Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
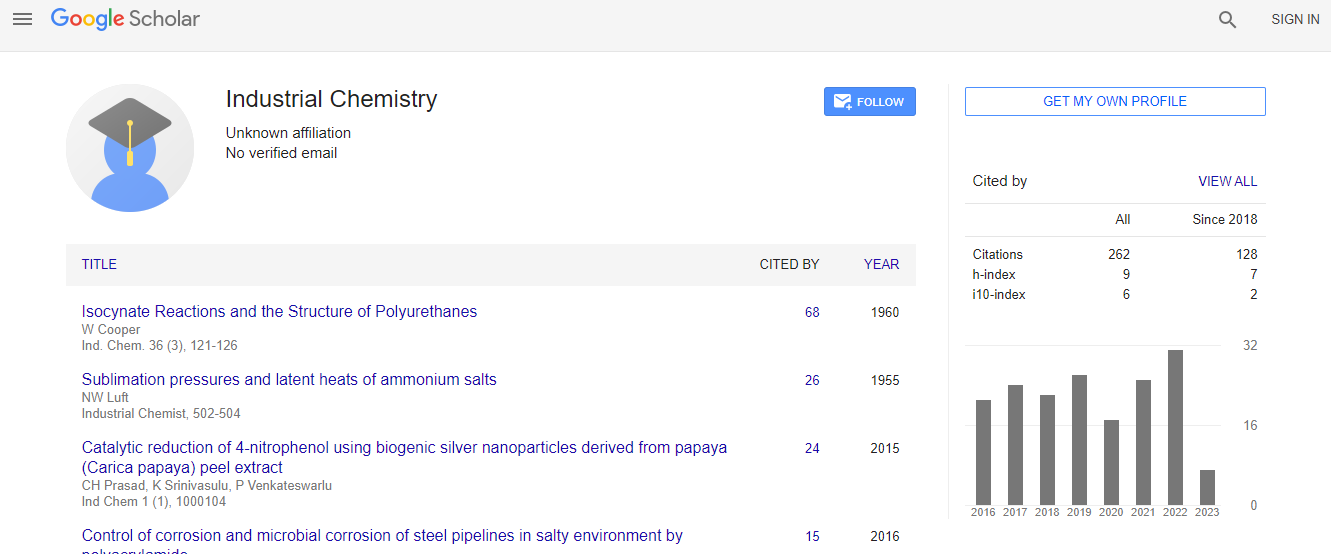
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 262
Industrial Chemistry received 262 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Monte Carlo analysis of KRITZ-2 critical benchmarks on the reactivity temperature coefficient using ENDF/B-VII.1 and JENDL-4.0 nuclear data libraries
International Conference on Industrial Chemistry
Sanae E L Ouahdani
Abdelmalek Essaadi University, Morocco
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Ind Chem
Abstract
A set of KRITZ-2 experiments light water moderated lattices with uranium oxide and mixed-oxide fuel rods, at room and elevated temperatures, performed in the early 1970â�?�?s have been assessed. Using the MCNP6.1 code with the most recent cross section libraries: JENDL-4 and ENDF/B-VII.1, the critical experiments KRITZ: 2-1, KRITZ: 2-13, and KRITZ: 2-19 were analyzed. We have used the Makxsf and NJOY utilities to handle the data in the specific temperatures not available in the MCNP6.1.1 original data. The detailed comparisons of the calculated and measured effective multiplication factors and pin power distributions for UO2 and MOX fuelled cores presented in this work demonstrate a good agreement between calculation and measurements. The maximum deviation of the calculation from the experimental data for keff, is 0.58% (absolute value) obtained for the KRITZ 2:1at 248.5�?°C using ENDF/B-VII.1 data. To investigate better the influence of cross sections differences on the reactivity and temperature coefficient, we break down the infinite multiplication factor into its components using a pin cell model. We have also calculated the non-leakage probability and the associated temperature coefficient. For the Reactivity Temperature Coefficient, our analysis has shown that the tendency of a negative error (overestimation by calculation of the absolute value of the RTC) usually observed when analyzing similar UO2 and MOX LWR lattices is confirmed. However, the level of the calculation error has been reduced significantly by using Monte Carlo modeling associated with the most recent nuclear data libraries.Biography
Email: selouahdani@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi