Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
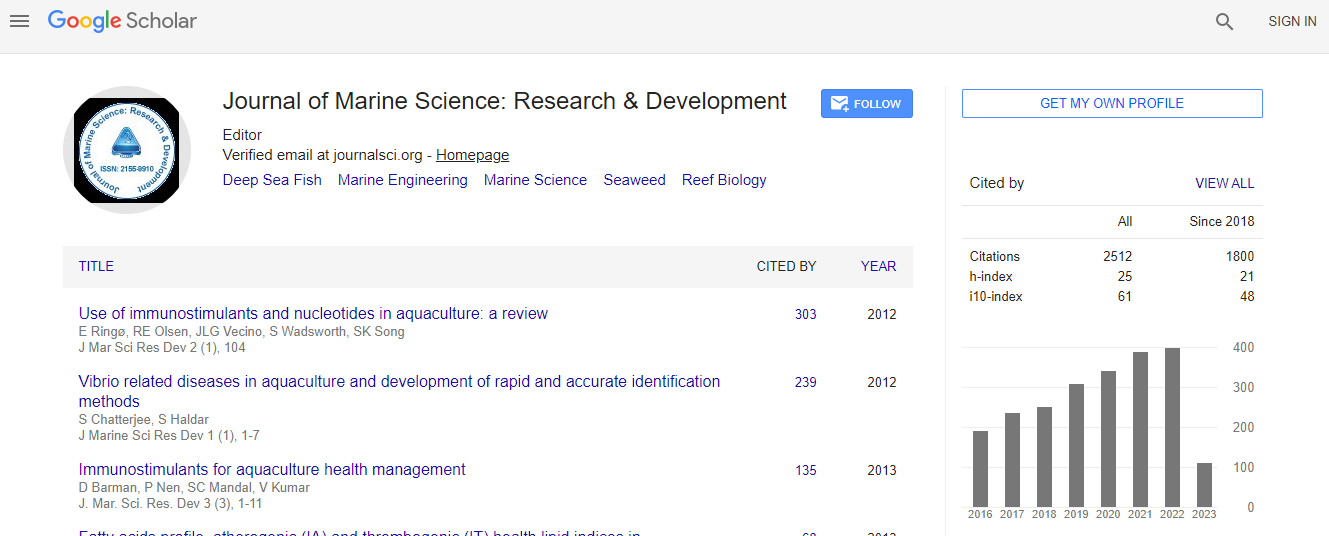
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Determination of atmospheric aerosol particle size distribution with multi-wavelength lidar
4th International Conference on Oceanography & Marine Biology
T Stacewicz
University of Warsaw, Poland
Keynote: J Marine Sci Res Dev
Abstract
Aerosols belong to main components of atmosphere. Understanding their optical properties and the distribution in the atmosphere is crucial for assessing their role in local and global scale. Active remote sensing with multi-wavelength lidars are especially useful for atmospheric investigation since they enable determination of range resolved Aerosol Particle Size Distribution (APDS). The sensing consists in sending of laser pulses at several wavelengths �» (�» = 1, 2, â�¦, ��). The light that is backscattered at distance z reaches the lidar receiver, where wavelength separated and digitized. In consequence it provides the signals S1(z), S2(z), â�¦, S��(z): Here z0 corresponds to lidar position, A�» are the wavelength dependent apparatus constants while �±�»(z) and �²�»(z) denote the spatial distribution of total atmospheric extinction and backscattering coefficients respectively: Where, QA and QB are absorption and scattering efficiencies, both depending on particle radius r. Therefore, the inversion of multi-wavelength lidar signals can provide n(r,z) function â�� range resolved APDS. During our presentation a method and software to retrieve profiles of APSD from lidar signals will be presented. Their application for experimental studies of maritime aerosol as well as the properties of aerosol under cumulus cloud base will be presented.Biography
T Stacewicz has completed his PhD from Faculty of Physics at University of Warsaw (Poland). He is a Professor at this University. His scientific activity concerns optics, laser spectroscopy and its application in atmospheric sciences and in medicine. He has published more than 90 papers in reputed journals.
Email: tadstac@fuw.edu.pl

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi