Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
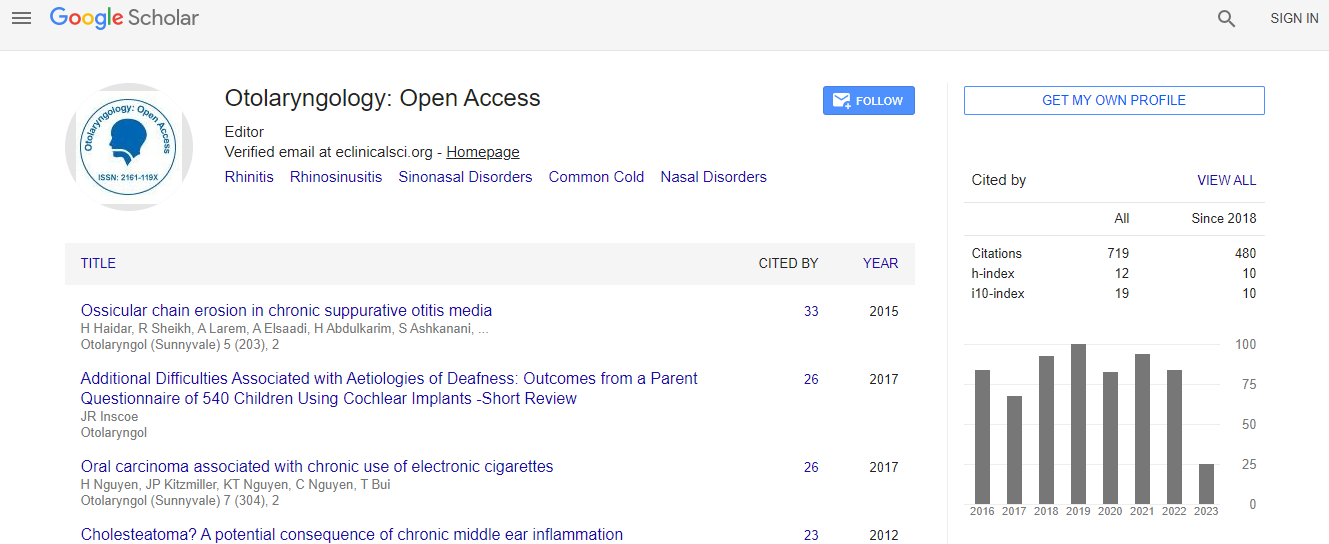
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The button graft technique: A new technique for repair of small tympanic membrane perforations
International Conference on Aesthetic Medicine and ENT
Ahmed Mohammed Abdelghany
Benha University, Egypt
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Otolaryngology
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate a new composite cartilage-perichondrium graft (button graft) for repair of small-sized tympanic membrane perforations and to compare its success rate with that of the underlay and overlay techniques with temporal fascia or tragal perichondrium. Design: Prospective, sequential allocation of surgical technique study. Setting: Tertiary care university hospital. Patients: One hundred and ninety five (195) patients aged 14-42 years with central, uncomplicated tympanic membrane perforations with completely visualized margins affecting less than 25% of the tympanic membrane, distributed in three groups: 1 (underlay), 2 (overlay) and 3 (button graft). Interventions: Patients were allocated in sequence to: 1 underlay graft, 2 overlay graft and 3 cartilage tympanoplasty with button graft technique. Patients were operated on under local anesthesia. Main Outcome Measures: Postoperative status of the tympanic membrane, hearing improvement, duration of surgery and incidence of complications at 12 months postoperative. Results: Group-1 (underlay) had 66 patients; group-2 (overlay) had 65; and group-3 (cartilage) had 66. Success was defined as the complete closure of the tympanic membrane one year after the operation. The success rates were 98.5% (65 of 66), 97% (63 of 65) and 98.5% (65 of 66) cases and the mean air-bone gap gains were 10.18 (-5.4) dB, 8.5 (+6.5) dB and 9.1 (+5.1) dB for groups-1, 2 and 3, respectively. No bone conduction threshold or speech discrimination score worsening was noted. The mean durations of the operative procedure were 35-8.4 (range 22-63), 42-6.8 (range 33-75) and 23-6.3 (range 15-41) min for groups-1, 2 and 3, respectively (P=0.02). Tympanic membrane retraction occurred in three cases in underlay group-1 and tympanic membrane cholesteatoma pearls occurred in two cases in overlay group-2. Conclusions: The button graft technique is an effective and fast alternative for the repair of small tympanic membrane perforations if complete visualization of the margin is possible. The shorter time taken with the button grafts is mainly due to the non-requirement for a skin incision. The results are comparable to those of the underlay and overlay techniques.Biography
Email: ahmedent@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi