Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
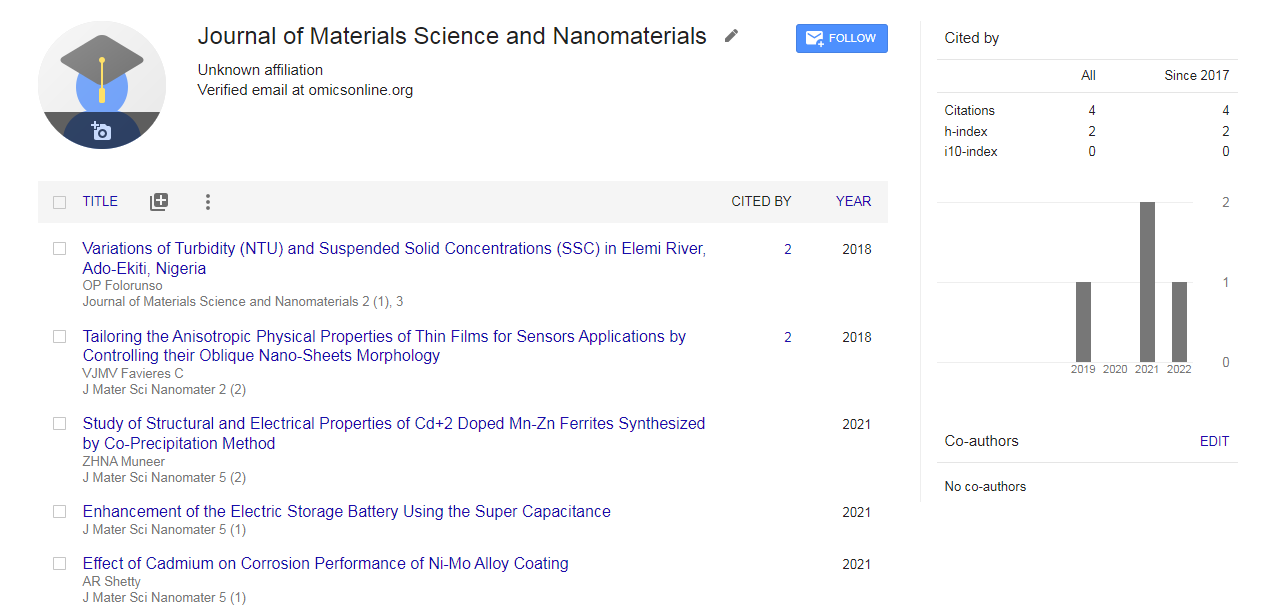
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 8
Journal of Materials Science and Nanomaterials received 8 citations as per Google Scholar report
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Nano sized photocatalyst for sustainable environmental pollution management applications
36th International Conference on NANOMATERIALS AND NANOTECHNOLOGY
Lai Chin Wei
University of Malaya, Malaysia
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Mater Sci Nanomater
Abstract
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is one of the most attractive transition-metal oxides photocatalyst because of its superior physical and chemical properties, which has been widely applied in environmental clean-up (photocatalytic pollution removal) as well as antibacterial/antiviral coating applications. The performance of TiO2 in these applications highly depends on its structural, electronic, optical, and morphological as well as the surface properties (exposed facets). Great effort has been devoted to adjust these properties and apparent progress has been made on the synthesis of the 0-, 1-, 2-, and 3-dimensional nanostructured TiO2 materials. Today, the presentation will cover the synthesis of TiO2-based nanomaterials and their sustainable environmental pollution management applications. The morphology was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and elemental composition investigated using energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) showed peaks for Zn and O only. The exact size of ZnO particles and its crystalline nature were investigated from transmission electron microscopy (TEM),High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED). The TEM showed the size range of the ZnO NPs to be â�?¼ 10â�?�?15 nm at 400 �?°C, â�?¼ 15â�?�?25 nm at 600 �?°C and â�?¼ 25â�?�?30 at 800 �?°C which are in good agreement with the SEM observation. The band gap energy was calculated from UV diffuse reflectance spectra and found to be 3.42, 3.38 and 3.35 eV for 400, 600 and 800 �?°C respectively. The fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of leaf extract confirmed the presence of phyto constituents such as amines, amides, quinines and ketones in the leaf extract. The ZnO NPs calcined at 400 �?°C having higher band gap energy and smaller size was used for photocatalytic degradation. The studies showed the efficiency greater than 90% towards degradation of 20 ppm Congo red dye solution at 0.24 g/L ZnO NPs in 1 h at pH 9.Biography
Dr. Lai [PhD, BEng(Hons) | PEng, PTech, CEng (UK), MIEM, MIMechE (UK)] is currently an associate professor in Nanotechnology & Catalysis Research Centre, University of Malaya. Lai’s main research interests are in the areas of chemically modified metal oxide photocatalysts, functionalized nanomaterials/ nanocomposite and carbon graphene materials, especially apply in environmental pollution management and solar energy technology.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi