Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
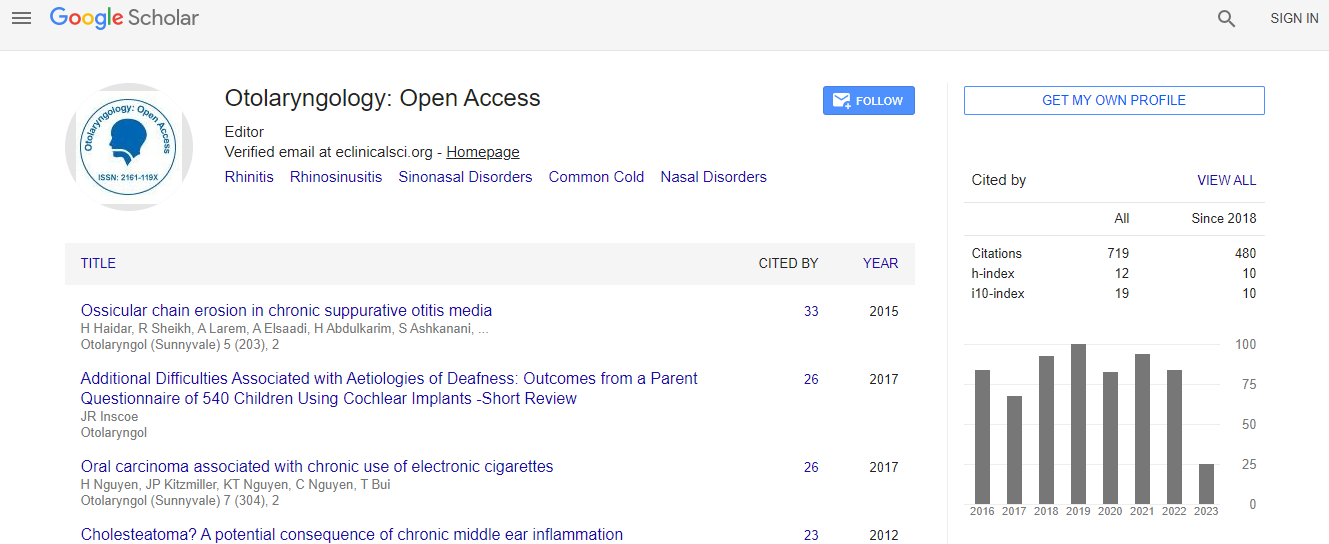
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effects of an auditory lateralization training in children suspected to central auditory processing disorder
International Conference on Aesthetic Medicine and ENT
Farzaneh Zamiri Abdollahi, Yones Lotfi, Abdollah Moosavi, Enayatollah Bakhshi and Hamed Sadjedi
AVA Research Group, Iran
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Otolaryngology
Abstract
Introduction: Central auditory processing disorder [(C)APD] refers to a deficit in auditory stimuli processing in nervous system that is not due to higher-order language or cognitive factors. One of the problems in children with (C)APD is spatial difficulties which have been overlooked despite their significance. Localization is an auditory ability to detect sound sources in space and can help to differentiate between the desired speech from other simultaneous sound sources. Aim of this research was investigating effects of an auditory lateralization training on speech perception in presence of noise/competing signals in children suspected to (C)APD. Methods: In this interventional study, 60 children suspected to (C)APD were selected based on multiple auditory processing assessment subtests. They were randomly divided into two groups: control and training groups. Training program consisted of detection and pointing to sound sources delivered with interaural time differences under headphones for 12 formal sessions. Spatial word recognition score and monaural selective auditory attention testwere used to follow the auditory lateralization training effects. Results: This study showed that in the training group, mSAAT score and spatial WRS in noise (p value�0.001) improved significantly after the auditory lateralization training. Conclusions: We used auditory lateralization training for six weeks and showed that auditory lateralization can improve speech understanding in noise significantly. The generalization of this results needs further researches.Biography
Email: audiology_zamiri@yahoo.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi