Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
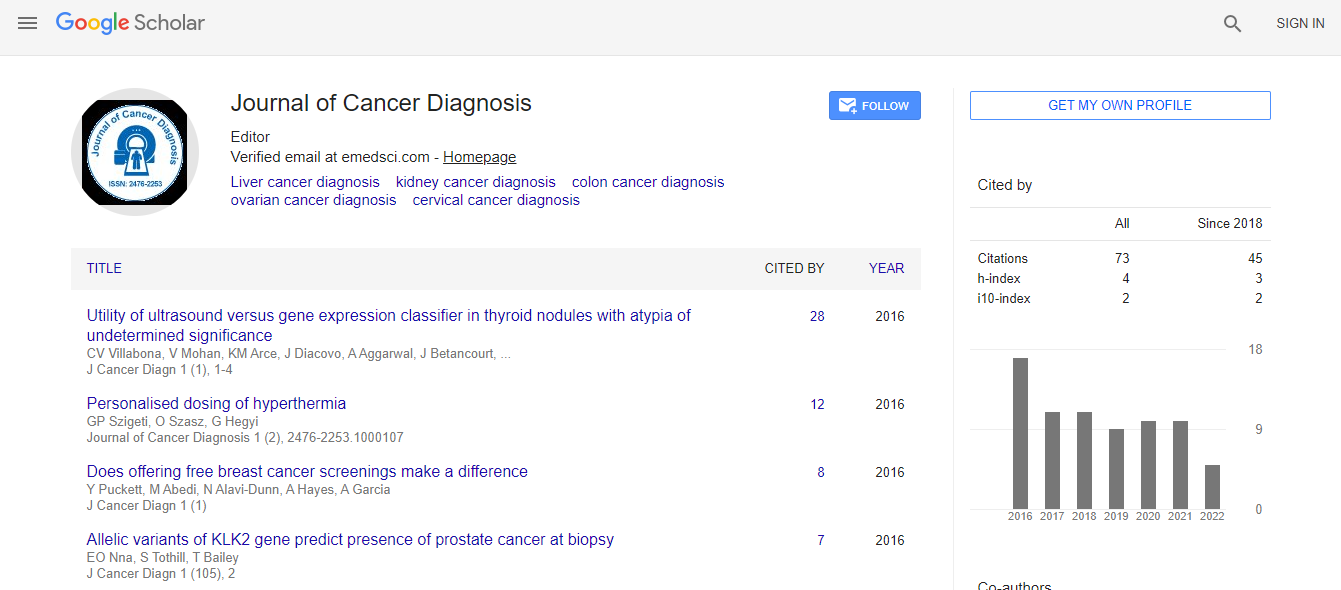
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 95
Journal of Cancer Diagnosis received 95 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The role of Glutathione Peroxidase enzyme 4 (GPX4) in human squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity
Joint Event on International Conference on Cancer Research & Diagnostics & 16th Asia Pacific Biotechnology Congress
Masakatsu Fukuda and Hideaki Sakashita
Meikai University, Japan
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Cancer Diagn
Abstract
GPX family, a selenoprotein, was first described as an enzyme that protects hemoglobin from oxidative degradation. The expression and activity of GPX4 depends on selenium. The liver is particularly sensitive to moderate selenium deficiency since other organs such as brain and reproductive system take up selenium with higher priority. Selenium-containing enzyme GPX4 antagonizes this damage by reducing lipid hydroperoxides to respective hydroxides. However, the role of GPX4 in human oral cancer remains unclear. Then, this study examined the role of GPX4 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Five Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HOSCC) cell lines, HSC-2, HSC-3, HSC-4, Ca9-22 and SAS, were used in this study. As a result of real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting, GPX4 expression levels were the highest in SAS cells. GPX4 knockdown with GPX4 siRNA in SAS cells revealed to decrease the cell number. Then, suspecting apoptosis-induced cell death, caspase activity was also determined. It was indicated that GPX4 knockdown in SAS cells did not lead to apoptosis via the activation of caspases. In other words, it was suggested that GPX4 knockdown in SAS cells led to non-apoptotic cell death such as ferroptosis. In addition, the localization of GPX4 and p53 proteins in HOSCC tissues were examined using immuno-histochemistry. The positive reaction for MAb GPX4 was observed on the membrane of tumor cells in HOSCC tissues. Meanwhile, p53 immunoreactivity was clearly observed, especially consistent with GPX4 positive cells. These findings suggest that GPX4 plays a significant role in the proliferation of oral cancer.Biography
Masakatsu Fukuda has completed his PhD from Nihon University and Postdoctoral studies from International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France. He is currently working as a Junior Associate Professor of Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Department of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Sciences, Meikai University School of Dentistry. He has published more than 45 papers in reputed journals.
E-mail: fukudam@dent.meikai.ac.jp

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi