Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
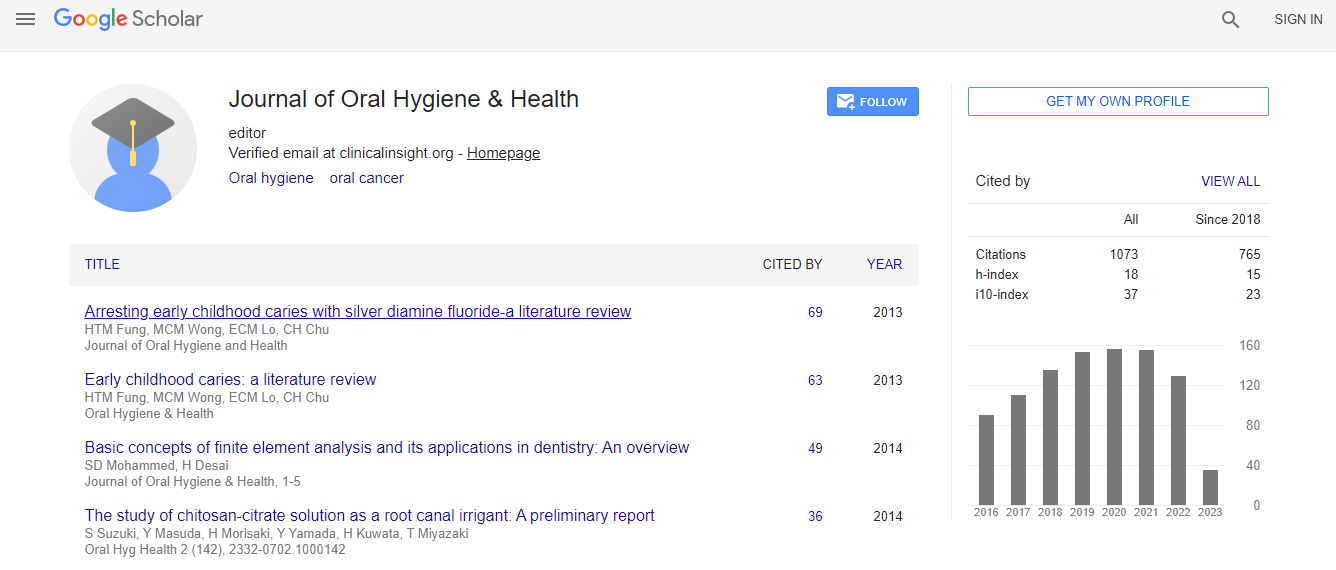
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1073
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health received 1073 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Assessment of the fitness of removable partial denture frameworks manufactured using additive manufacturing/selective laser melting
44th International Conference on Dental Research and Oral Health
Selma Saadaldin
Western University, Canada
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Oral Hyg Health
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: 3D printing selective laser melting additive manufacturing considered as the future for removable partial denture (RPD) fabrication. Fitness accuracy is an important criteria for removable partial dentures that will affect its success The purpose of this study is to compare the fitness accuracy of digitally produced RPD using selective laser melting additive manufacturing technology with ones that were produced by lost wax/ casting method and with combined digital and conventional frameworks Methodology: Cl I Kennedy classification RPD frameworks were fabricated. There were 3 groups: 3DP-G1 where frameworks produced digitally through digital designing and then the frameworks printed by selective laser melting additive manufacturing. C-G2 where the framework produced by lost wax/casting method. and the third group (SP-G3 ) where the framework produced by scanning wax-up of the framework and then printed as in the first group. 6 frameworks were produced from each group, Fitness accuracy of the frameworks was assessed by three methods: 1. subjective clinician assessment through specific criteria. 2. by calculating spaces at five specified locations under the frameworks when seated on the master casts using images imported from micro-CT . Finally, spaces at the same locations were measured by using light-body polyvinyl siloxane impression materials.Results: Clinicians found that all frameworks were seated well without rocking of rotation or lateral movement. There was no significant difference among the spaces calculated underneath the18 frameworks for the three various groups at significance level of (�±=.05). Although the spaces detected in the micro-CT images were remarkably higher than the ones from the silicone registration materials. Conclusions: RPD frameworks that produced by 3D printing technology using selective laser melting additive manufacturing have a high level of fitness accuracy that are comparable to the ones produced by lost wax/casting method.Biography
Selma Saadaldin is prosthodontist, faculty member at Schulich Dentistry, Western universit, She got her BDS and Master’s degree from Baghdad University, later she got her PhD in Dental materials from Western University. Currently she is doing her post graduate studies in Dental education at University of Dundee, UK. She has multicultural educational background as she worked different dental schools in Canada, UAE Saudi Arabia and Iraq.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi