Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Google Scholar citation report
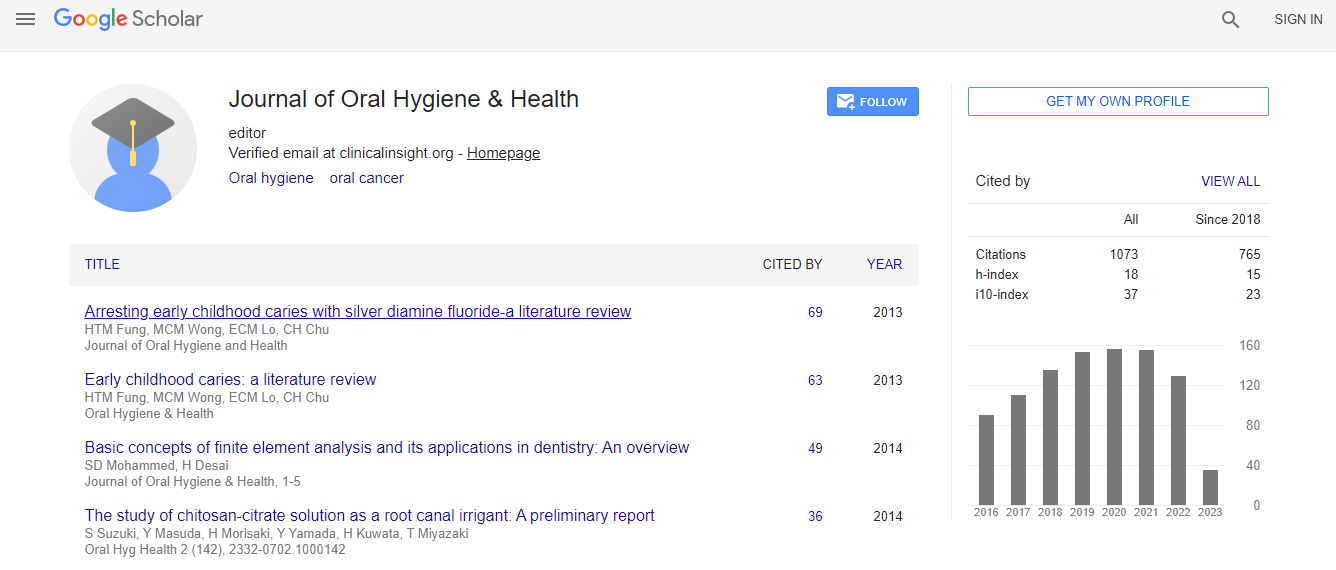
Citations : 1073
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health received 1073 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Oral disease-dental anxiety-brain-immune connections
13th International Conference and Exhibition on Dental Medicine
Yong-Geun Choi
Korea University, South Korea
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Oral Hyg Health
Abstract
Dental professionals have made remarkable progress on the better understanding of oral diseases and the more developed clinical technology for the prevention and treatment of it. However, anxiety of visiting dentist has been considered a factor beyond the capability of dentist to control over. Nevertheless, it was evidenced that dental anxiety is a powerful underlying factor determining the prevalence and prognosis of oral diseases. Deteriorated chewing function is closely linked with the diminished food choice that is one of the strongest environmental challenges to the survival of humans. Change of social activity due to the unacceptable aesthetic as well as speaking function of oral system is a critical challenge to humans, the very complicatedly net-worked social beings. Amygdala, a brain region specializing in facial recognition, displays exaggerated responses to the unfamiliar face of dentist that is processed as an attacker to threaten the security and safety. Directly, psychosocial stress due to the deteriorated daily function of oral system can increase the pro-inflammatory level of cytokine IL-6. As an indirect pathway, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) is activated by the stress. Key hormone secreted by adrenal gland such as cortisol acts on immune cells and suppresses the immune systems, which aggravates the already present oral diseases. The vicious cycle can be interrupted by changing amygdala�s process of the unfamiliar face of dentist. Based on the fact that seeing fearful or angry or unfamiliar face invoke stress reactivity in the amygdala results in avoidance of dental utilization, solutions for patient�s avoidance behavior can be inferred.Biography
Email: ebdent@snu.ac.kr

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi