Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Google Scholar citation report
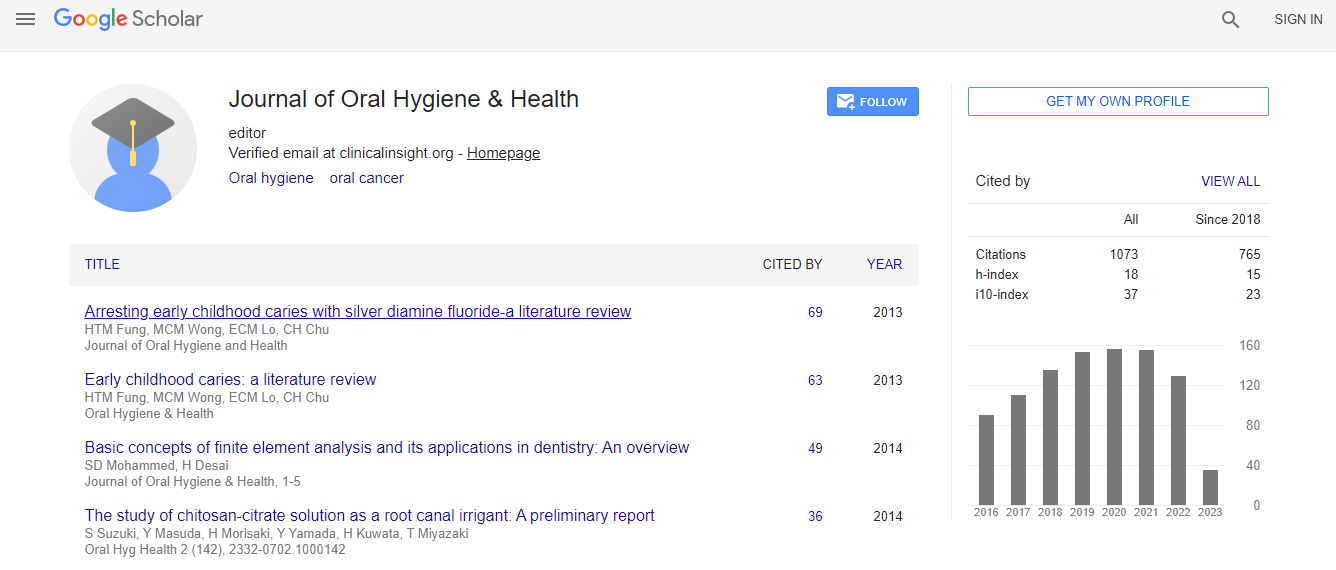
Citations : 1073
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health received 1073 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Maxillofacial infection in Libya
2nd International Conference on Restorative Dentistry and Prosthodontics
Mohamed Elarbi BDS, MMEDSC, FFDRCSI, FICS
Chairman of Arab board scientific council in maxillofacial surgery, Libya
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Oral Hyg Health
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the review medical records from patients who had maxillofacial infections between January 2008 and January 2016. Methods: Retrospective analysis of 91 patients: 51 males (56%) and 40 females (44%) admitted to Ali Omar Askar (AOA) University hospital for Neurosurgery, Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery department, Esbea, Tripoli Libya was carried out. Epidemiology, type, causes of infection treatment carried out and complications were discussed. Results: A total of 91 patients with maxillofacial infection of which 51 were male (56%), 40 females (44%) were analyzed. 85 patients had odontogenic infections (93%): 45 males (52.9%) & 40 females (47.1%), and 6 had non-odontogenic infections (7%). The odontogenic infections occurred mostly at the mandible and its associated spaces: 74 cases (87%) involving the posterior teeth (82%). The main cause was dental caries: 80 cases (94%). The most commonly affected facial anatomic region was the submandibular duct in 39 cases (45.9%). Surgical treatment was required in all the cases. Conclusions: Maxillofacial infections require proper urgent treatment, to avoid complications, which can be serious. Their management is primarily surgical (incision, drainage with extraction of offending tooth as required which require skilled anaesthetic airway management. Immediate admission, monitoring vital signs and high doses of antibiotics, with intravenous fluids for rehydration are required. Complications: Mediastinitis and cavernous sinus thrombosis were reported in two cases.Biography
Email: mselarbi@hotmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi