Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
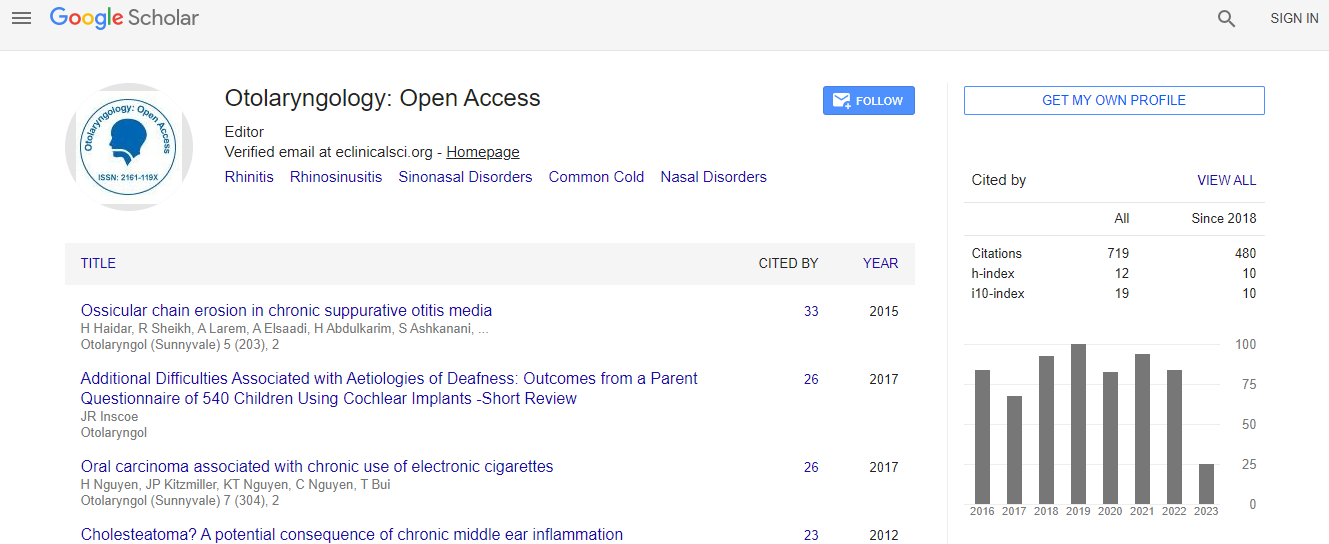
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effects of Bifi dobacterium breve feeding strategy and delivery modes on experimental allergic rhinitis mice
4th International Conference on Rhinology and Otology
Yang Xu, Ren J, Yang F L, Lv D, Hung S, Zhang J, Lin P, Liu S X, Zhang N and Bachert C
Sichuan University, China
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Otolaryngol
Abstract
Background: Diff erent delivery modes may aff ect the susceptibility to allergic diseases. It is still unknown whether early intervention with probiotics would counteract this eff ect. Objectives: Th e eff ect of diff erent delivery modes on immune status and nasal symptoms was investigated on established allergic rhinitis (AR) mouse model. In addition, the immunoregulatory eff ects and mechanisms of diff erent feeding manners with Bifi dobacterium breve were examined. Methods: Live lyophilized B. breve was orally administered to BALB/c mice born via vaginal delivery (VD) or cesarean delivery (CD) for 8 consecutive weeks, aft er which they were sensitized by ovalbumin (OVA) to establish experimental AR. Nasal symptoms, serum immunoglobulins, cytokines, splenic percentages of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T(Treg) cells and nasal eosinophil infi ltration were evaluated. Results: Compared with VD mice, mice delivered via CD demonstrated more serious nasal symptoms, higher concentrations of OVA-specifi c immunoglobulin (Ig) E, more nasal eosinophil and lower percentages of splenic CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells aft er establishing experimental AR. Th ese parameters were reversed by administering B. breves shortly aft er birth. However, the eff ect of B. breve did not diff er between diff erent delivery modes. Conclusion: CD aggravates the nasal symptoms of AR mice compared to VD. Th is is the fi rst report that oral administration of B. breve shortly aft er birth can signifi cantly alleviate the symptoms of AR mice born via both deliveries, probably via activation of the regulatory capacity of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells.Biography
Yang Xu is currently pursuing his PhD in West China School of Medicine, Sichuan University, China. He focuses on scientiï¬ c research about rhinology and otology.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi