got h-index 1, which means every article in The Neurologist: Clinical & Therapeutics Journal has got 1 average citations.
Recently Published Articles
-
High Similitudes and Collaborations Exist Between the Central Nervous System and the Eye
Vicki Everett -
Most Appropriate Data Mining Strategies
Tom Robbie -
Extrinsic Determinants of the Desire for Food Craving
Tom Franklin -
Automated Applications in Neurosurgery
Adams Dev -
Fundamentals for Powerful Learning and Fruitful Transformation
Adam Davy -
Aicardi: A Neurodevelopmental Problem
Yuri Yokoma

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi