Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
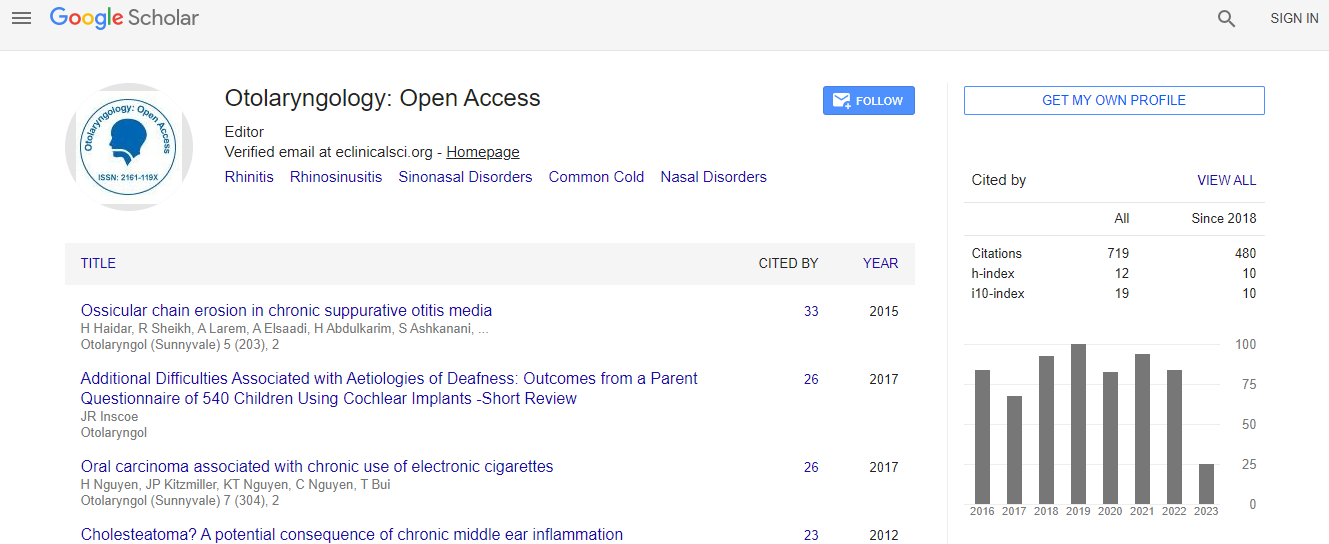
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Microscopic biploar vs cold steel dissection tonsillectomy in pediatric patients
Global Summit and Medicare Expo on Head & Neck Surgery
Ashish Vashishth
Columbia Asia Hospital, India
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Otolaryngol (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate and compare microsurgical bipolar dissection tonsillectomy (MBDT) with traditional cold steel dissection tonsillectomy (CSDT). This was a comparative interventional study carried out in the otolaryngology department of a tertiary referral institute. In total, 60 patients planned for tonsillectomy were included in the study and were randomly divided into two groups. The results were compared in terms of operative time, intra-operative blood loss and postoperative pain and morbidity including the time taken for resumption of oral feeding and the amount of slough formation and edema observed at various times postoperatively. Mean operative time in the CSDT group (23.35�±7.10 min) was significantly longer (p<0.001) than in the MBDT group (13.90�±4.10 min). Intraoperative blood loss was significantly lower in the MBDT group (9.77�±4.10 ml) when compared with the CSDT group (33.45�±8.54 ml) (p<0.001). Early postoperative pain and time to resumption of first oral intake were lower in the MBDT group, though the differences were not statistically significant (p>0.05). Late postoperative pain measured on day 7 and time to resumption of a normal diet were not significantly higher in the MBDT group. No difference was found between the two techniques in terms of postoperative hemorrhage. No major complications occurred in either group. MBDT reduces operative time and intraoperative blood loss by providing better visualization of blood vessels under microscopic vision and combines the advantage of hemostatic cautery dissection and vessel coagulation. This, along with no significant difference in postoperative pain and morbidity, makes this technique particularly advantageous especially in the pediatric population with a low circulation volume.Biography
Email: drashishvashishth@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi