Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
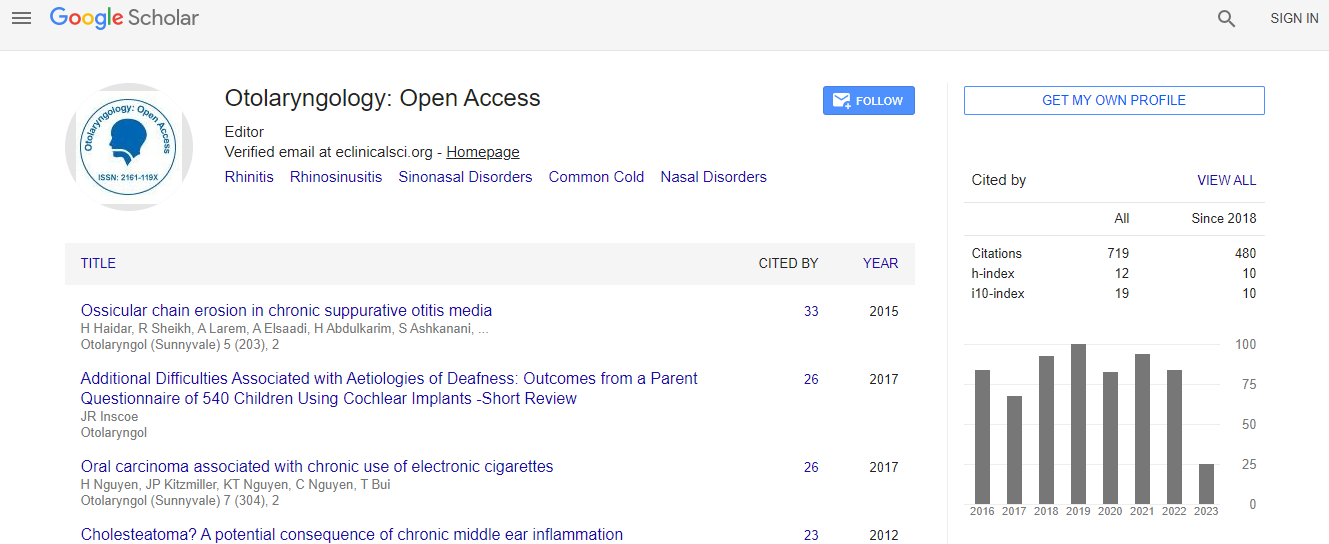
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Treatment of inferior turbinate hypertrophy by (810 nm) diode laser and electrocoagulation (A comparative study)
Global Summit and Medicare Expo on Head & Neck Surgery
Adnan Qahtan Khalaf1 and Lutfi Ghulam Awazli2
1Al-Yarmouk Teaching Hospital, Iraq 2University of Baghdad, Iraq
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Otolaryngol (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Aim: This prospective study was carried out to evaluate the efficacy of diode laser (810 nm) and electrocautery in treatment of nasal obstruction attributable to inferior turbinate hypertrophy as a comparative study. Introduction: Hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate is a common cause of chronic nasal obstruction. Etiology for mucosal turbinate hypertrophy includes chronic hypertrophic rhinitis both allergic and non-allergic rhinitis in which there is swelling of the sub-mucosa due to dilatation of the sub-mucosal venous sinusoid. A number of interventions are available for the treatment of inferior turbinate hypertrophy. An ideal procedure should be associated with minimal discomfort or adverse reactions and should preserve the physiological function of the turbinate. Materials & Methods: This prospective study was carried out in Al-Yarmouk Teaching Hospital/Department of Otolaryngology from August 2013 to November 2013. Fourteen patients who complained from nasal obstruction due to inferior turbinate hypertrophy were included in this study. Diagnosis was made by anterior rhinoscopy and fiberoptic examination. The turbinate hypertrophy in one side was reduced by using diode laser while the other side was reduced by electrocoagulation without telling the patient�s which side is treated by using the diode laser. We used both subjective symptoms and objective tests to assess the efficacy of diode laser (810 nm) and electrocautery in treatment of nasal obstruction attributable to inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Results: The symptoms of nasal obstruction, post-operative pain, crustation, bleeding, time of healing and complication were less with diode laser (810 nm) comparing with the electrocoagulation. Conclusion: Diode laser photocoagulation for inferior turbinate reduction is effective and well tolerated when used to treat patients with turbinate hypertrophy not responding to medical treatment.Biography
Email: Adnan_khtan@yahoo.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi