Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
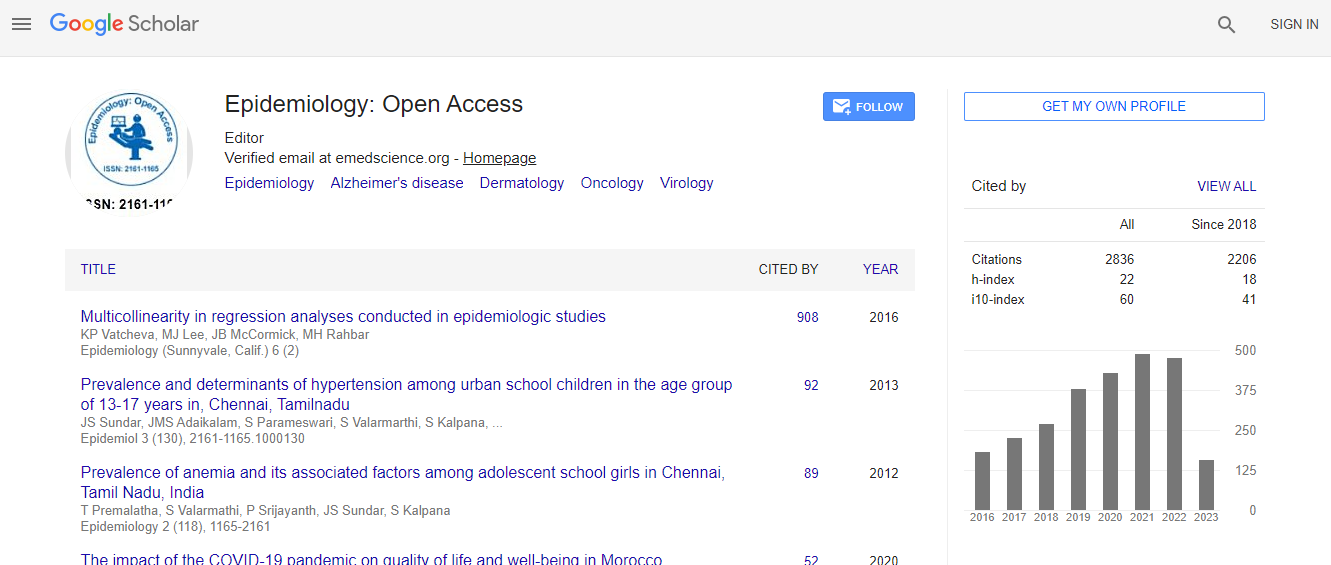
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
PERSISTENT ORGANIC POLLUTANTS IMPAIR INSULIN SECRETORY FUNCTION OF PANCREATIC BETA-CELLS: HUMAN AND IN VITRO EVIDENCE
6th International Conference on EPIDEMIOLOGY & PUBLIC HEALTH
Yu-Mi Lee, Chae-Myeong Ha, Se-A Kim, Themis Thoudam, Sungmi Park, In-Kyu Lee, Duk-Hee Lee, Dae-Jung Kim, Hyeon-Chang Kim, Hyo-Bang Moond and Young-Ran Yoon
Kyungpook National University, Republic of Korea Ajou University School of Medicine, Republic of Korea Yonsei University College of Medicine, Republic of Korea Hanyang University, Republic of Korea
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Persitent organic pollutants (POPs), especially organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have emerged as a new risk factor of type 2 diabetes (T2D). We evaluated whether chronic exposure to low-dose POPs affects insulin secretory function of beta-cells in humans and in vitro cells. Serum concentrations of OCPs and PCBs were measured in 200 non-diabetic adults. Mathematical-model-based insulin secretion indices were estimated using a 2-hour 7-sample oral glucose tolerance test. Insulin secretion by INS1E beta-cells was measured after 48-hour treatment with 3 OCPs or a PCB mixture. Static second-phase insulin secretion significantly decreased with increasing serum concentrations of OCPs. Adjusted means were 63.2, 39.3, 44.1, 39.3, 39.7, and 22.3 across six categories of a summary measure of OCPs (Ptrend = 0.02). Dynamic first-phase insulin secretion remarkably decreased only among insulin-sensitive individuals with increasing concentrations of OCPs (Ptrend = 0.02); the insulin levels among subjects with high OCPs were about 30% of those with low OCPs. Compared to OCPs, PCBs showed weaker associations. The decreased insulin secretion by INS1E beta-cells was observed for even 1 pM OCPs. Our data from human subjects and in vitro cell experiments suggest that chronic exposure to low-dose POPs, especially OCPs, can induce pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as ��?the Environmental Health Action Program (2016001370002).�Biography
Yu-Mi Lee is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University. He was a Clinical Fellow in Kyungpook National University from 2013 to 2015. He took residency training in Kyungpook National University from 2010 to 2013 and also took MD training at Kyungpook National University from 2003 to 2009.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi